ML Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter 16 Chapter Test
Question 1.
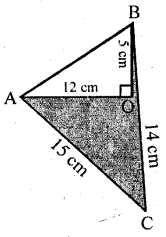
(a) Calculate the area of the shaded region.
(b) If the sides of a square are lengthened by 3 cm, the area becomes 121 cm2. Find the perimeter of the original square.
Answer:
(a) In the figure,
OA ⊥ BC
AC = 15 cm, AO = 12 cm, BO = 5 cm,
BC = 14 cm
∴ OC = BC – BO = 14 – 5 = 9 cm
Area of right ∆AOC
= 12 base × altitude
= 12 × 9 × 12 cm2 = 54 cm2
(b) Let the side of original square = x cm
Then length of given square = (x + 3) cm
Area = side × side
⇒ 121 = (x + 3)(x + 3)
⇒ (11)2 = (x + 3)2
⇒ 11 = x + 3 ⇒ x + 3 = 11
⇒ x = 11 – 3 cm ⇒ x = 8 cm
Question P.Q.
The given figure shows a kite in the shape of a square with a diagonal 32 cm and an isosceles triangle of base 8 cm and side 6 cm each. How much paper is used in making the kite ? Ignore the wastage of the paper is making the kite.
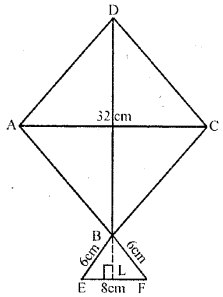
Answer:
Length of each diagonal of the square ABCD = 32 cm
i.e. AC = BD = 32 cm
Base EF of isosceles ∆BEF = 8 cm
and each side = 6 cm
Draw BL ⊥ EF
Area of square = ( Diagonal )22
= (32)22=10242cm2 = 512 cm2
In ∆BEL, ∠L = 90°
BL2 = BE2 – EL2 (Pythagoras Theorem)
= (6)2 – (4)2 = 36 – 16 = 20
∴BL = √20 = √4×5 = 2√5 cm
Area of isosceles triangle = 12 Base × alt.
= 12 × 8 × 2√5 cm2
= 8√5 cm2
∴ Total area of the kite = (512 + 8√5) cm2
= 512 + 8 (2.236) cm2
= 512 + 17.89 = 529.89 cm2
Question 2.
(a) Find the area enclosed by the figure (i) given below. All measurements are in centimetres:
(b) Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD shown in figure (ii) given below. All measurements are in centimetres.
(c) Calculate the area of the shaded region shown in figure (iii) given below. All measurements are in metres.
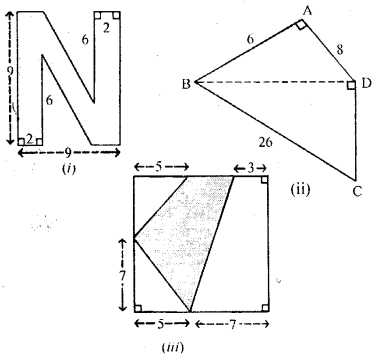
Answer:
(a) Area of figure (i) = Area of ABCD – Area of both triangles
= (9 × 9) – (12×5×6) × 2 cm2
= (81 – 15 × 2)
= (81 – 30) cm2 = 51 cm2
(b) In ∆ ABD By Pythagoras theorem,
⇒ BD2 = AB2 + AD2 ⇒ BD2 =(6)2 + (8)2
⇒ BD2 = 36 + 64 ⇒ BD2 = 100 ⇒ BD = 10cm
In ∆BCD
By Pythagoras theorem
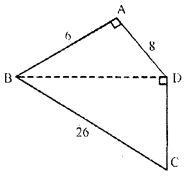
BC2 = BD2 + CD2
⇒ (26)2 = (10)2 + (CD)2
⇒ 676 = 100 + CD2
⇒ CD2 + 100 = 676 ⇒ CD2 = 676 – 100
⇒ CD2 = 576 ⇒ CD = √576 cm ⇒ CD = 24 cm
Area of given fig.= Area of ∆ ABD + Area of ∆ BCD
= 12 × Base × height + 12 × Base × height
= 12 × AB × AD + 12 × CD × BD
= [12 × 6 × 8 + 12 × 24 × 10]cm2 = [3 × 8 + 12 × 10] cm2
= (24 + 120) cm2 = 144 cm2
(c) Area of figure (iii) = Area of ABCD – (Area of Jst part + Area of 2nd part + Area of 3rd part)
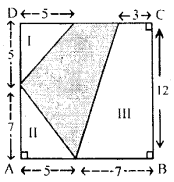
Hence, required area of given figure = 54 m2
Question 3.
Asifa cut an aeroplane from a coloured chart paper (as shown in the adjoining figure). Find the total area of the chart paper used, correct to 1 decimal place.
Answer:
The whole figure of an aeroplane consists 5 figures, three triangles, one rectangle and one trapezium
Take midpoint M of AB
∴ AM = MB = 1 cm
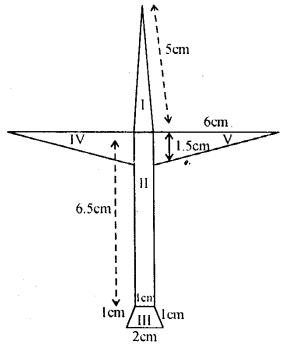
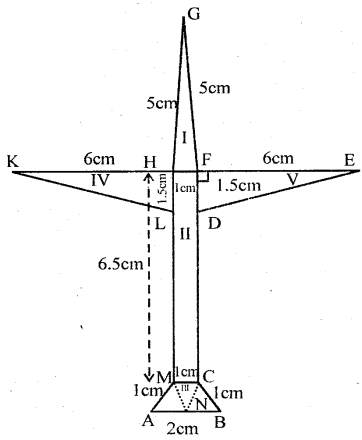
Join MN and CN
Their ∆ AMN, ∆NCB and ∆ MNC are equilateral traingles having 1 cm side each
Now area of ∆ GHF
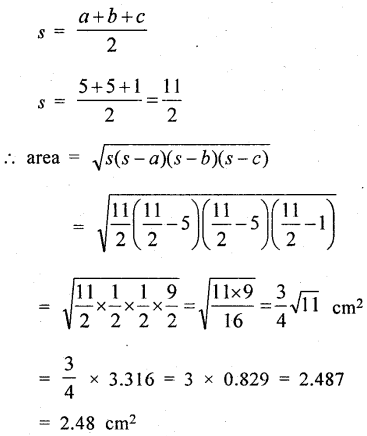
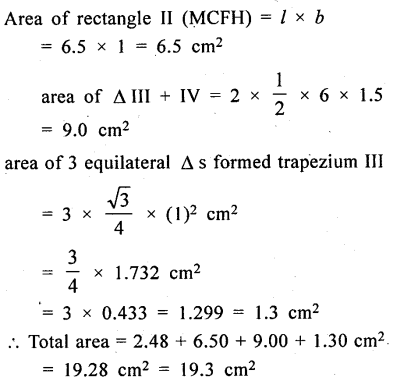
Question 4.
If the area of a circle is 78.5 cm2, find its circumference. (Take π = 3.14)
Answer:
Area of a circle = 78.5 cm2
Let r be the radius
∴ r2 = Area π=78.503.14 = 25 = (5)2
∴ r = 5 cm
Now circumference = 2πr
= 2 × 3.14 × 5 cm = 31.4 cm
Question 5.
From a square cardboard, a circle of biggest area was cut out. If the area of the circle is 154 cm2, calculate the original area of the cardboard.
Answer:
Area of circle cut out from the square board = 154 cm2
Let r be the radius
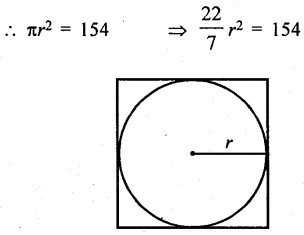
⇒ r2 = 154×722 = 49 = (7)2
⇒ r = 7 cm
Now side of the square = 7 × 2 = 14 cm
∴ Area of the original cardboard
= a2 = (14)2 = 196 cm2
Question 6.
(a) From a sheet of paper of dimensions = 2m × 1·5m, how many circles can you cut of radius 5cm. Also find the area of the paper wasted. Take π = 3·14.
(b) If the diameter of a semicircular protractor is 14cm, then find its perimeter.
Answer:
Length of sheet of paper = 2m = 200cm
Breadth of sheet = 1·5 m = 150 cm
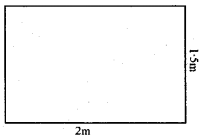
Area = l × b = 200 × 150 cm2
Radius of circle = 5cm.
∴ No. of circles in lengthwise
= 2005×2 = 20
and widthwise = 15010 = 15
∴ No. of circles = 20 × 15 = 300
Area of one circle = πr2
= 3·14 × 5 × 5 cm2
Area of 300 circles
= 300 × 314100 × 25 cm2 = 23550 cm2
∴ Area of the remaining portion = Area of square – area of 300 circles
= (30000 – 23550) cm2
= 6450 cm2
(b)Diameter of semicircular protractor = 14cm.
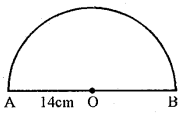
∴ Its perimeter = 12πd + d
= 12 × 227 × 14 + 14 = 22 + 14 = 36 cm
Question 7.
A road 3.5 m wide surrounds a circular park whose circumference is 88 m. Find the cost of paving the road at the rate of Rs. 60 per square metre.
Answer:
Width of the road = 3.5 m
Circumference of the circular park = 88 m
Let r be the radius of the park
∴ 2πr = 88
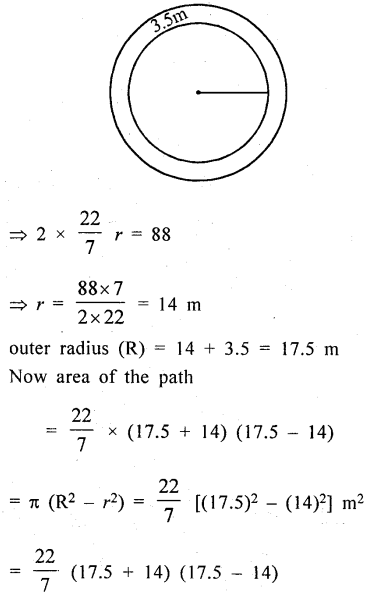
= 227 × 3.15 × 3.5 m2 = 346.5 m2
Rate of paving the road = Rs. 60 per m2
∴ Total cost = Rs. 60 × 346.5
= Rs. 20790
Question 8.
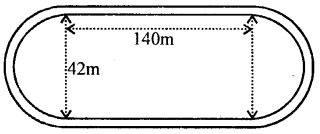
The adjoining sketch shows a running tract 3.5 m wide all around which consists of two straight paths and two semicircular rings. Find the area of the track.
Answer:
Width of track = 3.5 m.
Inner length of rectangular base = 140 m
and width = 42 m
Outer length = 140 + 2 × 3.5 = 140 + 7
= 147 m
and width = 42 + 2 × 3.5 = 42 + 7 = 49 m
Radius of inner semicircle (r) = 422 = 21m
and outer radius (R) = 21 + 3.5 = 24.5 m
Now area of track = 2(140 × 3.5) + 2 × 12π (R2 – r2)
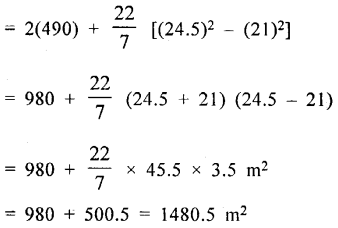
Question 9.
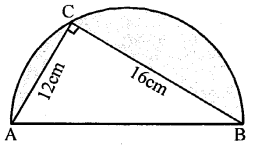
In the adjoining figure, O is the centre of a circular arc and AOB is a line segment. Find the perimeter and the area of the shaded region correct to one decimal place. (Take π = 3.142)
Answer:
In a semicircle, ∠ACB = 90°
∴ ∆ ABC is a right angled triangle
Now AB2 = AC2 + BC2 (Pythagoras Theorem)
= 122 + 162
= 144 + 256 = 400
= (20)2
∴ AB = 20 cm
∴ Radius of semicircle = 202 = 10 cm
(i) Area of shaded portion
= Area of semicircle – area of ∆ ABC
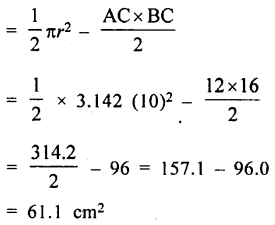
(ii) Perimeter of shaded portion
= circumference of semicircle + AC + BC
= πr + 12 + 16 = 3.142 × 10 + 28
= 31.42 + 28 = 59.42 cm = 59.4 cm
Question 10.
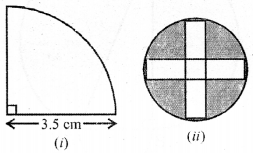
(a) In the figure (i) given below, the radius is 3·5 cm. Find the perimeter of the quarter of the circle.
(b) In the figure (ii) given below, there are five squares each of side 2 cm.
(i) Find the radius of the circle.
(ii) Find the area of the shaded region. (Take π = 3.14).
Solution:
(a) Radius of quadrant = 3·5 cm
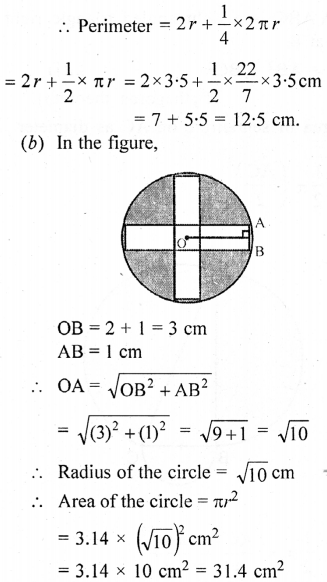
Area of 5 square of side 2 cm each
= (2)2 × 5 = 4 × 5 = 20 cm2
∴ Area of shaded portion = 31.4 – 20
= 11.4 cm2
Question 11.
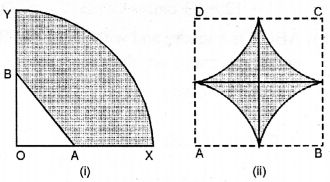
(a) In the figure (i) given below, a piece of cardboard in the shape of a quadrant of a circle of radius 7 cm is bounded by perpendicular radii OX and OY. Points A and B lie on OX and OY respectively such that OA = 3 cm and OB = 4 cm. The triangular part OAB is removed. Calculate the area and the perimeter of the remaining piece.
(b) In the figure (ii) given below, ABCD is a square. Points A, B, C and D are centres of quadrants of circles of the same radius. If the area of the shaded portion is 2137 cm2, find the radius of the quadrants. Take π = 227.
Solution:
(a) Radius of quadrant = 7 cm
OA = 3 cm, OB = 4 cm
∴ AX = 7 – 3 = 4 cm and
BY = 7 – 4 = 3 cm
∴ AB2 = OA2 + OB2 = (3)2 + (4)2 = 9 + 16 = 25
⇒ AB = √25 = 5cm
Now (i) Area of shaded portion
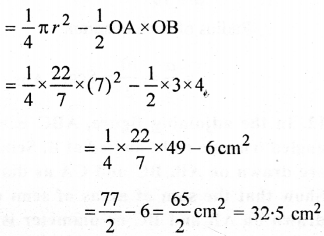
(ii) Perimeter of shaded portion
= 14(2πr) + AX + BY + AB
= 12 × 227 × 7 + 4 + 3 + 5
= 11 + 12 = 23 cm.
(b) ABCD is a square and with centres A, B, C and D quadrants are drawn.
Let side of square = a
∴ Radius of each quadrant = a2
∴ Area of shaded portion
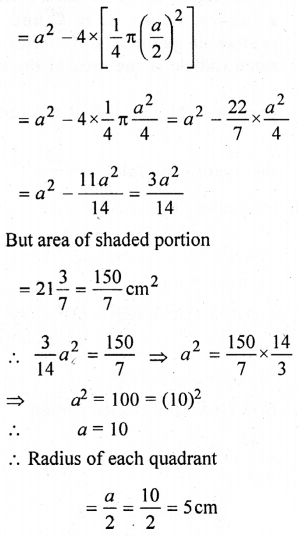
Question 12.
In the adjoining figure, ABC is a right angled triangle right angled at B. Semicircle are drawn on AB, BC and CA as diameter. Show that the sum of areas of semi circles drawn on AB and BC as diameter is equal to the area of the semicircle drawn on CA as diameter.
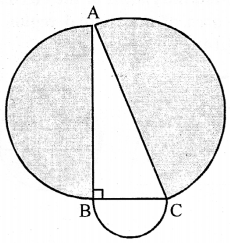
Answer:
∆ ABC is a right angled triangle right angled at B
∴ AC2 = AB2 + BC2 …(i) (Pythagoras theorem)
Now area of semicircle on AC as diameter
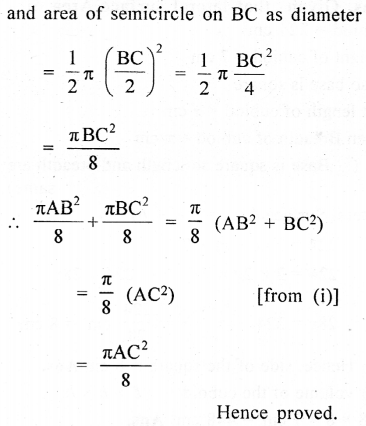
Question 13.
The length of minute hand of a clock is 14 cm. Find the area swept by the minute hand in 15 minutes.
Solution:
Radius of hand = 14 cm
∴ Area swept in 15 minutes
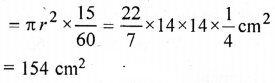
Question 14.
Find the radius of a circle if a 90° arc has a length of 3·5 π cm. Hence, find the area of sector formed by this arc.
Solution:
Length of arc of the sector of a circle = 3·5 π cm
and angle at the centre = 90°

Question 15.
A cube whose each edge is 28 cm long has a circle of maximum radius on each of its face painted red. Find the total area of the unpainted surface of the cube.
Solution:
Edge of cube = 28 cm
∴ Surface area = 6 a2 = 6 × (28)2 cm2
= 6 × 28 × 28 = 4704 cm2
Now diameter of each circle = 28 cm
∴ Radius = 282 = 14 cm
∴ Area of each circle
= πr2 = 227 × 14 × 14cm = 616 cm2
and area of such 6 circles drawn on 6 faces of cube = 616 × 6 = 3696 cm2
∴ Area of remaining portion of the cube
= 4704 – 3696 = 1008 cm2
Question 16.
Can a pole 6.5 m long fit into the body of a truck with internal dimensions of 3.5m, 3 m and 4m?
Answer:
No,
Because length of pole = 6.5 m
But internal dimensions of truck are 3.5 m, 3 m and 4 m all of these dimensions are less than that of 6.5 m. So that pole cannot fit into the body of truck with given dimensions.
Question 17.
A car has a petrol tank 40 cm long, 28 cm wide and 25 cm deep. If the fuel consumption of the car averages 13.5 km per litre, how far can the car travel with a full tank of petrol ?
Answer:
Capacity of car tank = 40cm × 28cm × 25cm
= (40 × 28 × 25) cm3 = 40×28×251000 litre (∵ 1000cm3 = 1 litre)
Average of car = 13.5 km per litre
Then, distance travelled by car
= 40×28×251000 × 135km

Hence, The car can travel 378 km with a full tank of petrol.
Question 18.
An aquarium took 96 minutes to completely fill with water. Water was filling the aquarium at a rate of 25 litres every 2 minutes. Given that the aquarium was 2 m long and 80 cm wide, compute the height of the aquarium.
Answer:
Water fill in 2 minutes = 25 litres
Water fill in 1 minutes = 252
Water fill in 96 minutes = 252 × 96 litres
= 25 × 48 litres = 1200 litres
i.e. Capacity of aquarium = 1200 litres ……(1)
But, Length of aquarium = 2m = 2 × 100 cm = 200 cm
Breadth of aquarium = 80 cm
Let height of aquarium = h cm
Then, capacity of aquarium = 200 × 80 × h cm3
= 200×80×h1000 litre = 15 × 80 × h litre
= 16 h litre
From (1) and (2)
16h = 1200 ⇒ h = 120016 cm ⇒ h = 75 cm
Hence, height of aquarium = 75 cm
Question 19.
The lateral surface area of a cubiod is 224 cm2. Its height is 7 cm and the base is a square. Find :
(i) a side of the square, and
(ii) the volume of the cubiod.
Answer:
Given that lateral surface Area of a cubiod = 224 cm2
Height of cubiod = 7 cm
Also base is square
Let length of cubiod = x cm
Then Breadth of cubiod = x cm (∵ Base is square so length and breadth are same)
Lateral Surface Area = 2 (l + b) × h
⇒ 224 = 2 (x + x) × 7
⇒ 224 = 2 × 2x × 7 ⇒ 224 = 28x
⇒ 28x = 224 ⇒ x = 22428 cm = 8 cm
(i) Hence, side of the square = 8 cm
(ii) volume of the cuboid = = l × b × h
= 8 × 8 × 7 cm3 = 448 cm3
Question 20.
If the volume of a cube is V m3, its surface area is S m2 and the length of a diagonal is d metres, prove that 6√3 V = S d.
Solution:
Volume of cube = (V) = (Side)3
Let a be the side of the cube, then
V = a3 and S = 6a2
Diagonal (d) = √3. a.
Now Sd = 6a2 × √3 a = 6√3 a3
= 6√3 V (∵ V = a3)
Hence 6√3 V = Sd.
Question 21.
The adjoining figure shows a victory stand, each face is rectangular. All measurement are in centimetres. Find its volume and surface area (the bottom of the stand is open).
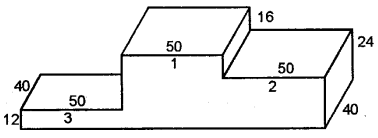
Solution:
In the figure, it has three parts as indicated by 3, 1 and 2.
∴ Volume of part (3) = 50 × 40 × 12 cm3 = 24000 cm3
Volume of part (1) = 50 × 40 × (16 + 24) cm3
= 50 × 40 × 40 cm3 = 80000 cm3
and volume of part (2) = 50 × 40 × 24 cm3
= 48000 cm3
Total volume = (24000 + 8000 + 48000) cm3 = 153000 cm3
Now total surface area = Area of front and back + area of vertical faces + area of top faces
= 2 (50 × 12 + 50 × 40 + 50 × 24) cm2 + (12 × 40 + 28 × 40 + 16 × 40 + 24 × 40) cm2 + 3 (50 × 40) cm2
= 2 (600 + 2000 + 1200)cm2 + (480 + 1120 + 640 + 960) cm2 + 3 × 2000 cm2
= 2 (3800) + 3200 + 6000 cm2
= 7600 + 3200 + 6000 = 16800 cm2
Question 22.
The external dimensions of an open rectangular wooden box are 98 cm by 84 cm by 77 cm. If the wood is 2 cm thick all around, find :
(i) the capacity of the box
(ii) the volume of the wood used in making the box, and
(iii) the weight of the box in kilograms correct to one decimal place, given that 1 cm3 of wood weighs 0.8 gm.
Answer:
Given that external dimensions of open rectangular wooden box = 98 cm, 84 cm, and 77 cm.
Thickness = 2 cm
Then internal dimensions of open rectangular wooden box (98 – 2 × 2 )cm, (84 – 2 × 2) cm (77 – 2) cm
= (98 – 4) cm, (84 – 4) cm, 75 cm = 94 cm, 80 cm, 75 cm
(i) Capacity of the box = 94cm × 80cm × 75cm = 564000 cm3
(ii) Internal volume of box = 564000 cm3
External volume of box = 98cm × 84cm × 77 cm = 633864 cm3
Volume of wood used in making the
Box = 633864 cm3 – 564000 cm33 = 69864 cm3
(iii) Weight of 1 cm3 wood = 0.8 gm
Weight of 69864 cm3 wood = 0. 8 × 69864 gm
= 0.8×698641000kg=55891.21000kg
= 55.9 kg (Correct to one decimal)
Question 23.
A cuboidal block of metal has dimensions 36 cm by 32 cm by 0.25 m. It is melted and recast into cubes with an edge of 4 cm.
(i) How many such cubes can be made ?
(ii) What is the cost of silver coating the surfaces of the cubes at the rate of Rs. 1.25 per square centimetre ?
Answer:
Given, dimensions of cuboidal block are 36 cm, 32 cm, 0.25 m.
Volume of cuboidal block = 36 cm × 32 cm × 0.25 m
= 36 cm × 32 cm × (0.25 × 100) cm = (36 × 32 × 25) cm3
Volume of cube having edge is 4 cm
= 4 cm × 4 cm × 4 cm = 64 cm3
(i) Number of cubes

(ii) Total surface area of one cube
= 6 (a)2 = 6 (4)2 cm2 = 6 × 4 × 4 cm2 = 96 cm2
Total surface area of 450 cube = 450 × 96 cm2 = 43200 cm2
Cost of silver coating the surface for 1 cm2 = Rs. 1.25
cost of silver coating the surface for 43200 cm2
= 43200 × 1.25 = Rs. 54000
Question 24.
Three cubes of silver with edges 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm are melted and recast into a single cube. Find the cost of coating the surface of the new cube with gold at the rate of Rs. 3.50 per square centimetre.
Solution:
Volume of First cube = (edge)3
= (3 cm)3 = 3 × 3 × 3 cm3 = 27 cm3
Volume of second cube = (edge)3
= (4 cm)3 = 4 × 4 × 4 cm3 = 64 cm3
Volume of third cube = (edge)3
= (5 cm)3 = 5 × 5 × 5 cm3 = 125 cm3
Total volume = (27 + 64 + 125) cm3 = 216 cm3
Made new cube whose volume = 216 cm3
(edge)3 = 216 cm3 ⇒ (edge)3 = (6cm)3
⇒ edge = 6 cm.
Surface area of new cube = 6 (edge)2
= 6 (6)2 cm2 = 6 × 6 × 6 cm2 = 216 cm2
Cost of coating the surface for 1 cm2
= Rs. 3.50
Cost of coating the surface for 216 cm2
= Rs. 3. 50 × 216 = Rs. 756
