Nature Vocabulary: Nature and environment are utterly beautiful, and it never fails to amaze people. The natural elements of this world have given us the opportunity to live a healthy life. The environment consists of many components such as mountains, deserts, oceans, stars, planets and this environment vocabulary list includes all these terminologies. In this article, we have developed a list of nature vocabulary, which will help you have a better understanding of the earth.
List of Nature Vocabulary Words in English
Name of Nature Vocabulary Words
Without the world’s environment, life on Earth would be extremely difficult, nearly impossible. Even though we have become so advanced, we have still not been able to go above nature. Nature offers us the most beautiful things, which makes life on Earth worthwhile. In this article, we have also included a description of these natural components which will make the process of learning even more fun.
List of Natural Elements
- Grass
- Soil
- Canal
- Clouds
- Rain
- Mountain
- Planet
- Bridge
- Plateau
- Forest
- Hill
- Lighthouse
- Island
- Estuary
- Bay
- River
- Riverbank
- Beach
- Sea
- Ocean
- Desert
- Stone
- Pond
- Water
- Plant
- Moss
- Flower
- Bush
- Sand
- Mud
- Stars
- Mine
- Road
- Tunnel
- Volcano
- Cave
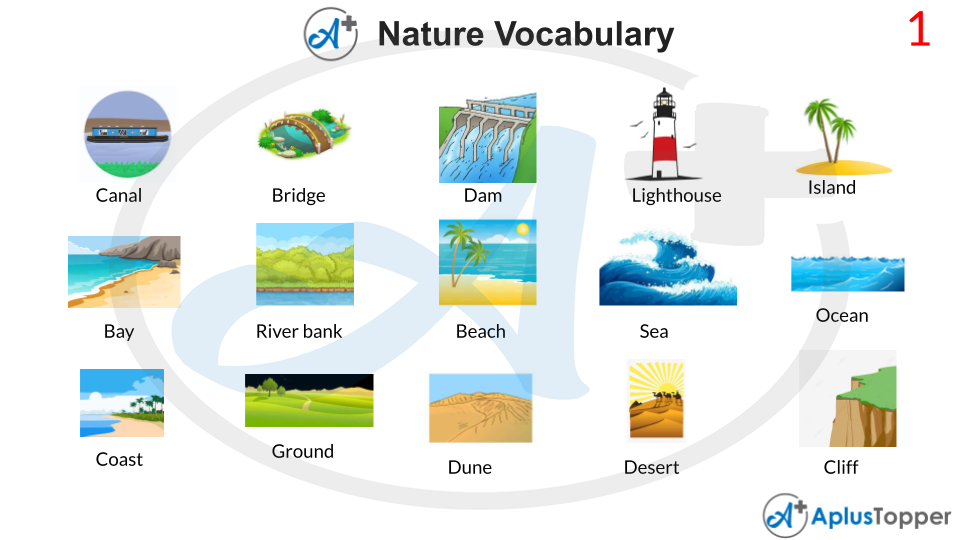
Description of the Nature Vocabulary Words
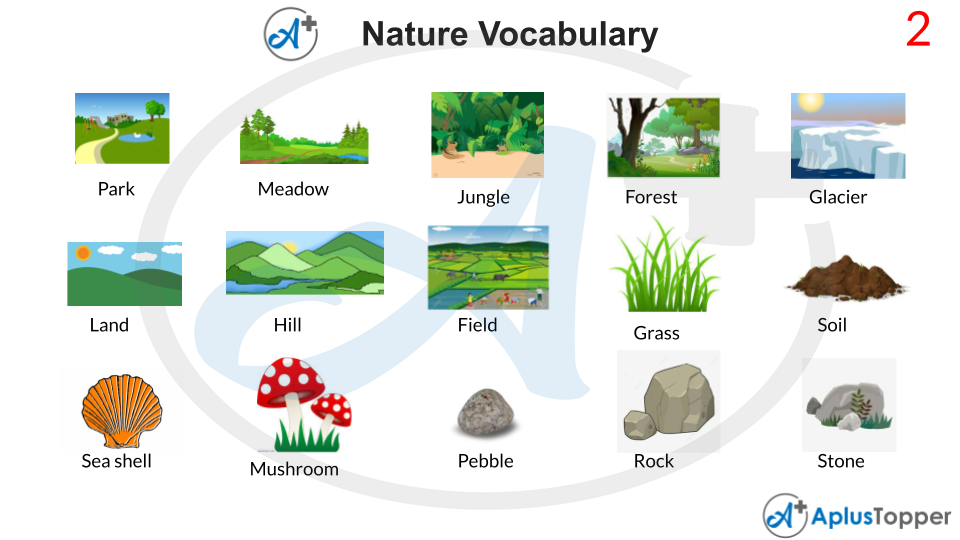
Grass
The grass is a plant having narrow leaves that grow from the base. Grass gets water from its roots in the ground. A common type of grass is used for covering the ground in a lawn and other places. It is a very common plant and can be found very easily grown in a number of areas. It prevents erosion by water and wind, adds visual appeal and helps in breaking down organic chemicals.
Soil
Soil is a loose surface material that covers most land. It consists of organic matter, inorganic particles, water, air as well as living organisms. It is formed from the weathering of rocks. Soil is highly necessary for life on earth. It provides an environment for plants for growing, prevents natural hazards like flooding, landslides and contains high levels of biodiversity.
Canal
A canal is a man-made waterway allowing ships and boats to pass from one water body to another. It also helps in conveying water for irrigation. Canals are fed by the rainwater received from the rivers, and that water is used for irrigation. They also provide water for hydroelectricity, fishery development, drinking water supply and navigation.
Clouds
Clouds are a mass of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere. They are created when the evaporated water vapour (from water bodies) turns into liquid water droplets. These tiny water droplets are formed on minute particles such as dust floating in the air.
Rain
Rain is the drops of water falling from clouds. Rain is highly beneficial in many ways – it is suitable for soil and plants and helps prevent disasters such as droughts. Rain is a source of fresh water for several cultures where lakes, rivers or aquifers aren’t easily available. It makes modern life possible by providing the water needed for industry, agriculture, hygiene and electrical energy.
Mountain
A mountain is a huge natural rise of the Earth’s surface. Mountains generally have sloping, steep sides and rounded or sharp ridges, and a high point called a summit or peak. Mountains are one of the main tourist spots for people to visit. They visit there for the beautiful scenery. Farmers graze their animals on mountainous slopes. Many types of trees, such as coniferous trees, grow in the mountains.
Planet
A planet is a massive celestial object orbiting a star. Planets are smaller in size compared to stars, and they don’t produce light. It is a celestial body that has mass. There are celestial objects known as satellites that orbit the planets. Our solar system has eight planets orbiting around the star – the sun.
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built over a railway, road or river – without blocking the structures underneath – so that people and vehicles can cross from one side to another. Bridges have made it easier to connect two places which is a relatively long distance into a comparatively shorter one.
Plateau
A plateau is a flat, raised landform that sharply rises above the surrounding area on at least one side. They are among the four significant landforms – plains, mountains and hills. Plateaus can be found in every continent, and people have learned to use them for their benefit. Plateaus are used for ranching, farming, hunting, fishing, sightseeing, mountain biking, developing roads and mining.
Forest
A forest is a section of land that has many forests. Forests are essential for the importance and growth of many places across the world. Forests are an ecosystem including many plants and animals. Forests have 80% of the planet Earth’s biomass. Forests have many uses for humans, such as for getting timber, fibre, essential oils, medicinal use, bamboo, fuelwood and also helps to stop soil erosion.
Hill
A hill is a section of land that has risen higher than everything surrounding it. They are not as high as mountains and are less steep. Hills have been used for homes and urbanization for many years. The higher elevation has helped people to avoid natural disasters such as floods. They are also famous for sightseeing and tourism.
Lighthouse
It is a building, tower or another type of structure topped with a very bright light known as a beacon. It is used to warn mariners about the dangers of dangerous rocky coasts and shallow waters, helping guide the vessels safely into and out of the harbours. Most lighthouses also have fog signals like horns, canons or bells, which sends sound for warning to ships about hazards during low visibility periods.
Island
An island is a piece of land surrounded by water on all sides like a river, lake or sea. Islands are smaller in comparison to continents. Island ecosystems are biodiversity hotspots as well as are home to rare species. They are also conversation frontiers and sea-level indicators.
Estuary
An estuary is a partly closed coastal water body where the fresh water from streams and rivers mixes with saltwater from the oceans. Estuaries and their surrounding landmasses are places of transition from land to sea. It provides critical habitat for species – such as amphibians, fish, insects, birds and other wildlife – which are valuable recreationally, commercially and culturally.
Bay
A bay is an inlet of a sea or another water body generally smaller than a gulf which is partially surrounded by land. It is a mall water body set off from the main water body. Plate tectonics is the primary process by which many bays are formed. The largest bay in the world is the Bay of Bengal, which was also formed by plate tectonics.
River
A river is a water stream flowing through a channel on the surface of the ground. It is a ribbon-like water body that flows downhill due to the gravitational force. Humans use river water for a lot of purposes such as drinking water, irrigation in agriculture, transportation, for producing electricity from hydroelectric dams. They are even used for leisure activities such as boating, rafting and swimming.
Riverbank
The passage where rivers flow is called the river bed, and the land on each side is known as river banks. Riverbanks offer valuable habitats for wildlife, which supports a wide range of animal and plant species. It also supplies food, shade and shelter as well as protection to the aquatic environment from polluted surface runoff.
Beach
The beach is a narrow land strip separating a water body from the land. It is a landmass along the coast of a sea, ocean, river or lake. Beaches are often used for recreational purposes – they bask in the sun, swim or just relax. Beaches also provide protection to the residents that live near the ocean, acting as a buffer against the powerful waves and high winds.
Sea
A sea is smaller compared to oceans and generally located where the oceans meet the land. Generally, it is partially enclosed by land. Sea has been used for many purposes such as travel, trade, power generation, mineral extraction, warfare and leisure activities.
Ocean
Oceans are large areas of water between the continents. Oceans are extremely big, and they can join smaller seas together. Oceans cover 72% of the planet. There are five main oceans – Pacific, Atlantic, Southern, Arctic, and Indian ocean. The oceans give humans the opportunity to trade and give many people jobs in trade, shipping, fishery, tourism and travel.
Desert
A desert is a location that receives less than ten inches of rain each year. Deserts are extremely dry and might either be very cold and very hot. Deserts are famous for tourism. Some plants and animals can survive only in deserts, such as cactus and camels, respectively.
Stone
A stone is a hard substance formed with mineral matter. They are used as the base of preparation for various constructions. They are also used for typical building work such as in foundation, flooring etc. Stones are used as a part of the architectural beauty of different types of structures.
Pond
A pond is a water body surrounded by land on all sides, but they are smaller than lakes. Most ponds are not more than six or seven feet deep. They are also habitats of various organisms such as amphibians, reptiles, fish, waterfowl as well as some mammals. Many ponds also provide water for livestock and agriculture.
Water
Water is a transparent, odourless and colourless liquid that forms the most significant parts of the world. It forms the lakes, seas, rivers and rain. It is a chemical element that is the basis of life on earth. Without water living organisms wouldn’t have been sustained on this planet. It is also used for cooking, bathing, washing clothes, in agriculture, industries and for generating electricity.
Plant
Plants are living things growing in the earth which has stems, roots and leaves. They are essential for every ecosystem. They provide oxygen, without which life on earth would be unimaginable. They are also the primary source of products like food, medication, rubber, paper, wood and many more. They are also used symbolically like mythology, art and literature.
Moss
Mosses are small non-vascular plants, non-woody plants absorbing water and nutrients primarily by their leaves and harvesting sunlight and carbon dioxide for creating food by photosynthesis. They aid in soil erosion control by absorbing moisture and providing surface cover. They are sometimes also used in home decoration and florist trade.
Flower
Flowers are the parts of the plants which is typically brightly coloured, grow at the end of the stems, and only survives for some time before it turns into a fruit. It is the fruit-bearing part of the plants, which consists of reproductive organs. They are used for medicine, crafts, air purifiers, beauty products and even clothing.
Bush
A bush is a big plant that is smaller than a tree and has many branches. Bushes are used for the main beautification of a landscape. They can be grown in gardens, orchids, usually for beautifying backgrounds. They help in environmental conversation by stopping soil erosion, water wastage and also help in restoring the green cover of Earth.
Sand
Sand is a type of loose granular material that blankets the beaches, deserts and riverbeds of the world. The most widely found component of sand is silicon dioxide in the form of quartz. Sand has many compositions; however, it is defined by its grain size. There are many advantages of sand, such as using water infiltration, making sandpaper as a raw material in constructions and many more.
Mud
Mud is soil, silt, loam or clay mixed with water. It generally forms after rainfall or near water sources. Its malleability and low cost make it ideal as a building material. It offers better insulation compared to steel and concrete structures.

Stars
Stars are giant celestial bodies mostly made of hydrogen and helium, which produces light and heat from the churning nuclear forges inside its cores. Apart from the sun, the tiny dots of light that we see in the sky are light-years from Earth. In earlier times, stars helped humans to navigate through the Earth.
Mine
Mining is the process of extraction of metals and minerals from the earth. Mining is needed to produce services, goods and infrastructure, which will improve the quality of living. Mining materials are required for constructing hospitals, roads, to build houses and automobiles, computing satellites and computes, generating electricity and providing many other services and goods enjoyed by the consumers.
Road
A road is a long, narrow stretch having a smoothed and paved surface, usually made for travelling by motor vehicles, carriage etc., from one point to another. There are many advantages of building roads, such as makes transport more economical, providing door-to-door services, it can be used as a feeder to other modes of transportation, and the loading and unloading cost is much lower.
Tunnel
A tunnel is a passageway located underground, dug through the surrounding earth, soil and rock. They are mostly enclosed except the entrance and exit points. These are made usually under a hill or sea. They allow unobstructed and rapid transport facilities in the big congested cities.
Volcano
A volcano is a conical mountain having an opening in the earth’s crust through which lava, gases, and volcanic ash escapes. Beneath the volcano, liquified magma – consisting of dissolved gases – rises through these cracks on Earth’s surface. Volcanoes can offer people many benefits like volcanic rocks and volcanic ash, which provides fertile land resulting in high crop yield for farmers.
Cave
A cave or a cavern is a naturally occurring opening on the earth’s surface that is large enough for human exploration. These cavities are formed by many types of rocks after undergoing many processes. The most common and largest caves are created by a chemical reaction between the circulating groundwater and bedrock, which is composed of dolomite or limestone.
