Kerala Plus One Accountancy AFS Previous Year Question Paper March 2018 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus One |
| Subject | Accountancy |
| Category | Plus One Previous Year Question Papers |
Time Allowed: 21/2 hours
Cool off time: 15 Minutes
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions to Candidates
- There is a ‘cool off time of 15 minutes in addition to the writing time.
- You are not allowed to write your answers nor to discuss anything with others during the ‘cool off time’.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with the questions and to plan your answers.
- Read questions carefully before you answering.
- All questions are compulsory and the only internal choice is allowed.
- When you select a question, all the sub-questions must be answered from the same question itself.
- Calculations, figures, and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non-programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Answer all questions from question numbers 1 to 7. Each carry one score. (7 × 1 = 7)
Question 1.
Find the odd one out
a) Cash
b) Bank
c) Stock
d) Furniture
Answer:
d) Furniture
Question 2.
Which accounting principle/concept is based on the policy of playing safe?
Answer:
Principle of conservatism / Prudence
Question 3.
Cheque received from Johnson ₹ 5,000/- deposited into bank. Bank intimates that it was dishonored. But it is not recorded in cash book. Identify the type of error.
Answer:
Error of omission (Complete omission)
Question 4.
A promissory note is drawn by ………..
a) Investor
b) Debtor
c) Bank
d) Creditor
Answer:
b) Debtor
Question 5.
Write the equation on which the statement of affairs is prepared from incomplete records.
Answer:
Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Question 6.
ALU stands for ……….
Answer:
Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
Question 7.
In DBMS the element used to get only the required data as output is ………..
Answer:
Queries
Answer all questions from question numbers 8 to 13. Each carries two scores. (6 × 2 = 12)
Question 8.
Complete the diagram.
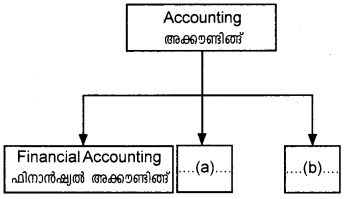
Answer:
a) ManagementAccounting
b) CostAccounting
Question 9.
List out any two advantages of maintaining petty cash book.
Answer:
Advantages of Maintaining Petty cash book
- Saving of time and effort of chief cashier
- Effective contorl over cash disbursement
Question 10.
Rectify the following errors.
a) Sales day book overcast by ₹ 9,000/-.
b) Paid rent to Salim ₹ 1,000/- debited to his personal account.
Answer:

Question 11.
List out any two factors affecting the depreciation of fixed assets in a business.
Answer:
Factors affecting the depreciation of fixed assets are as follows
- Cost of asset
- Estimated useful life
- Estimated net residual value
- Depreciable cost of an asset
Question 12.
Calculate the operating profit from the following profit and loss account.
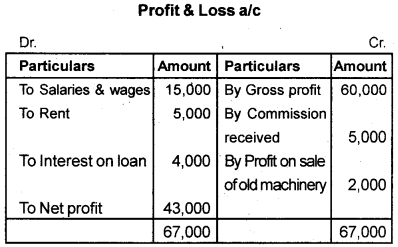
Answer:
Operating profit = Net profit + Non operating Expenses – Non operating income.
= (43000 + 4000) – 2000
Operating profit = 45,000
OR
Operating profit = (Gross profit – operating expenses) + operating income
= (60,000 – 15000 + 5000) + 5000
= 40,000 + 5000
= 45,000
Question 13.
List out any four advantages of Computerized Accounting System.
Answer:
- Speed-Accounting data is processed faster by using computer acconting system.
- Real time user interface
- Automated document production
- Generate quality reports
- Accounting data is updated automatially
Answer any five from question numbers 14 to 19. Each carries three scores. (5 × 3 = 15)
Question 14.
Explain the following accounting concepts.
a) Going concern
b) Dual aspect
c) Consistency
Answer:
a) Going concern concept:
According to this concept, the business unit is assumed to have an indefinite life. There is no intention to wind up or end the business in the near future.
b) Dual aspect concept:
According to this concept, each and every business transaction has two aspects a giving aspect (credit) a receiving aspect (debit) and ultimately it affect a change in the composition of assets and liabilities.
c) Consistency principle:
According to this principle, the accounting practies should remain the same from one year to another.
For eg: stock-in-trade should be valued according to one method from one year to another.
Question 15.
Show the effect of the following transactions on Assets, Liabilities and Capital through accounting equation.
a) Started business with cash ₹ 2,00,000/-
b) Purchased goods from Manu ₹ 10,000/-
c) Sold goods to Rinu (costing ₹ 6,000) for ₹ 8,000/-
Answer:
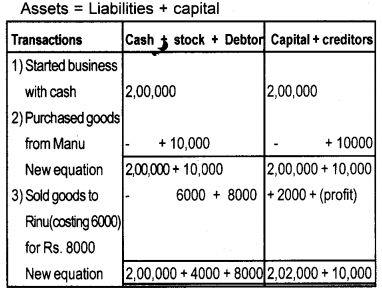
Assets = Liabilities + capital
2,12,000 = 10,000 + 2,02,000
Question 16.
Lekshmi Enterprise’s cash book showed a debit balance of ₹ 18,000/-. Its passbook showed credit balance of ₹ 20,000/-. State any three possible reasons for this differences in balance.
Answer:
The reasons for the difference between cash book balance and passbook balance are as follows :
- Cheques issued but not presented for payment
- Direct payment by a customer into the trader’s bank account
- Cheque paid into bank for collection but not yet collected
Question 17.
Prepare a Trial Balance from the following balances.
| Cash | ₹ 28.000/- |
| Bank overdraft | ₹ 7,000 |
| Purchases | ₹ 20,000/- |
| Sales | ₹ 32,000- |
| Capital | ₹ 40,000/- |
| Land & Buildings | ₹ 31,000/- |
Answer:
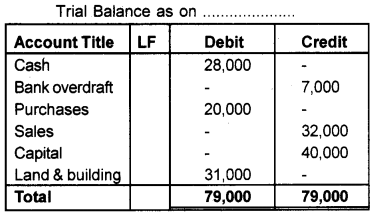
Question 18.
Pass the adjusting entry on the following.
a) Salary outstanding ₹ 2,000/-
b) Depreciation on machinery ₹ 3,000/-
C) Interest on capital ₹ 1,000/-
Answer:

Question 19.
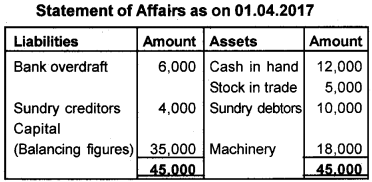
Calculate capital on 1st April, 2017 by preparing statement of affairs from the following balances on that date.
| Cash in hand | ₹ 12,000/- |
| Bank overdraft | ₹ 6,000/- |
| Machinery | ₹ 18,000/- |
| Sundry debtors | ₹ 10,000/- |
| Sundry creditors | ₹ 4,000/- |
| Srock in trade | ₹ 5,000/- |
Answer:
Answer any five from question numbers 20 to 25. Each carries four scores. (5 × 4 = 20)
Question 20.
Briefly explain the objectives of accounting.
Answer:
Objectives of Accounting are given below:
- To maintain a systematic record of all financial transaction in books of accounts.
- To ascertain the profit earned or loss incurred by a business during an accounting period.
- To ascertain the financial position of the business concern.
- To provide meaningful information to different group of people having interest in the business.
Question 21.
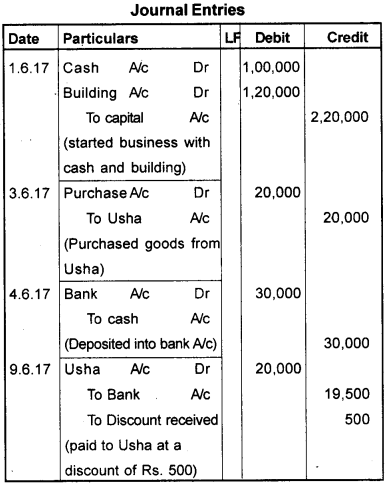
Journalize the following transactions.
| 2017 June | |
| June 1 | June 1 Started Business with cash ₹ 1,00,000/- Building ₹ 1,20,000/- |
| June 3 | June 3 Purchased goods from Usha ₹ 20,000/- |
| June 4 | June 4 Deposited into bank ₹ 30,000/- |
| June 9 | June 9 Paid to Usha ₹ 19,500/- |
Answer:
Question 22.
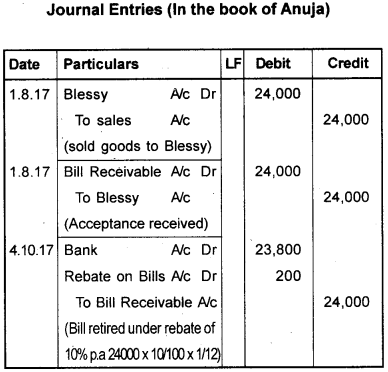
On August 1, 2017 Anuja sold goods to Blessy for ₹ 24,000/- and immediately draw a bill on Blessy for three months for the same amount. Bill accepted and returned to Anuja, On October 4, 2017 Blessy retired her acceptance at rebate of 10% p.a. Pass the journal entries in the books of Anuja.
Answer:
Question 23.
Arrange the following assets in the order of permanence.
a) Cash in hand
b) Land and building
c) Sundry debtors
d) Stock in trade
e) Furniture
f) Cash at bank
g) Bills receivable
h) Plant & Machinery
Answer:
Assets in the order of permanence:
1. Land and Building
2. Plant and Machinery
3. Furniture
4. Stock in trade
5. Sundry Debtors
6. Bill Receivable
7. Cash at bank
Question 24.
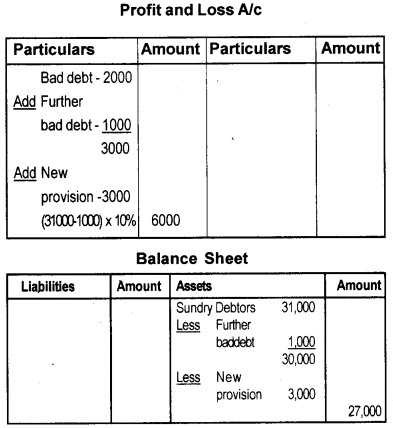
From the extract of Trial Balance and additional information, show how the items will appeared in the final accounts of Mrs. Shamla.
| particulars | Debit | credit |
| Sundry debtors | 31,000 | – |
| Bad debts | 2,000 | – |
Additional information:
a) Write off further Bad debts ₹ 1,000/-
b) Provision for bad debts @ 10%
Answer:
Question 25.
Calculate total purchase from the following data during 2017.
| Total creditors as on 1.1.2017 | ₹ 37,000/- |
| Cash paid to creditors during 2017 | ₹ 63,000/- |
| Discount received | ₹ 7,000/- |
| Total creditors as on 31.12.2017 | ₹ 47,000/- |
| Cash purchases during 2017 | ₹ 72,000/- |
Answer:
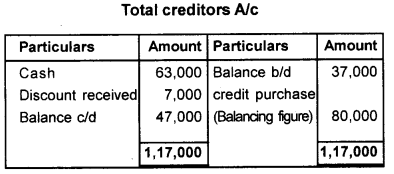
Total purchase = cash purchase + credit purchase
= 72,000 + 80,000
= 1,52,000
Answer any two from question numbers 26 to 28. Each carries five scores. (2 × 5 = 10)
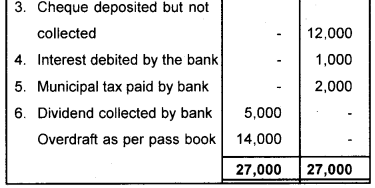
Question 26.
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement from the following information.
a) Overdraftas per the cash book ₹ 12,000/-
b) Cheque issued but not presented ₹ 8,000/-
c) Cheque deposited but not collected ₹ 12,000/-
d) Interest debited by bank ₹ 1,000/-
e) Muncipal Tax paid by bank as per standing instruction ₹ 2,000/-
f) Dividend collected by bank ₹ 5,000/-
Answer:

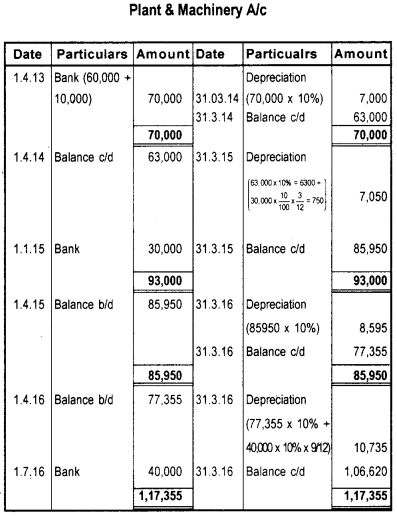
Question 27.
Athulya bought Plant & Machinery on 01.04.2013 for ₹ 60,000/-. Erection charges amounting to ₹ 10,000/-. On 01.01.2015 a new Machinery purchased for ₹ 30,000/-. On 01.07.2016 an additional Machinery purchased for ₹ 40,000/-. Prepare Plant & Machinery account by charging depreciation @ 10% on diminishing balance method for first four years asssuming that the books are closed on 31st March every year.
Answer:
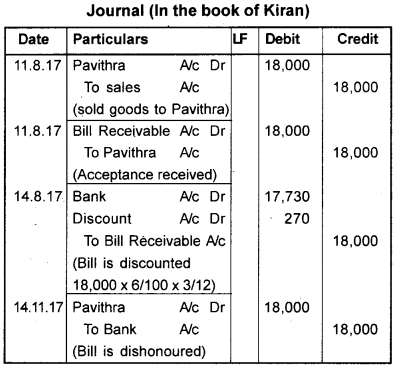
Question 28.
On 11.08.2017 Pavithra purchased goods from Kiran for 18,000/-. Kiran draws a 3 months bill on Pavithra and get it accepted. On 14.08.2017 Kiran discounted the bill @ 6% p.a. with his bank. On due date Pavithra dishonoured the bill. Record journal entries in the books of Kiran.
Answer:
Answer any two from question numbers 29 to 31. Each carries eight scores. (2 × 8 = 16)
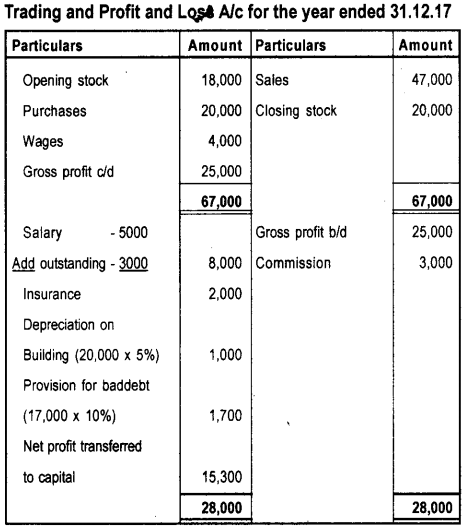
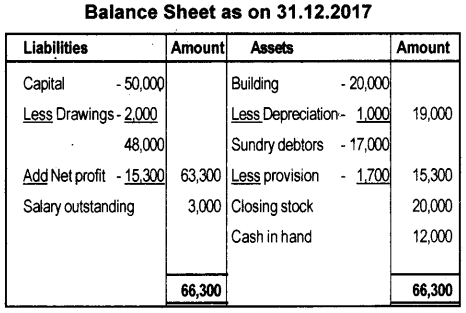
Question 29.
Prepare the Trading and Profit & Loss account and Balance Sheet of Ramakrishna Textiles from the following Trial Balance as on 31st December 2017.
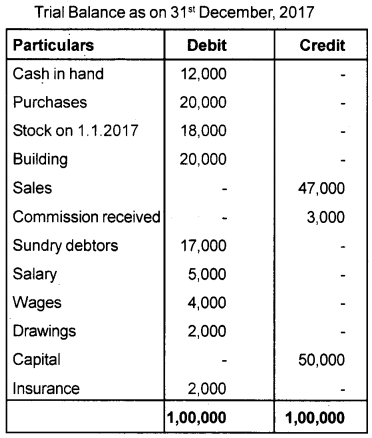
Additional information:
a) Stock on 31.12.2017 ₹ 20,000/-
b) Salary outstanding ₹ 3,000/-
c) Depreciate building @ 5%
d) Provision for bad debts @ 10%
Answer:
Question 30.
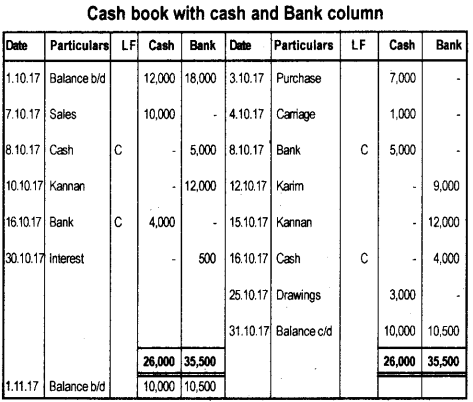
For the month of October 2017, prepare double column cash book from the following transactions. October 2017
| October 2017 | |
| Oct 1 | Cash in hand ₹ 12,000/- Cash at bank ₹ 18,000/- |
| Oct 3 | Purchased goods ₹ 7,000/- |
| Oct 4 | Carriage paid ₹ 1,000/- |
| Oct 7 | Sold goods for cash ₹ 10,000/- |
| Oct 8 | Deposited into bank ₹ 5,000/- |
| Oct 10 | Received cheque from Kannan ₹ 12,000/- deposited into bank |
| Oct 12 | Issued cheque to Karim ₹ 9,000/- |
| Oct 15 | Kannan’s cheque dishonoured |
| Oct 16 | Withdrew from bank for office use ₹ 4,000/- |
| Oct 25 | Withdrew cash for personal use ₹ 3,000/- |
| Oct 30 | Interest credited by bank ₹ 500/- |
Answer:
Question 31.
Explain the following with suitable examples.
a) Current asset
b) Source document
c) Error of commission
d) Key attribute
Answer:
a) Current Asset:
Current assets are those assets which get converted into cash within an operating cycle generally one year. Current are assets held on a short term basis.
Examples are Sundry debtors, Bill Receivables, stock, cash and bank balances.
b) Source Document:
Source document is a written document to be used in support of entry made in the accounts. They provide information about the transaction involved and helps in verifying the correctness of books of accounts.
Examples are the receipts, bill, cash memos, invoices, salary bill etc.
c) Error of commission:
Errors committed when transactions are incorrectly recorded are called error of commission. These are errors caused by wrong posting, wrong balancing, wrong totalling etc.
Examples are:-
- Sales return from Manu Rs. 1500 were posted to his account as Rs. 1000
- Cash received from Karan Rs. 5000 posted to Amal.
d) Key Attributes:
An attribute which contains unique values for identifying the entity instance is called identifier or key attribute of an entity type.
Examples are:-
- “Roll No” is a key attribute of entity type ‘student’.
- “Employee ID” is a key attribute of entity type ‘Employee’.
- “Code” is a key attribute of entity type ‘Accounts’.
