ML Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Chapter Test
Solve the following (1 to 3) equations :
Question 1.
(i) x(2x + 5) = 3
(ii) 3x2 – 4x – 4 = 0
Solution:
(i) x(2x + 5) = 3
{∵ 2 ×(-3) = -6
∴ – 6 = 6 × (-1)
5 = 6 – 1}
⇒ 2x2 + 5x – 3 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 6x – x – 3 = 0
⇒ 2x(x + 3) – 1(x + 3) = 0
⇒ (x + 3)(2x – 1) = 0
Either, x + 3 = 0, then x = -3
or 2x – 1 =0, then 2x = 1 ⇒ x = 12
∴ x = -3, 12
(ii) 3x2 – 4x – 4 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 6x + 2x – 4 = 0
{∵ 3 × (-4) = -12
∴ -12 = -6 × 2
-4 = -6 + 2}
⇒ 3x(x – 2) + 2(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2) (3x + 2) = 0
Either, x – 2 = 0, then x = 2
or 3x + 2 = 0, then 3x = -2 ⇒ x = −23
∴ x = 2, −23
Question 2.
(i) 4x2 – 2x + 14 = 0
(ii) 2x2 + 7x + 6 = 0
Solution:
(i) 4x2 – 2x + 14 = 0
⇒ 16x2 – 8x + 1 = 0
⇒ 16x2 – 8x + 1 =0
⇒ 16x2 – 4x – 4x + 1 =0
⇒ 4x(4x – 1) – 1 (4x – 1) = 0
⇒ (4x – 1) (4x – 1) = 0 ⇒ (4x – 1)2 = 0
⇒ 4x – 1 = 0 => 4x = 1
∴ x = 14,14
(ii) 2x2 + 7x + 6 = 0
{∵ 2 × 6 = 12
∴ 12 = 3 × 4
7 = 3 + 4}
⇒ 2x(x + 2) + 3(x + 2) = 0
⇒ (x + 2) (2x + 3) = 0
Either, x + 2 = 0. then x = -2
or 2x + 3 = 0, then 2x = -3 ⇒ x = −32
∴ x = -2, −32
Question 3.
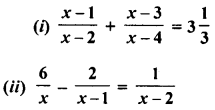
Solution:
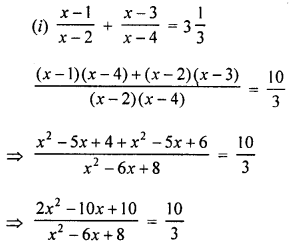
⇒ 10x2 – 60x + 80 = 6x2 – 30x + 30
⇒ 10x2 – 60x + 80 – 6x2 + 30x – 30 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 30x + 50 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 15x + 25 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 10x – 5x + 25 = 0
{∵ 2 × 25 = 50
∴ 50 = -10 × (-5)
-15 = -10 – 5}
⇒ 2x(x – 5) – 5(x – 5) = 0
⇒ (x – 5) (2x – 5) = 0
Either, x – 5 = 0, then x = 5
or 2x – 5 = 0, then 2x = 5 ⇒ x = 52
∴ x = 5, 52
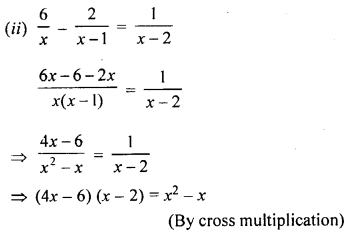
⇒ 4x2 – 8x – 6x + 12 = x2 – x
⇒ 4x2 – 14x + 12 – x2 + x = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 13x + 12 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 4x – 9x + 12 = 0
{∵ 3 × 12 = 36
∴ 36 = (-4) × (-9)
-13 = -4 – 9}
⇒ x(3x – 4) – 3(3x – 4) = 0
⇒ (3x – 4) (x – 3) = 0
Either, 3x – 4 = 0, then 3x = 4 ⇒ x = 43
or x – 3 = 0, then x = 3
∴ x = 3, 43
