How has the Model of the Atom Changed Over the Years?
The Atomic Structure
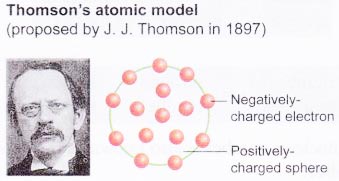
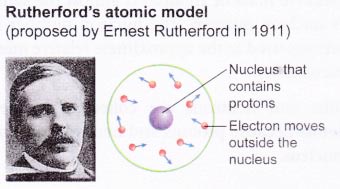
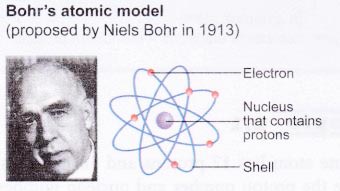
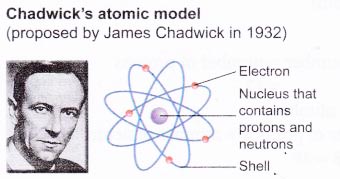
The historical development of atomic models:
Over the last 100 years, scientists have done investigations which show that atoms are made up of even smaller particles.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
People also ask
- How would you describe the Structure of an Atom
- What was Rutherford’s Original Hypothesis
- What did Bohr Contribute to the Theory of an Atom
- What are the Characteristics of Electron, Proton and Neutron
- Explain Bohr Bury rules for Distribution of Electrons into Different Shells
- What are the Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones of an Element
- What did Dalton Contribute to the Understanding of the Atom
- What is the Definition of Atom and Molecule
- What is Atomic Mass
Subatomic Particles Examples
Subatomic particles of an atom:
- Atoms are made up of three types of smaller particles, namely protons, neutrons and electrons.
- These particles are known as subatomic particles.
- The relative masses and charges of these three subatomic particles are shown in Table 2.4. The masses and charges are measured relative to a proton because their actual values are incredibly small.
Relative masses and charges of subatomic particlesSubatomic particle Symbol Relative mass Relative electric charge Proton P 1 + 1 Neutron n 1 0 Electron e– 1/1840 -1 - Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom while electrons surround the nucleus.
Nucleus contains protons and neutrons
(a) As the masses of protons and neutrons are greater than electrons, most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
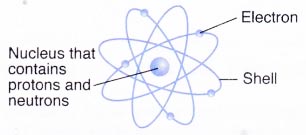
(b) The nucleus has an overall positive charge due to the positively-charged protons in it.
(c) An atom consists of an equal number of electrons and protons. Hence, an atom is electrically neutral.
How do you determine the number of nucleons?
Proton number and nucleon number:
- Scientists use the proton number and nucleon number to describe an atom.
- Proton number of an element is the number of protons in its atom.
- Since atoms are neutral, the proton number is also the number of electrons in the atom.
- Each element has its own proton number. For example, sodium has a proton number of 11. Hence, all atoms of sodium have 11 protons. Oxygen has a proton number of 8, so all oxygen atoms have 8 protons.
- Nucleon number of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons in its atom. From definition,
nucleon number = number of protons + number of neutrons
However, number of protons = proton number
Therefore,
nucleon number = proton number + number of neutrons
or
number of neutrons = nucleon number – Proton number - The nucleon number is also known as the mass number.
- The relative mass of an atom is almost the same as its nucleon number. The nucleon number is sometimes used as the approximate relative mass in calculations.
- Protons and neutrons are collectively called nucleons because protons and neutrons occupy the nucleus.
- In a neutral atom, number of electrons = number of protons.
Proton number and Nucleon number Example Problems with Solutions
1. A chlorine atom has 17 protons and 18 neutrons.What are the proton number and nucleon number of the atom?
Solution:
Proton number = number of protons = 17
Nucleon number= number of protons + number of neutrons
= 17 + 18
= 35
2. Lithium has a proton number of 3 and a nucleon number of 7. How many protons, electrons and neutrons are present in an atom of lithium?
Solution:
Number of protons = proton number = 3
An atom is neutral.
Therefore,
number of electrons = number of protons = 3
Number of neutrons
= nucleon number – proton number
= 7 – 3
= 4
What element is represented by the symbol N?
Symbols of elements:
- Each element is given a name and a symbol. Some examples of elements and their symbols are shown in Table.
Element Symbol Element Symbol Hydrogen H Sodium Na Helium He Magnesium Mg Lithium Li Aluminium Al Beryllium Be Silicon Si Boron B Phosphorus P Carbon C Sulphur S Nitrogen N Chlorine Cl Oxygen O Argon Ar Fluorine F Potassium K Neon Ne Calcium Ca - Notice that:
(a) each symbol consists of one or two letters. For elements with two-letter symbols, the first letter is always a capital letter while the second letter is always a small letter.
(b) for most elements, the letters used in their symbols take either the first letter or the first and another letter of their names. Some examples include the symbols of hydrogen, H; neon, Ne and magnesium, Mg.
(c) for some elements, the symbols come from Latin names such as natrium (Na) for sodium and kalium (K) for potassium. - The standard representation for an atom of any element shows the proton number and the nucleon number of the element. It can be written as follows:
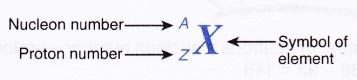
For example, a sodium atom is represented as 2311Na. This means that sodium has a proton number of 11 and a nucleon number of 23. - Sometimes an element is represented by using only the nucleon number. For example, 2311Na is represented by sodium-23.
Representation of Atom Example Problems with Solutions
1. A carbon atom has 6 protons and 7 neutrons. Represent the atom in the form of AZX.
Solution:
The symbol of carbon is C.
A denotes the nucleon number.
Nucleon number = number of protons + number of neutrons
= 6 + 7 = 13
Z denotes the proton number.
Proton number = number of protons = 6
Hence, the carbon atom is represented as 136C.
2. Phosphorus-32 has 17 neutrons. What are the proton number and nucleon number of the atom? Represent the atom in the form of AZX.
Solution:
The symbol of phosphorus is P.
Proton number = nucleon number – number of neutrons
= 32-17 = 15
Nucleon number = 32
Hence, the phosphorus atom is represented as 3215P.
