NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles, are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles Ex 5.1
Question 1.
Find the complement of each of the following angles:

Solution:
- Complement of the angle 20° = 90° – 20° = 70°
- Complement of the angle 63° = 90° – 63° = 27°
- Complement of the angle 57° = 90° – 57° = 33°.
Question 2.
Find the supplement of each of the following angles:

Solution:
- Supplement of the angle 105° = 180° – 105° = 75°
- Supplement of the angle 87° = 180° – 87° = 93°
- Supplement of the angle 154° = 180° – 154° = 26°.
Question 3.
Identify which of the following pairs of angles are complementary and which are supplementary.
- 65°, 115°
- 63°, 27°
- 112°, 68°
- 130°, 50°
- 45°,45°
- 80°, 10°.
Solution:
(i) 65°, 115°
∵ 65° + 115° = 180°
∴ The given pair of angles are supplementary.
(ii) 63°, 27°
∵ 63° + 27° = 90°
The given pair of angles are complementary.
(iii) 112°, 68°
∵ 112° + 68° = 180°
∴ The given pair of angles are supplementary.
(iv) 130°, 50°
∵ 130° + 50° = 180°
∴ The given pair of angles are supplementary.
(v) 45°, 45°
∵45° + 45° = 90°
∴ The given pair of angles are complementary.
(vi) 80°, 10°
∵ 80° + 10° = 90°
∴ The given pair of angles are complementary.
Question 4.
Find the angle which is equal to its complement.
Solution:
Let the angle be x°.
Its complement = 90° – x°
According to the question,
x° = 90° – x0
⇒ x° + x° = 90°
⇒ 2x° = 90°
⇒ x° = \(\frac { { 90 }^{ \circ } }{ 3 }\) = 45°
Question 5.
Find the angle which is equal to its supplement.
Solution:
Let the angle be x°.
Its supplement = 180° – x°
According to the question,
x° = 180° – x°
⇒ x° + x° = 180°
⇒ 2x° = 180°
⇒ x° = \(\frac { { 180 }^{ \circ } }{ 3 }\) = 90°
Hence, the required angle is 90°.
Question 6.
In the given figure, ∠ 1 and ∠ 2 are supplementary angles.

If ∠1 is decreased, what changes should take place in ∠ 2 so that both the angles still remain supplementary.
Solution:
∠ 2 will increase as much as ∠ 1 decreases.
Question 7.
Can two angles be supplementary if both of them are:
- acute ?
- obtuse ?
- right ?
Solution:
- No ! two acute angles cannot be supplement
- No ! Two obtuse angles cannot be supplementary.
- Yes ! Two right angles are always supplementary.
Question 8.
An angle is greater than 45°. Is its complementary angle greater than 45° or equal to 45° or less than 45°.
Solution:
Its complementary angle is less than 45°.
Question 9.
In the adjoining figure:

- Is ∠1 adjacent to ∠2 ?
- Is ∠ AOC adjacent to ∠ AOE ?
- Do ∠ COE and ∠ EOD form a linear pair ?
- Are ∠ BOD and ∠ DOA supplementary ?
- Is ∠ 1 vertically opposite to ∠ 4 ?
- What is the vertically opposite angle of ∠ 5 ?
Solution:
- Yes ! ∠ 1 is adjacent to ∠ 2.
- No ! ∠ AOC is not adjacent to ∠ AOE.
- Yes! ∠ COE and ∠ EOD form a linear pair.
- Yes ! ∠ BOD and ∠ DOA are supplementary.
- Yes ! ∠ 1 is vertically opposite to ∠ 4.
- The vertically opposite angle of ∠ 5 is ∠ 2 + ∠ 3, i.e., ∠ COB.
Question 10.
Indicate which pairs of angles are:

- Vertically opposite angles.
- Linear pairs.
Solution:
- ∠ 1 and ∠ 4 ; ∠ 5 and ∠ 2 + ∠ 3
- ∠ 4 and ∠ 5 ; ∠ 5 and ∠ 1
Question 11.
In the following figure, is ∠ 1 adjacent to ∠ 2 ? Give reasons.

Solution:
No ! ∠ 1 is not adjacent to ∠ 2 because their vertex is not common.
Question 12.
Find the values of the angles x, y and z in each of the following:

Solution:

Question 13.
Fill in the blanks:
- If two angles are complementary, then the sum of their measures is
- If two angles are supplementary, then the sum of their measures is
- Two angles forming a linear pair are
- If two adjacent angles are supplementary, they form a
- If two lines intersect at a point, then the vertically opposite angles are always
- If two lines intersect at a point, and if one pair of vertically opposite angles are acute angles, then the other pair of vertically opposite angles are
Solution:
- 90°
- 180°
- supplementary
- linear pair
- equal
- obtuse angles
Question 14.
In the adjoining figure, name the following pairs of angles.

- Obtuse vertically opposite angles
- Adjacent complementary angles
- Equal supplementary angles
- Unequal supplementary angles
- Adjacent angles that do not form a linear pair.
Solution:
- ∠ AOD and ∠ BOC
- ∠ EOA and ∠ AOB
- ∠ BOE and ∠ DOE
- ∠ EOC and ∠ EOA
- ∠ AOB and ∠ AOE ; ∠ AOE and ∠ EOD ; ∠ EOD and ∠ DOC.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles Ex 5.2
Question 1.
State the property that is used each of the following statements ?
- If a || b, then ∠ 1 = ∠ 5.
- If ∠ 4 = ∠ 6, then a || b.
- If ∠ 4 + ∠ 5 = 180°, then a || b.

Solution:
- If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal then the pair of corresponding angles have equal measure.
- If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal then the pairs of alternate interior angles are equal.
- If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary.
Question 2.
In the following figure, identify:

- the pairs of corresponding angles.
- the pairs of alternate interior angles.
- the pairs of interior angles on the same side of the transversal.
- the vertically opposite angles.

Solution:
- ∠ 1 and ∠ 5, ∠ 2 and ∠ 6, ∠ 4 and ∠ 8, ∠ 3 and ∠ 7
- ∠ 3 and ∠ 5, ∠ 2 and ∠ 8
- ∠ 3 and ∠ 8, ∠ 2 and ∠ 5
- ∠ 1, ∠ 3, ∠ 2, ∠ 4, ∠ 5, ∠ 7, ∠ 6 and ∠ 8
Question 3.
In the adjoining figure, p || q. Find the unknown angles.
Solution:
a = 55°, b = 125°, c = 55°, d = 125°, e = 55°, f= 55°.
Question 4.
Find the value of x in each of the following figures if l || m.

Solution:
- x = 70°
- x = 100°.
Question 5.
In the given figure, the arms of two angles are parallel. If ∠ ABC = 70°, then find

Solution:
- 70°
- 70°
Question 6.
In the given figures below, decide whether l is parallel to m.


Solution:
- l is not parallel to m
- l is not parallel to m
- l || m
- l is not parallel to m
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles MCQ
Important Multiple Choice Questions
1. When the sum of the measures of two angles is 90°, the angles are called
(а) supplementary angles
(b) complementary angles
(c) adjacent angles
(d) vertically opposite angles.
2. The sum of the measures of two complementary angles is
(a) 180°
(b) 60°
(c) 45°
(d) 90°.
3. The measure of the complement of the angle 30° is
(а) 30°
(b) 16°
(c) 60°
(d) 160°.
4. Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Two acute angles can be complementary to each other
(b) Two obtuse angles can be complementary to each other
(c) Two right angles can be complementary to each other
(d) One obtuse angle and one acute angle can be complementary to each other.
5. The measure of the complement of the angle 46° is
(a) 90°
(b) 46°
(c) 16°
(d) 136°.
6. What is the measure of the complement of the angle 80°?
(a) 10°
(b) 100°
(c) 36°
(d) 20°.
7. Which pair of the following angles are complementary?


8. The measure of the angle which is equal to its complement is
(a) 30°
(b)60°
(c) 46°
(d) 90°.
9. Which of the following pairs of angles is not a pair of complementary angles?
(a) 60°, 30°
(b) 66°, 34°
(c) 0°, 90°
(d) 160°, 30°.
10. What is the measure of the complement of the angle 90°?
(а) 90°
(b) 0°
(c) 180°
(d) 46°.
11. When the sum of the measures of two angles is 180°, the angles are called
(a) adjacent angles
(b) complementary angles
(c) vertically opposite angles
(d) supplementary angles.
12. The sum of the measures of two supplementary angles is
(a) 90°
(b) 180°
(c) 360°
(d) none of these.
13. The measure of the supplement of the angle 120° is
(a) 30°
(b)45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°.
14. Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Two acute angles can be supplementary.
(b) Two right angles can be supplementary.
(c) Two obtuse angles can be supplementary.
(d) One obtuse angle and one acute angle cannot be supplementary.
15. The measure of the supplement of the angle 90° is
(a) 45°
(b) 60°
(c) 30°
(d) 90°.
16. The measure of the angle which is equal to its supplement is
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 90°
(d) 60°.
17. Which of the following pairs of angles is not a pair of supplementary angles?
(a) 90°, 90°
(b) 32°, 58°
(c) 0°, 180°
(d) 76°, 104°.
18. What is the measure of the supplement of the angle 0°?
(a) 45°
(b) 90°
(c) 120°
(d) 180°.
19. Which pair of the following angles are not supplementary?


20. The measure of the supplement of the angle 179° is
(a) 1°
(b) 2°
(c) 3°
(d) 4°.
21. Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Two adjacent angles can be complementary.
(b) Two adjacent angles cannot be supplementary
(c) An acute angle cannot be adjacent to an obtuse angles.
(d) Two right angles cannot be adjacent angles.
22. The angles in a linear pair are
(a) complementary
(b) supplementary
(c) not adjacent angles
(d) vertically opposite angles.
23. Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Two acute angles can form a linear pair.
(b) Two obtuse angles can form a linear pair
(c) Two right angles can form a linear pair
(d) One obtuse angle and one acute angle cannot form a linear pair.
24. Which of the following pairs of angles form a linear pair?

25. The sum of the measures of the angles in a linear pair is
(a) 90°
(b) 180°
(c) 360°
(d) none of these.
26. Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Two vertically opposite angles can be acute
(b) Two vertically opposite angles can be obtuse
(c) Two vertically opposite angles can be right angles
(d) Two vertically opposite angles may be unequal.
27. Which of the following statements is false?
(a) When a transversal cuts two parallel lines, each pair of corresponding angles are equal.
(b) When a transversal cuts two parallel lines, each pair of alternate interior angles are equal.
(c) When a transversal cuts two parallel lines, each pair of interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary.
(d) A transversal cuts two parallel lines in three points.
28. In the following figure, ∠ AOB and ∠ BOC are

(a) complementary angles
(b) supplementary angles
(c) adjacent angles
(d) none of these.
29. In the following figure, reflex ∠ AOB is equal to

(a) 60°
(b) 120°
(c) 300°
(d) 360° .
30. Which of the following statements is false?
(a) When a transversal cuts two lines, such that pairs of corresponding angles are equal, then the lines have to be parallel.
(b) When a transversal cuts two lines such that pairs of alternate interior angles are equal, then the lines have to be parallel.
(c) When a transversal cuts two lines such that pairs of interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary, then the lines have to be parallel.
(d) When a transversal cuts two lines such that pairs of interior angles on the same side of the transversal are complementary, then the lines have to be parallel.
31. In the following figure, two straight lines AB and CD are intersecting each other at the point 0 and the angles thus formed at 0 are marked, then the value of ∠x – ∠y is

(a) 56°
(b) 118°
(c) 62°
(d) 180°.
32. In the following figure, tell which pair of angles are not corresponding angles?

(a) ∠1, ∠ 5
(b) ∠ 2, ∠ 6
(c) ∠ 3, ∠ 7
(d) ∠ 3, ∠ 5.
33. See the figure of Q. 32 above. Which pair of angles are alternate interior angles?
(a) ∠ 1, ∠ 5
(b) ∠ 2, ∠ 6
(c) ∠ 3, ∠ 7
(d) ∠ 3, ∠ 5.
34. In the following figure, a transversal cuts two parallel lines l and m at points G and H respectively and the angles thus formed are marked. If ∠ 1 is an acute angle, then, which of the following statements is false?

(а) ∠ 1 + ∠ 2 = 180°
(b) ∠ 2 + ∠ 5 = 180°
(c) ∠ 3 + ∠ 8 = 180°
(d) ∠ 2 + ∠ 6 = 180°.
35. In the following figure, a transversal c intersects two parallel lines a and b at A and B respectively and the angles formed at A and B are marked. Tell which of the following pairs of angles need not be equal?

(a) ∠ 1, ∠ 2
(b) ∠1, ∠ 3
(c) ∠ 1, ∠ 5
(d) ∠ 2, ∠ 8.
36. Which of the following pairs of angles are not adjacent angles?

37. Find the measure of the angle which is double of its complementary angle?
(a) 60°
(b) 30°
(c) 45°
(d) 120°.
38. Find the measure of the angle which is half of its supplementary angle?
(a) 60°
(b) 120°
(c) 90°
(d) 45°.
39. In the following figure, if ∠ 1 + ∠ 3 = 120°, then ∠ 2 + ∠ 4 is equal to

(a) 60°
(b) 120°
(c) 240°
(d) 80°
40. In the following figure, if ∠ 1 + ∠ 2 = 100°, then the measure of ∠ 4 is equal to

(a) 50°
(b) 100°
(c) 80°
(d) 130°.
41. In the following figure, ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = 230°, then the measure of ∠4 is equal to

(a) 130°
(b) 80°
(c) 65°
(d) 90°
42. In the following figure EF || GH. Then, the measure of ∠x is equal to

(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 40°
43. In the following figure, l || m. Find the measure of ∠ x.

(a) 60°
(b) 45°
(c) 30°
(d) none of these
44. In the following figure, AB || DG and BC || EF. Also, ∠ ABC = 60°. Then, the measure of ∠ DEF is

(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 45°
(d) 120°.
45. Find the value of x in the following figure, if l || m.

(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) none of these.
ANSWERS

HINTS/SOLUTIONS
1. Definition of complementary angles
2. Definition of complementary angles
3. 90° – 30° = 60°.
5. 90°- 45° = 45°.
6. 90° – 80° = 10°.
7. 60°+ 30° = 90°.
8. x° + x° = 90° ⇒ x° = 45°.
9. 150° + 30° = 180° ≠ 90°.
10. 90° – 90° = 0°.
11. Definition of supplementary angles.
12. Definition of supplementary angles.
13. 180° – 120° = 60°.
15. 180° – 90° = 90°.
16. x° + x° = 180° ⇒ x° = 90°.
17. 32° + 58° = 90° ≠ 180°.
18. 180° – 0° = 180°.
19. 120° + 90° = 210° ≠ 180°.
20. 180° – 179° – 1°.
22. Definition of a linear pair of angles.
24. 120° + 60° = 180°.
25. Definition of a linear pair of angles.
29. ∠ AOB = 360° – 60° = 300°.
31. ∠x – ∠y = (180° – 62°) – 62° = 118°- 62° = 56°.
32. ∠ 3, ∠ 5 are alternate interior angles.
33. Definition of alternate interior angles.
34. ∠ 2 = ∠ 6, corresponding angles.
35. ∠ 1, ∠ 2 simply make a linear pair.
37. x° = 2(90° – x°) ⇒ x° = 60°.
38. x° = 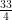
39. ∠ 2 + ∠ 4 = 360°- (∠ 1 + ∠ 3) = 360°- 120° = 240°
40. ∠1 = ∠2; ∠1 + ∠2 = 100°
∴ ∠ 1 = 50°
∴ ∠ 4 = 180° – 50° = 130°.
41. ∠ 4 = 360° – 230° = 130°.
42. (x + 30°) + 120° = 180° ⇒ x = 30°.
43. x + x + 60° = 180° ⇒ x = 60°.
44. ∠ DEF = ∠ DGC = ∠ ABC = 60°.
45. x + 120° = 180° ⇒ x = 60°.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
