Management Of Biodegradable Wastes
SEGREGATION OF WASTES
Garbage or waste may be in the form of fruit or vegetable peels, discarded objects, wrapping materials, wasted food as household garbage, or discarded chemicals and fertilizers washed into rivers, domestic sewage, etc. These wastes can be segregated into biodegradable and non-biodegradable. Wastes that rot (undergo degradation) by the action of decomposers (tiny organisms found in the soil) are called biodegradable wastes. Dead plants and animals and their products (e.g., fruit and vegetable peels, paper, and leaves) decay very easily These wastes mix with the soil and produce manure. Wastes that do not rot by the action of decomposers are called non-biodegradable wastes. For example, glass, plastic, and metals. Many of them can be recycled to produce new things.
 Depending on the type of wastes, two garbage bins—one for biodegradable wastes and other for non-biodegradable wastes should be used. This will help in easy sorting and recycling of wastes to make beneficial products. Green bins are for biodegradable wastes like vegetables and fruit peels, spoilt food, tea leaves, egg shells, tissue paper, leaves, hair, etc. Blue bins are for recyclable wastes like glass bottles, plastic wastes, old batteries, chocolate wrappers, polythene bags, etc.
Depending on the type of wastes, two garbage bins—one for biodegradable wastes and other for non-biodegradable wastes should be used. This will help in easy sorting and recycling of wastes to make beneficial products. Green bins are for biodegradable wastes like vegetables and fruit peels, spoilt food, tea leaves, egg shells, tissue paper, leaves, hair, etc. Blue bins are for recyclable wastes like glass bottles, plastic wastes, old batteries, chocolate wrappers, polythene bags, etc.
Some of the ways to manage biodegradable wastes are as follows:
Composting
Since biodegradable or organic wastes like vegetable peels, waste food, leaves, dead flowers, and egg shells can be recycled, they are converted into manure by burying them in compost pits. Recycling of organic wastes like vegetable peels, waste food, leaves, etc., by burying them in compost pits is called composting. Composting is a simple and almost effortless process of recycling. The biodegradable wastes are degraded by the action of small organisms like bacteria and fungi. There is also a different kind of composting where a kind of earthworm called red worms (or red wrigglers) act on wastes and degrade them.

This type of composting with the help of a type of earthworm called red worms, is called vermicomposting. Red worms break down the organic matter into nutrient-rich manure which increases soil fertility. Vermicompost can be made in 3-4 weeks and it appears as loose soil-like material. One should not put animal product or oily substance in the pit as it could lead to the growth of disease causing organisms.
Landfills
Large areas used for waste disposal are called landfills. Landfill is another method to manage huge amount, of biodegradable waste. In a landfill, garbage is buried in such a way that it does not damage the environment. Garbage buried inside landfills stay here for a long time as it decomposes very slowly. After a landfill is full, it can be converted into a park. For example, Indraprastha Park in New Delhi is built on a landfill site.
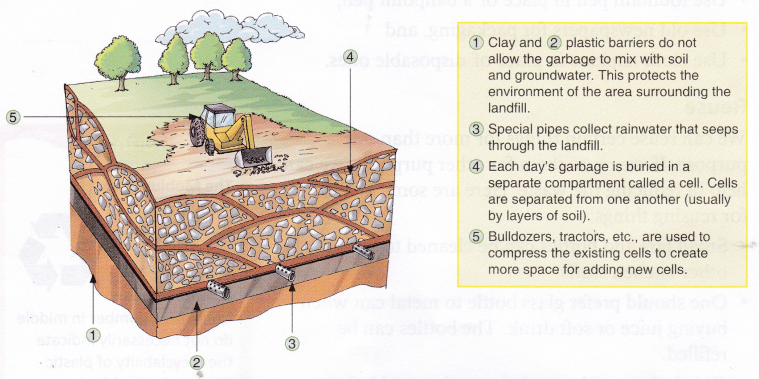
- Clay.
- Plastic barriers do not allow the garbage to mix with soil and groundwater. This protects the environment of the area surrounding the landfill.
- Special pipes collect rainwater that seeps through the landfill.
- Each day’s garbage is buried in a separate compartment called a cell. Cells are separated from one another (usually by layers of soil).
- Bulldozers, tractors, etc., are used to compress the existing cells to create more space for adding new cells.
Activity
Aim: To show that materials rot in soil and this rotting is affected by wrapping materials in plastic bag.
Materials needed: A wooden crate, soil, dried leaves and grass, fruit and vegetable peels and a plastic bag.
Method:
- Keep dried leaves and fruit and vegetable peels inside the wooden crate.
- Place some leaves and vegetable/fruit peels in a plastic bag and tie its mouth. Place the plastic bag inside the same wooden crate.
- Put moist soil inside the wooden crate such that the objects are covered inside it. Keep the crate outside, taking care that the soil remains moist. Observe the contents after about three weeks.
Observation: Dried leaves and fruit and vegetable peels rotted and got mixed with the soil. The contents inside the plastic bag rotted but could not get mixed with soil because plastic bag could not be degraded.
Conclusion: Biodegradable materials degrade over a period of time but non- biodegradable materials do not.
