Math Labs with Activity – Find the Incentre of a Given Triangle
OBJECTIVE
To find the incentre of a given triangle by the method of paper folding.
Materials Required
- A sheet of white paper
- A geometry box
Theory
The point of intersection of the internal bisectors of the angles of a triangle is called its incentre.
Procedure
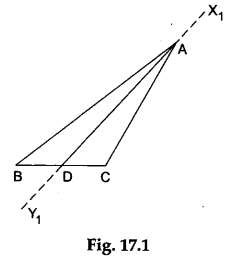
Step 1: Draw any triangle on the sheet of white paper.
Mark its vertices as A, B and C. We shall find the incentre of ΔABC.
Step 2: Fold the paper along the line passing through vertex A such that the side AB falls over the side AC. Make a crease and unfold the paper. Draw a line X1Y1 along the crease. Mark the point D where the line X1Y1 intersects the side BC. Then, AD is the internal bisector of ∠A as shown in Figure 17.1.
Step 3: Fold the paper along the line passing through the vertex B such that the side BC falls over the side AB. Make a crease and unfold the paper. Draw a line X2Y2 along the crease. Mark the point E where the line X2Y2 intersects the side TIC. Then, BE is the internal bisector of ∠B as shown in Figure 17.2.
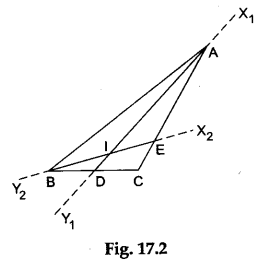
Step 4: Mark the point of intersection of the two angle bisectors as the point I.
Result
The point I is the incentre of the given ΔABC.
Remarks:
- The teacher must explain it to the students that since all the angle bisectors of a triangle meet at a point, it is sufficient to construct only two angle bisectors so as to obtain their point of intersection as the incentre.
- The incentre of each one of the triangles—acute-angled triangle, right-angled triangle and the obtuse-angled triangle—lies inside the triangle.
Math Labs with ActivityMath LabsMath Lab ManualScience LabsScience Practical Skills
