Kerala Plus One Accountancy AFS Previous Year Question Paper March 2019 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus One |
| Subject | Accountancy |
| Category | Plus One Previous Year Question Papers |
Time Allowed: 21/2 hours
Cool off time: 15 Minutes
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions to Candidates
- There is a ‘cool off time of 15 minutes in addition to the writing time.
- You are not allowed to write your answers nor to discuss anything with others during the ‘cool off time’.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with the questions and to plan your answers.
- Read questions carefully before you answering.
- All questions are compulsory and the only internal choice is allowed.
- When you select a question, all the sub-questions must be answered from the same question itself.
- Calculations, figures, and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non-programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Answer all questions from 1 to 7. Each carry one score. (7 × 1 = 7)
Question 1.
Find the odd one among the given users of accounting information.
a) Managers
b) Creditors
c) Tax Authorities
d) Labour unions
Answer:
a) Managers, others are external users of accounting information.
Question 2.
The accounting concept behind creating provision for doubtful debts is ……………
a) Consistency concept
b) Conservatism concept
c) Materiality concept
d) Objectivity concept
Answer:
b) Conservatism concept
Question 3.
The ‘Book of Original Entry’ is …………..
a) Cash book
b) Sales book
c) Purchases book
d) All of these
Answer:
d) All of these
Question 4.
The overdraft amount as per passbook will be reduced when:
a) Encashment of cheque issued to a supplier.
b) Direct payment made by a customer to the bank.
c) Interest on overdraft charged by the bank.
d) All of these.
Answer:
b) Direct payment made by a customer to the bank.
Question 5.
Which among the following is a TRUE statement?
a) Provision is an appropriation of profit.
b) Maintaining reserve is compulsory for every business.
c) Provision created even if the business incurs losses.
d) Provision for discount on debtors is created to meet the bad debt losses.
Answer:
c) Provision created even if the business incurs losses.
Question 6.
A bill of exchange is to be accepted by ……….
a) Debtor
b) Creditor
c) Drawer
d) Payee
Answer:
a) Debtor
Question 7.
Prepaid salary is treated as:
a) Expenses
b) Income
c) Asset
d) Liability
Answer:
c) Asset
Question 8.
Match the column ‘A’ with ‘B’. (5 × 1 = 5)
| A | B | |
| a) | Direct Expenses | i) Tally / Ex / Sage |
| b) | Total Debtors Account | ii) Libre Office Base / Ms Access |
| c) | Accounting Software | iii) Credit Sales |
| d) | Identifier | iv) Carriage inwards |
| e) | DBMS | v) Key attribute |
Answer:
| A | B | |
| a) | Direct Expenses | i) Carriage inwards |
| b) | Total Debtors Account | ii) Credit Sales |
| c) | Accounting Software | iii) Tally / Ex / Sage |
| d) | Identifier | iv) Key attribute |
| e) | DBMS | v) Libre Office Base / Ms Access |
Answer any four questions from 9 to 13. Each carries two scores. (4 × 2 = 8)
Question 9.
List out any four qualitative characteristics possessed by the accounting information to be useful for decision making.
Answer:
- Reliability
- Relevance
- Understandability
- Timeliness
- Comparability
Question 10.
The stationery items purchased for business use are treated as an expense and not shown as an asset in the books of accounts.
a) Identify the guiding concept of this accounting treatment.
b) Give any other example of observing this accounting concept.
Answer:
a) Materiality Principle
b) Amounts are rounded off to the nearest rupee.
Question 11.
From the given list, identify the type of errors which cause disagreement in Trial Balance.
a) Purchases return book overcast by Rs. 200/-.
b) Credit sales of Rs. 2,000/- omitted to be recorded in the sales book.
c) Purchase of furniture on credit for Rs. 8,000/-wrongly passed through the purchases book.
d) Cash sales of Rs. 3,000/- recorded in cash book omitted to be posted to the sales account.
Answer:
a) Purchases return book overcast by Rs. 200/-.
d) Cash sales of Rs. 3,000/- recorded in cash book omitted to be posted to the sales account.
Question 12.
On January 1, 2018 Amal sold goods, having list price of Rs. 15,000/- at a trade discount of 10%, on credit to Benny. On the same day, Amal draws a three months after date bill for the due amount in favour of Benny. The bill was duly accepted and returned by Benny. Based on the given case find out:
a) The amount of bill.
b) The date of maturity of bill.
Answer:
a) 15000 – (15000 × 10%) = 13,500
b) Date of maturity = 04/04/2018
Question 13.
List out the four essential functional areas or sub-systems of Management Information System (MIS).
Answer:
- Manufacturing Information System.
- Marketing Information System.
- Human Resource Information System.
- Accounting Information System.
Answer any five questions from 14 to 19. Each carries three scores. (5 × 3 = 15)
Question 14.
Classify the following assets as current assets and fixed assets.
a) Machinery
b) Cash in hand
c) Debtors
d) Bills Receivable
e) Furniture
f) Motor vehicles
Answer:
| Current Assets | Fixed Assets |
| Cash in hand | Machinery |
| Debtors | Furniture |
| Bills Receivable | Motor Vehicle |
Question 15.
Distinguish between the ‘Journal’ and the ‘Ledger’.
Answer:
| Journal | Ledger |
| 1) Book of primary entry. | 1) Book of secondary entry. |
| 2) Book for chronological record. | 2) Book for analytical record. |
| 3) The process of entering transactions is called journalizing. | 3) The process of recording in the ledger is called posting. |
Question 16.
Develop Accounting Equation for the following transactions:
a) Started a business with cash Rs. 80,000/- and furniture worth Rs. 20,000/-.
b) Goods purchased on credit Rs. 10,000/-.
c) Sold goods costing Rs. 4,000/-, for cash Rs. 5,000/-.
Answer:
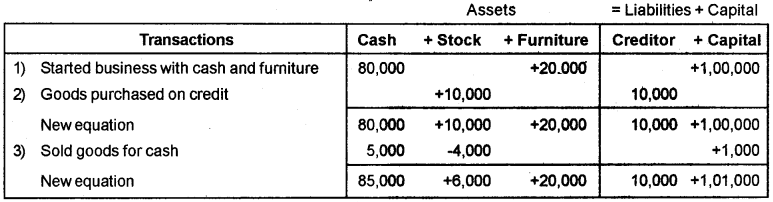
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
1,11,000 = 10,000 + 1,01,000
Question 17.
Name the source documents for recording transactions in the following special journals.
a) Purchase Book.
b) Purchases Return Book.
c) Sales Return Book
Answer:
a) Purchase Book – Invoice
b) Purchase Return Book – Debit Note
c) Sales Return Book – Credit Note
Question 18.
Explain the various objectives of preparing a Trial Balance.
Answer:
A Trial Balance is prepared with the following objectives:
- To ascertain the arithmetical accuracy of ledger accounts.
- To help in ascertaining errors.
- To provide a basis for preparing financial statements.
Question 19.
The Trial Balance of Kavitha Traders as on 31/03/ 2018, shows Debtors of Rs. 81,000/- and Bad debts of Rs. 3,000/-. At the time of preparing the Final Accounts they decided to write off further bad debts of Rs. 1,000/- and to create a provision for doubtful debts at 6% of the debtors.
Pass the necessary journal entries for adjusting these items in the books of Kavitha Traders.
Answer:

Answer any three questions from 20 to 23. Each carries four scores. (3 × 4 = 12)
Question 20.
Explain the implications of the following accounting concept.
a) Business entity concept.
b) Dual aspect concept.
c) Matching concept.
d) Full disclosure concept.
Answer:
a) Business entity concept: This concept assumes that the entity of business is different from its owners. The business is treated as a unit or entity separate from the person who control it.
b) Dual aspect concept: According to this concept, each and every business transaction has two aspects – a giving aspect and a receiving aspect. In other words, at least two accounts will be involved in recording a transaction.
c) Matching concept: This concept states that expenses incurred in an accounting period should be matched with revenues during that period.
d) Full disclosure concept: This concept states that all information significant to the users of financial statements should be disclosed.
Question 21.
Write any four examples of transactions to be recorded in the ‘Journal Proper’.
Answer:
- Purchase of furniture on credit.
- Sale of machinery on credit.
- Goods taken by owner for personal use.
- Goods lost by fire/theft.
- Goods distributed as free sample.
Question 22.
Pass rectification entries for the following errors located in the books of a sole trader.
a) Sale of old furniture for Rs. 3,500/- recorded in the sales book.
b) Wages paid Rs. 2,000/- for the erection of a new machinery debited to the wages account.
c) Credit purchase of goods from Kumar Traders for Rs. 5,000/- was posted to the credit of Kamal Traders account.
d) Goods costing Rs. 3,200/- taken over by the proprietor for personal use was omitted to be recorded in the journal.
Answer:

Question 23.
Explain the two methods of arranging various items (Marshalling) in a Balance Sheet by giving suitable example.
Answer:
There are two methods of arranging various items in a balance sheet. They are:
a) Order of Liquidity:
Under this method, assets are presented in the order of their liquidity. The most urgent liability is shown first and the least urgent to pay is shown last.
In the order of liquidity
Assets
- Cash in hand
- Cash at bank
- Sundry debtors
- Stock
- Furniture
- Building
- Goodwill
Liabilities
- Bills payable
- Sundry creditors
- Bank overdraft
- Loans
- Capital
b) Order of permanence
Under this method, permanent assets and liabilities are shown first followed by current assets and current liabilities.
In the order of permanence
Assets
- Goodwill
- Building
- Furniture
- Stock
- Sundry debtors
- Cash at bank
- Cash in hand
Liabilities
- Capital
- Loans
- Bank overdraft
- Sundry creditors
- Bills payable
Answer any five questions from 24 to 29. Each carries five scores. (5 × 5 = 25)
Question 24.
Prepare Rajan’s account in the books of Gopal, by posting the following transactions and brought down its balance to the next month.
| 2018 March | Rs. | |
| 1 | Amount due from Rajan | 12,000 |
| 5 | Sold goods on credit to Rajan | 8,000 |
| 12 | Rajan returned goods worth | 1,000 |
| 21 | Received cash from Rajan | 5,000 |
Answer:
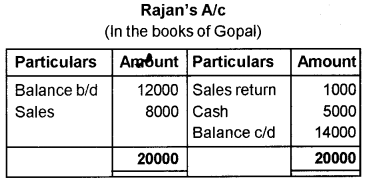
Question 25.
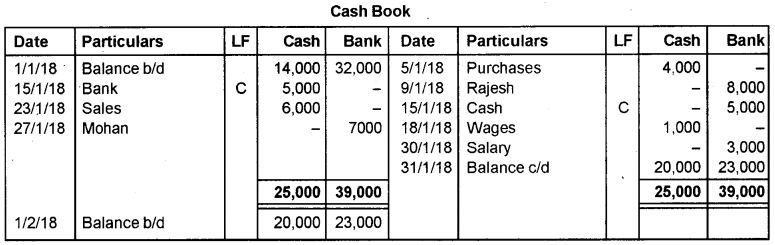
Prepare a double column cash book from the following transactions for the month of January 2018.
| 2018 January | Rs. | |
| 1 | Cash in hand Cash at bank | 14,000 32,000 |
| 5 | Purchased goods for cash | 4,000 |
| 9 | Issued cheque to Rajesh | 8,000 |
| 15 | Cash withdrawn from bank | 5,000 |
| 18 | Paid wages | 1,000 |
| 23 | Sold goods for cash | 6,000 |
| 27 | Cheque received from Mohan, deposited into bank | 7,000 |
| 30 | Paid salary by cheque | 3,000 |
Answer:
Question 26.
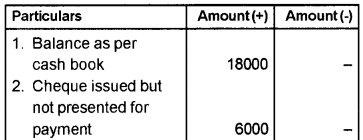
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 31/ 03/2018, from the given details:
a) Balance as per cash book Rs. 18,000/-.
b) Cheque issued but not presented for payment Rs. 6,000/-.
c) Cheque paid into bank, but not collected Rs. 9,000/-.
d) Interest on deposit credited in passbook only Rs. 200/-.
e) Insurance premium paid by bank not recorded in cash book Rs. 1,000/-.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 31/03/2018

Question 27.
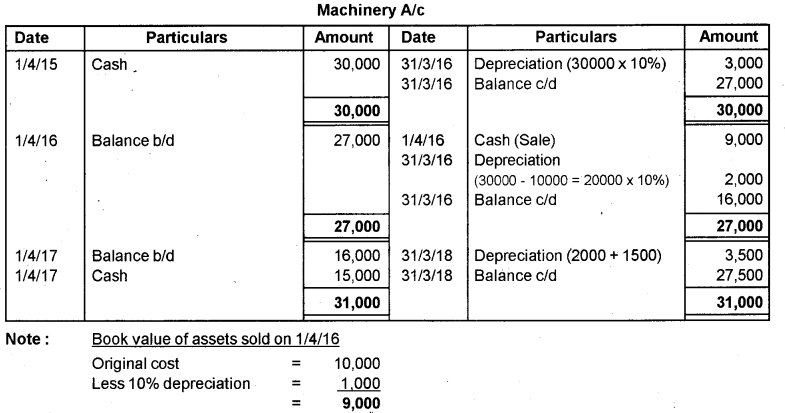
Arun Traders purchased a machinery by paying Rs. 30,000/- on 01/04/2015. They decided to write off depreciation @ 10% per annum under the fixed installment method. On 01/04/2016 machinery having original cost of Rs. 10,000/- was sold out at its book value. On 01/04/2017 another machinery was purchased for Rs. 15,000/-. Prepare the Machinery account for the first three years.
Answer:
Question 28.
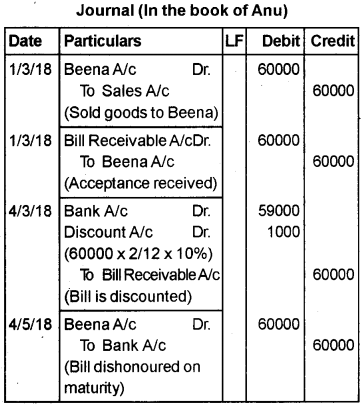
Anu sold goods worth Rs. 60,000/- to Beena on March 1, 2018. For ensuring the payment, Anu draws a two months bill on the same day and Beena duly accepted and returned it. On March 4, 2018, this bill was discounted by Anu with her bank at a discount of 10% per annum. But on the due date the bill was dishonoured for nonpayment.
Pass the journal entries of the bill transactions in the books of Anu.
Answer:
Question 29.
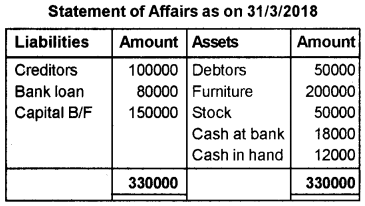
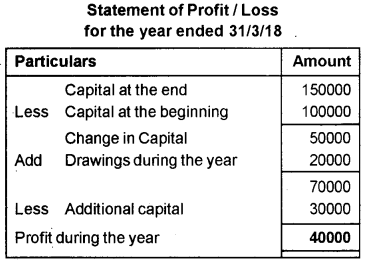
Mrs. Sundas started a coolbar on April 1, 2017 with a capital investment of Rs. 1,00,000/-. She did not maintain her books of accounts as per the double entry system. During the year she introduced further capital of Rs. 30,000/- and withdraw Rs. 20,000 for personal purposes. On March 31, 2018 her financial position was as follows.
| Rs. | |
| Total Creditors | 1,00,000 |
| Bank loan | 80,000 |
| Total debtors | 50,000 |
| Furniture | 2,00,000 |
| Stock | 50,000 |
| Cash in hand | 12,000 |
| Cash at bank | 18,000 |
Calculate the profit or loss made by Mrs. Sundas during the first year of running the business, by using the Statement of Affairs Method.
Answer:
Answer any one question from 30 to 31. Each carries eight scores. (1 × 8 = 8)
Question 30.
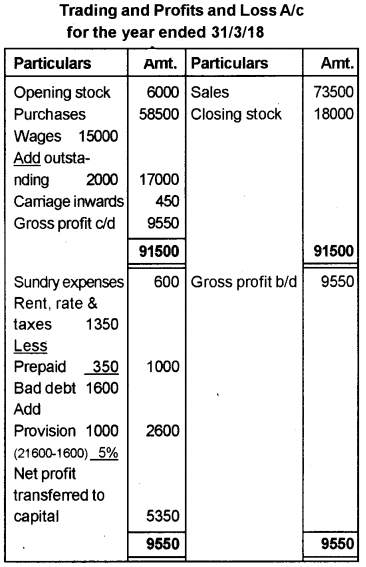
Prepare the Trading and Profit and Loss account and Balance Sheet from the given Trial Balance and additional information.
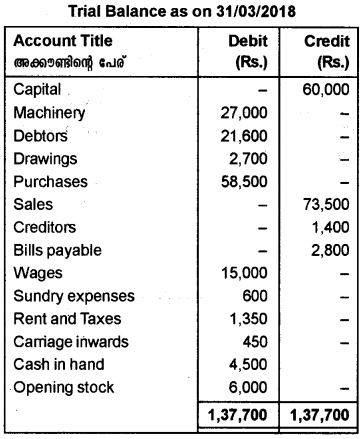
Additional information:
a) Closing stock is valued at Rs. 18,000/-.
b) Wages outstanding Rs. 2,000/-.
c) Prepaid rent Rs. 350/-.
d) Write off Rs. 1,600/- as bad debts.
e) Create a provision for doubtful debts at 5% of the debtors.
Answer:
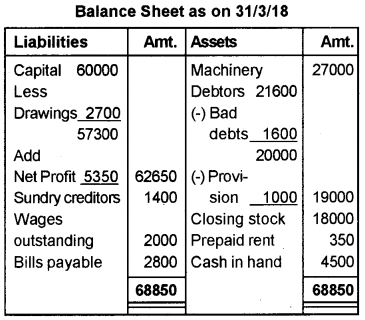
Question 31.
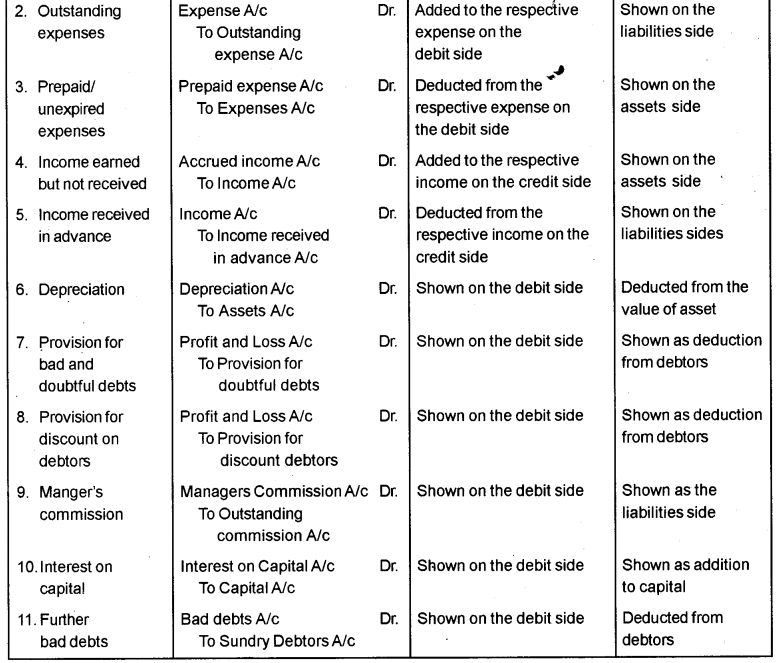
Explain any eight adjustments usually needed to ensure that the final accounts reveal the true profit or 14. loss and the true financial position of the business.
(Hint: The journal entries of various adjustments and their treatment in the final accounts should be included).
Answer: