Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds Containing Functional Groups
We have millions of organic compounds. As number of organic compound is very big it is difficult to remember their names individually.To overcome this problem they have to be properly named. For this, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) had been formed, and one of its responsibilities is to name the organic and inorganic compounds in a systematic order. The basic idea behind the systematic nomenclature is that there should be only one name for the given structure
throughout the world and also there should be only one structure for the given name.
IUPAC stands for International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. IUPAC names are used for International communication. Rules for IUPAC Naming of Organic Compounds :
(i) Select the possible longest chain containing the functional group.
e.g.
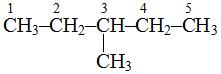 , longest chain contains 5 carbon atoms.
, longest chain contains 5 carbon atoms.
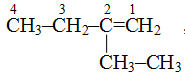 , longest chain contains 4 carbon atoms.
, longest chain contains 4 carbon atoms.
(ii) The number of carbon atoms in the parent compounds is denoted by proper prefix :
Meth for one eth for two Prop for three
but for four pent for five hex for six
hept for seven oct for eight non for nine
e.g., in CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–CH2–CH3 the parent chain contains 6 Carbon atoms, it is called
Hexane. ane is the suffix for alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons) having single bonds only.
(iii) Groups attached to the parent chain are indicated by their names and prefixing the number of carbon to which they are attached in parent chain.
Alkyl group CH3— is called methyl
has general C2H5—is called ethyl
formula CnH2n+1 CH3CH2CH2— is called n-propyl
Example.
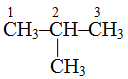
is called 2-methylpropane because methyl group is attached to second carbon atom.
(iv) The counting of carbon chain is done in such a way that the carbon attached to the alkyl group or functional group gets the minimum number, e.g.,
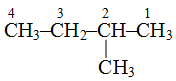 is 2-methylbutane and not 3-methylbutane.
is 2-methylbutane and not 3-methylbutane.
(v) If more than one identical groups are attached to same or different carbon atoms, prefix the numbers of carbon to which they are attached. The number of these groups are indicated as : di for two, tri for three, tetra for four and so on, e.g.
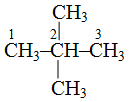 2, 2-dimethylpropane because there are two methyl groups (dimethyl) and both are attached to second carbon therefore 2, 2-dimethylpropane because parent carbon chain contains three carbon atoms Similarly,
2, 2-dimethylpropane because there are two methyl groups (dimethyl) and both are attached to second carbon therefore 2, 2-dimethylpropane because parent carbon chain contains three carbon atoms Similarly,
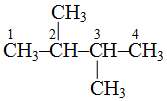 is 2, 3-dimethylbutane
is 2, 3-dimethylbutane
(vi) For double bond in alkenes suffix-ene, for triple bond suffix-yne is used in alkynes. In alkenes and alkynes, number of carbon atoms after which double or triple bond is present is also prefixed, e.g.,
![]() is but-2-ene because double bond is after second carbon atom.
is but-2-ene because double bond is after second carbon atom.
Read More:
