What is meant by the calorific value of a fuel?
- Fuels are substances that can normally burn readily in air or oxygen to produce large quantity of heat.
- Examples of some common fuels are petroleum, natural gas and coal. These are called fossil fuels.
- Different types of fuels have different heats of combustion. Heat of combustion is expressed in kilojoules per mole.
- In our daily life, it is not very practical to measure the quantity of a fuel in mole. We normally measure the quantity of a fuel by its mass.
- The calorific value or fuel value of a fuel is the amount of heat energy given out when one gram of the fuel is completely burnt in excess of oxygen.
- The unit for fuel value is kJ g-1.
- Fuel value is also known as heat value.
- A fuel with a high fuel value releases a lot of heat per gram when it burns.
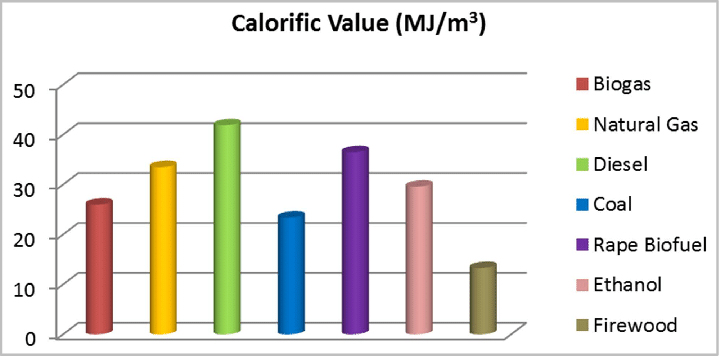
- Different types of fuels have different fuel values. Some fuels have very high fuel values but have low density, thus occupy a bigger volume. Others have high density but have low fuel values.
- Some fuels can cause environmental pollution. There are fuels with high fuel values but are not very economical, not easily available or non-renewable.
- The learning of thermochemistry helps us in the selection of a suitable fuel for a specific purpose.
- The table below shows the fuel values of some food and common fuels.
Substance Fuel value (kJ g-1) Apple 2 Egg 6 Bread 11 Wood 20 Coal 30 Butter 34 Gasoline 34 Kerosene 37 Natural gas 50 Hydrogen 143
The selection of a fuel to be used in industries depends on the following factors:
- Fuel value of the fuel
- Cost of the fuel
- Availability and sources of fuel
- Effect of the fuel on the environment
- Technology used to harness the energy from the fuel
- Storage space needed to store the fuel
Fuels with the following qualities are normally chosen:
- High fuel value
- Cheap
- Easily available
- Do not pollute the environment
- Easily harnessed
- Require less storage space
Calorific value example: The heat of combustion of ethanol is -1376 kj mol-1. Calculate the fuel value of ethanol.
[Relative atomic mass: H, 1; C, 12; O, 16]
Solution:

People also ask
- How can energy be changed in a chemical reaction?
- How does the energy level diagram show this reaction is exothermic?
- What is enthalpy of reaction?
- What is heat of precipitation?
- What is heat of displacement?
- What is the enthalpy of neutralization?
- What is the heat of combustion?
- Why is energy released when a bond is formed?
- Applications of exothermic and endothermic reactions in everyday life
