What are the physical properties of ammonia?
- Ammonia is a covalent compound with the following physical properties:
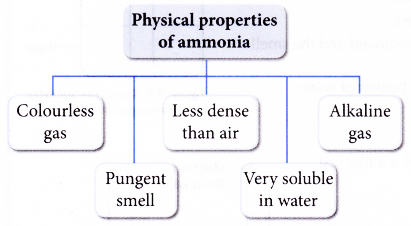
- Ammonia is very soluble in water, but it ionises partially in water to form a weak alkali. A 0.1 mol dm-3 ammonia solution has a pH of about 10.
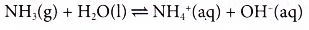
- Ammonia being alkaline can undergo neutralisation with acids to form ammonium salts.
Ammonia + Acid → Ammonium salt
Examples:
(a) Ammonia neutralises sulphuric acid to form ammonium sulphate.
2NH3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → (NH4)2SO4(aq)
(b) Ammonia gas reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to form dense white fumes of ammonium chloride. This is used as a test for detecting ammonia gas.
NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s) - Ammonia solution can react with solutions of some metal ions (except Na+ ion, K+ ion and Ca2+ ion) to produce precipitate of metal hydroxide.
Mn+(aq) + nOH–(aq) → M(OH)n(s)
Examples:
(a) Ammonia reacts with copper ions to produce a blue precipitate, copper(II) hydroxide.
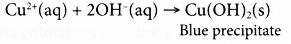
Copper(II) hydroxide dissolves in excess ammonia solution to form a dark blue solution.
(b) Ammonia reacts with zinc ions to produce a white precipitate, zinc hydroxide.
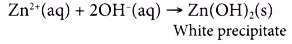
Zinc hydroxide dissolves in excess ammonia solution to form a colourless solution.
(c) Ammonia reacts with iron(III) ions to produce a brown precipitate, iron(III) hydroxide.
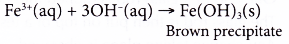
(d) Ammonia reacts with magnesium ions to produce a white precipitate, magnesium hydroxide.
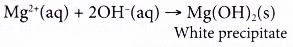
- Ammonia does not burn in air, but in the presence of platinum catalyst in oxygen, ammonia can burn to produce nitrogen dioxide.
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(l)
People also ask
- What is the Haber process used for?
- Uses of ammonia in our daily life
- How is Sulfuric Acid Made?
- Uses of sulphuric acid in daily life
- How Acid rain is formed equations?
Laboratory preparation of ammonia gas experiment
Aim: To investigate the properties of ammonia.
Materials: 0.1 mol dm-3 ammonia solution, 0.1 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution, ammonium chloride, calcium hydroxide, concentrated hydrochloric acid, soda-lime, distilled water, red litmus paper, pH paper.
Apparatus: Test tubes, beaker, U-tube, Bunsen burner, glass rod, delivery tube, stoppers.
Procedure:
Safety Measures
- Do not inhale ammonia gas.
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid is corrosive.
- Carry out this activity in a fume chamber.
A. Preparation of ammonia gas
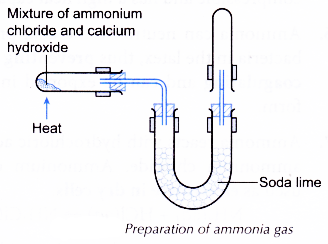
- One spatula of ammonium chloride is mixed with one spatula of calcium hydroxide.
- The apparatus as shown in Figure is set up.
- The mixture is heated strongly.
- The ammonia gas produced is collected in a few test tubes. The test tubes containing ammonia gas must be closed with stoppers.
B. Alkalinity of ammonia
- 5 cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 ammonia solution and 5 cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution are poured into two separate test tubes.
- A piece of pH paper is dipped into the solution in each test tube.
- The pH values of both solutions are recorded.
C. Colour, physical state, smell and solubility of ammonia
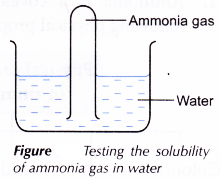
- The colour and physical state of ammonia are observed.
- The stopper of a test tube containing ammonia gas is removed and the smell of the gas is identified.
- A test tube containing ammonia gas is inverted into a beaker of water.
- All observations are recorded.
D. Density of ammonia
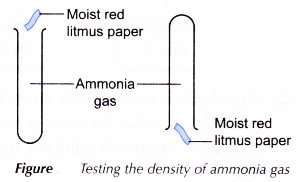
- A test tube containing ammonia gas is held upright and another test tube containing ammonia gas is held upside down.
- The stoppers of the two test tubes are removed.
- After 20 seconds, a piece of moist red litmus paper is put at the mouth of each test tube as shown in Figure.
- The colour of the red litmus paper is recorded.
E. Chemical property of ammonia
- One end of a glass rod is dipped into concentrated hydrochloric acid.
- The glass rod is then put on top of a test tube of ammonia gas.
- Any change taking place is observed.
Observations:
| Section | Observation | Inference |
| B | pH of ammonia solution is 10. pH of sodium hydroxide solution is 14. | Ammonia is a weak alkali. Sodium hydroxide is a strong alkali. |
| C | Colourless gas Pungent smell Water rushes up and fills up the whole test tube. | Ammonia is a colourless gas with a pungent smell. Ammonia is very soluble in water. |
| D | Moist red litmus paper on top of the upright test tube does not change colour. Moist red litmus paper under the inverted test tube turns blue. | Ammonia gas has escaped from the upright test tube and thus is slightly less dense than air. |
| E | Dense white fumes are formed. | Ammonia reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to form ammonium chloride. |
Discussion:
- Ammonia is a weak alkali and has a pH of 10.
- Ammonia is a colourless gas with a pungent smell.
- Ammonia is very soluble in water, ionises partially in water to form ammonium ions and hydroxide ions.
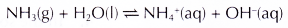
- Ammonia is slightly less dense than air.
- Ammonia reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to form ammonium chloride.
NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(S)
Conclusion:
Ammonia is an alkaline, colourless gas with a pungent smell. It is very soluble in water and is less dense than air. It reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to form dense white fumes of ammonium chloride.
