What is Matter and what are the Properties of a Solid, Liquid and Gas
Matter:
Anything which occupies space and has mass is called matter. Food, water, air, clothes, table, chair, plants and trees. Indian philosophers said that all the matter living or non-living, was made up of five basic elements air, earth, fire, sky and water. On the basis of its physical properties and on the basis of its chemical properties. On the basis of chemical properties the matter is classified as elements, compounds and mixtures.
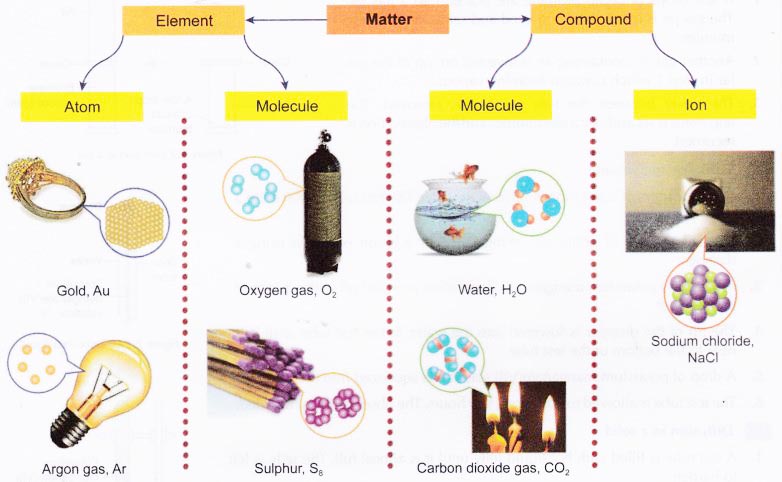
- An element is a substance that consists of only one type of atom.
- A compound is a substance that contains two or more elements that are chemically bonded together.
- Matter is made up of tiny and discrete particles. There are spaces between these particles.
- The particles may be atoms, molecules or ions.
- An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can participate in a chemical reaction.
- Metals and some non-metals such as carbon and noble gases exist as atoms.
- A molecule is a neutral particle that consists of two or more atoms which are chemically bonded together.
- An ion is a positively-charged or negatively- charged particle.
- Particles in matter are in motion. This has been confirmed by many experiments such as the diffusion of bromine.
- Diffusion occurs when the particles of a substance move between the particles of another substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
- The rate of diffusion of gas particles depends on their masses. Gases with low molecular masses diffuse faster than those with high molecular masses.
- The rate of diffusion is affected by the temperature.
(a) The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move and so the faster the diffusion.
(b) For example, the purple colour of potassium manganate(VII) spreads through the water much more quickly in hot water than in cold water.
People also ask
- Why does Diffusion take place
- Can Matter Change its State
- What is meant by the Kinetic Theory of Matter
Characteristics of particles of matter
Everything around us is made of tiny pieces or particles. The particles make up matter are atoms or molecules.
- The particles of matter are very, very small.
- The particles of matter have spaces between them.
- The particles of matter are constantly moving.
- The particles of matter attract each other.
Classification of matter
On the basis of physical states, all the matter can be classified into three groups.
- Solids
- liquids
- Gases
Properties of solids
- Solids have a fixed shape and a fixed volume.
- Solids cannot be compressed much.
- Solids have high densities. They are heavy.
- Solids do not fill their container completely.
- Solids do not flow.
Ex. Ice, wood, coal, stone, iron, brick
Properties of liquids
- Liquids have a fixed volume but they have no fixed shape. Liquids take the shape of the vessel in which they are placed.
- Like solids, liquids cannot be compressed much.
- Liquids have moderate to high densities. They are usually less dense than solids.
- Liquids do not fill their container completely.
- Liquids generally flow easily.
Ex. Water, milk, fruit juice, ink, groundnut oil, kerosene etc.
Properties of gases
- Gases have neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume. Gases acquire the shape and volume of the vessel in which they are kept.
- Gases can be compressed easily.
- Gases have very low densities. They are very. very light.
- Gases fill their container completely.
- Gases flow easily.
Ex. Air, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
Comparison of characteristic properties of solids, liquids and gases
S.no | Property | Solids | Liquids | Gases |
| 1 | Shape | Definite | Take the shape of the container, but do not necessarily occupy all of it. | Take the shape of the container by occupying whole of the space available to them. |
| 2 | Volume | Definite | Definite | Take the volume of the container. |
| 3 | Compressibility | Almost nil | Almost nil | Very large |
| 4 | Fluidity or Rigidity | Rigid | Fluid | Fluid |
| 5 | Density | Large | Large | Very small |
| 6 | Diffusion | Generally do not diffuse | Diffuse slowly | Diffuse rapidly |
| 7 | Free surfaces | Any number of free surfaces | Only one free surface | No free surface. |
Diffusion of Particles in a gas, a liquid and a solid Experiment
Aim: To investigate the diffusion of particles in a gas, a liquid and a solid.
Materials: Liquid bromine, 1 mol dnr3 potassium manganate(VII), KMnO4 solution, potassium manganate(VII) crystal, hot liquid jelly, water and tissue paper.
Apparatus: Gas jars and cover, dropper, test tubes, test tube rack, stopper, retort stand and clamp.
Procedure:
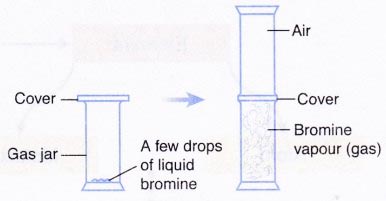
A. Diffusion in a gas
Safety Measure:
Liquid bromine is toxic and corrosive. Wear gloves when handling this substance. This activity must be carried out in a fume chamber.
- A few drops of liquid bromine are placed into a gas jar. The gas jar is immediately covered and set aside for a few minutes.
- Another gas jar containing air is inverted on top of the gas jar in step 1 which contains bromine vapour.
- The cover between the two gas jars is removed. The apparatus is set aside for a few mi nutes and the observation is recorded.
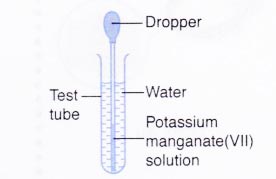
B. Diffusion in a liquid
- Three-quarters of a test tube is filled with water. The test tube is placed in a test tube rack.
- A small volume of potassium manganate(VII) solution is drawn using a dropper.
- Any excess potassium manganate(VII) solution is wiped off with a piece of tissue paper.
- The tip of the dropper is lowered into the water in the test tube until it is near to the bottom of the test tube.
- A drop of potassium manganate(VII) solution is squeezed into the water.
- The test tube is allowed to stand for a few hours. The observation is recorded.
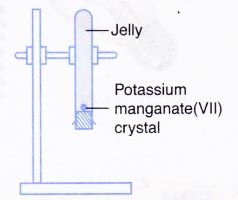
C. Diffusion in a solid
- A test tube is filled with hot liquid jelly until it is almost full. The jelly is left to harden.
- A small crystal of potassium manganate(VII) is put on top of the jelly.
- The test tube is stoppered and clamped upside down as shown in Figure below.
- The apparatus is left aside for a few days and the observation is recorded.
Observations:
| Section | Observation |
| A | The reddish-brown vapour spreads quickly throughout the two gas jars in a few minutes. |
| B | The purple colour of potassium manganate(VII) solution spreads slowly throughout the water. After a few hours, the water turns uniformly purple. |
| C | The purple colour of potassium manganate(VII) spreads very slowly into the jelly. After a few days, the jelly turns entirely purple. |
Discussion:
- (a) Diffusion in a gas:
Bromine gas is made up of tiny and discrete particles. These particles move randomly into the spaces between the air particles.
(b) Diffusion in a liquid:
Potassium manganate(VII) is made up of tiny and discrete particles. These particles move slowly into the spaces between the water molecules.
(c) Diffusion in a solid:
The potassium manganate(VII) crystal dissolves and the particles move very slowly into the spaces between the jelly particles. - The rate of diffusion of particles is highest in gases, lower in liquids and lowest in solids.
- This is due to the different arrangements of particles in solids, liquids and gases. The particles of a solid are packed closely together whereas the particles of a liquid are packed slightly loose. The particles of a gas are very far apart from each other and are in a random arrangement.
Conclusion:
Matter is made up of tiny and discrete particles that are in motion. Diffusion occurs slowest in solids, faster in liquids and the fastest in gases.
