Plants Vocabulary: Plants are multicellular organisms, which means they are living entities. They cannot, however, move like humans or other living creatures. They can grow practically anywhere on the planet, from snow-capped mountain peaks to arid deserts. Plants get their energy from the sun, which is the primary source of energy on the planet. They also supply energy to the ecology, which makes them necessary for any ecosystem. There is an extensive selection of words in English that one must know to add to their plant vocabulary list.
We see these plants in our surroundings in our daily lives, so we must know these names and their descriptions. Further in this article, you will get plant vocabulary words listed to improve your knowledge. Hence, we have made a curated and simple list of plants vocabulary for you to learn the names of plants along with their meanings and pictures.
Study the most important English Vocabulary Words identified by our experts and learn the right vocabulary to use in your day to day conversations.
List of Plants Vocabulary Words in English
Name of Plants Vocabulary Words
The different names of plants with pictures will help you increase your knowledge about plants and trees surrounding all of us. You will get the description of the listed plants that will improve your plant vocabulary list.
Thus, we have listed the detailed plant vocabulary and definitions as we should also know their descriptions to understand and know the significance of each of these plants.
List of Plants
- Wildflower
- Thistle
- Flower
- Conifers
- Herb
- Mushroom
- Weed
- Fern
- Orchids
- Cattail
- Reed
- Bamboo
- Climbers
- Ivy
- Shrub
- Moss
- Grass
- Creepers
- Palm tree
- Bush
- Corn
- Tree
- Liverworts
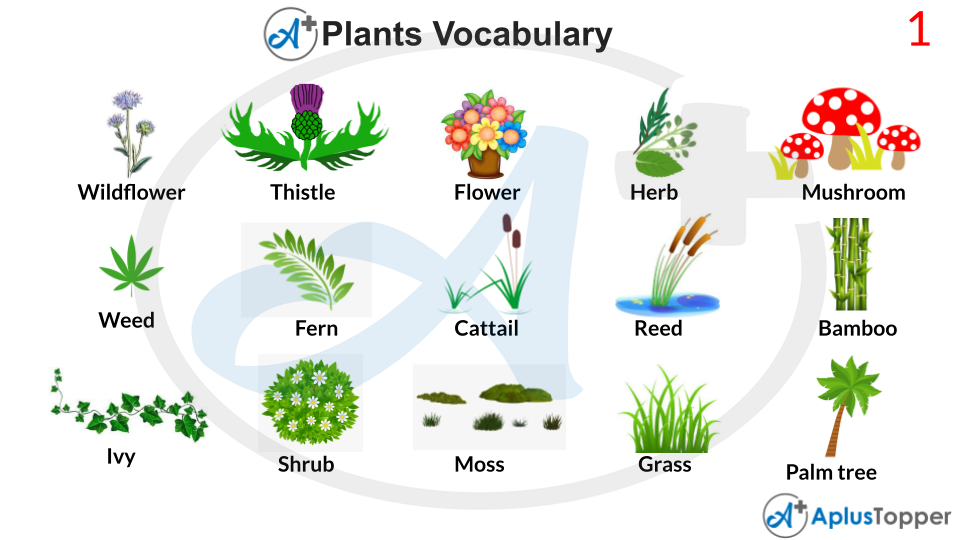
Description of the Plants Vocabulary Words
Wildflower
A flower that was not grown and planted in the wild is known as a wildflower. The plant appears as a native plant, and the tern refers to the plant as neither hybrid nor a selected cultivar.
Thistle
Flowering plants, which are characterized by leaves on the margins with sharp prickles, are called thistles. The plants adapt these prickles to protect them from being eaten by herbivores, and spikes occur all over the plant, stem, and the flat parts of the leaves.
Thistles are species of plants that are generally adapted to drier environments and have greater skinniness.
Flower
Sometimes known as a blossom or a bloom, the reproductive structure of flowering plants is called flowers. The biological function of flowers is providing mechanisms, facilitating reproduction for the union of sperm with the eggs.
When self-pollination occurs, flowers may perform or facilitate outcrossing, which results from crossing self-pollination.
Conifers
Conifers are a subset of gymnosperms that produce cone-bearing seed plants. Conifers have evergreen leaves that are needle-like or scale-like. They are vital as a source of softwood, as well as resins and turpentine.
Pinophyta, commonly known as Coniferophyta or Coniferae, is the scientific name for them. Pinopsida is the only extant class in the division. Conifers are all perennial woody plants that have secondary growth. Some examples of conifers include cedars, pines, cypresses, firs, junipers, larches, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews.
Herb
A widely distributed and general classification or group of plants that other plants consume for micro and macronutrients are called herbs. Herbs are excluded from vegetables. Herbs are usually used more for medicinal purposes or aromatic fragrances.
Herbs are green leafy flowering plants that can be dried or fresh, including fruits, barks, seeds, and barks.
Mushroom
A fleshy, fruit-bearing body of a fungus that typically occurs on the soil above the ground is called a mushroom. Mushrooms can appear on some food sources as well.
Mushrooms can either be highly poisonous, which leads to the death of organisms, or they can be edible.
Fungus on wooden objects sometimes develops into poisonous mushrooms as well. Mushrooms contain gills with microscopic pores that help the fungus spread to its surroundings, leading to more offspring mushrooms.
Weed
A plant that is considered useless or undesirable in particular or various situations is known as a weed. Weed is often called a plant in the wrong place. Weeds grow and develop by themselves and other plants and grow from their nutrients such as fertilizer, water, and natural sunlight.
The control of weed has taken a massive role in agricultural farms due to their absolute uselessness and, on top, taking up other spaces of plants desired to grow by a farming farm or farmers.
Fern
A group of vascular plants with phloem and xylem is called a fern (Polypodiosida). Ferns produce neither seeds nor flowers. By being vascular, they differ from mosses and other bryophytes, i.e., they have specialized tissues which absorb nutrients and water in life cycles in the dominant phase.
Ferns do not have paramount economic importance to farmers or agricultural farms, but ferns are used for food and medicines in some cases as biofertilizers or ornamental plants. Rhizomes are fern stems that grow underground on some species, especially epiphytic species.
Orchids
Orchids are a type of plant with complex flowers that are often beautiful or oddly formed, with a wide specialised lip called the labellum and, in some cases, a spur. Orchids are valuable hothouse plants that can be found all over the world, notably as epiphytes in tropical woods. They come in over 30,000 different species and have a wide range of appearances. Many have amazingly gorgeous blooms with stripes and patterns, while others have hairs and even warty lumps, making them visually unattractive.
Cattail
Aquatic or semi-aquatic herbaceous and rhizomatous plants are known as cattail or Typha. Cattails contain jointless stems which bear flowering spikes. These plants are unisexual and monoecious flowers that develop in dense racemes.
Cattails develop in newly exposed wet muds and are wetland plants. Cattails or Typha can survive for long periods in the soil. They are considered as dominant competitors over other plants in canopies that are dense.
Bamboo
Evergreen perennial flowering plants on the subfamily Bambusoideae of the family of grass are called bamboo. Bamboo is considered a rapidly growing plant due to its unique rhizome system dependency, and its stems are hollow and vascular in the cross-section.
Bamboos are considered a notable cultural and economic significance in East Asia, Southeast Asia, and South Asia. Due to its weight and high strength capability, bamboo is regarded as a building material and food source. Due to their power to weight ratio, bamboo is often substituted with wood and feels similar to timber.
Climbers
Plants with weak or delicate stems that grow with the help of external support, such as trees and other tall things, are known as climbers. To climb, these plants produce a twine or hook from their leaves. Some plants create unique roots that act as anchors for climbing around objects.
Many are vines with stems that wrap around trees and branches. Tendrils are peculiar structures that climbers utilise to climb trees. Grapevine, cucumber and money plant are some examples of climbers.
Ivy
In the family of Araliaceae, a genus of twelve to fifteen climbing evergreen and ground creeping plants are called Ivy. Ivies are naturally found in Macaronesia, Europe, north-western Africa, Taiwan, and across central-southern Asia to east Japan.
Ivies on the level ground grow up to five to twenty centimetres in height, but on suitable climbing surfaces like rocks, quarries, or natural rock outcrops, they reach up to thirty centimetres of height. Ivies have two types of leaf, one is the creeping type, and another is the climbing type.
Shrub
A small to medium-sized perennial woody plant is called a shrub. Their difference from the braid is made from their growth height as their maximum growth feet is two meters.
Moss
Small non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division of Bryophyta are called Moses. Their parent group is bryophytes, and they comprise liverworts, hornworts, and Moses.
Grass
Narrow leaves from the base of the soil are called grasses. Grasses have species of around seven eighty genera and approximately twelve thousand species.
Creepers
Creepers are plants with weak stems that use extended stems or branches to grow along the ground, around another plant, or up a wall. They have incredibly delicate stems that can’t stand up straight or hold their entire weight. Watermelon, pumpkin, sweet potato are examples of creepers. Creepers include a variety of ivy and other vines as well.
Palm tree
A flowering plants family in the order of Arecale are called palm trees or Arecaceae. These trees generally grow in tropical and sub-tropical climates. They are known for having evergreen leaves and their large compounds, which are known as fronds. These fronds are arranged at the top of an item that is unbranched.
Bush
A shrub or a small tree that belongs to the same family as shrubs, which grow collectively in a single place, is called a bush. Bushes are perennial woody plants that have persistent woody-like stems.
Corn
A grain first domesticated by people from southern Mexico about ten thousand years ago is corn or maize. Maize is a staple food diet nowadays all over the world. The total maize production in many parts of the world surpasses the production of wheat and rice. Maize is also used for animal food, maize ethanol, and other maize products such as corn syrup and corn starch.
Tree
In most species, a perennial plant with elongated stems or trunks and supporting branches and leaves are known as trees. Trees have narrower wooden crates, which later thickens by growing outwards and their primary growth is upwards.
Liverworts
Non-vascular plants with no blooms and no seeds are known as liverworts. They are tiny leafy plants with a width ranging from 2 to 20 mm. These are plants that thrive in a wet environment.
Many plant species are included in liverworts, and small species might sometimes be difficult to distinguish from mosses. The presence of rhizoids, which are tiny hair-like structures, is one way to distinguish liverworts. This primarily aids in their ability to absorb large amounts of water.
