How do you make detergent?
What is detergent?
- Any cleaning agent that is not a soap is a detergent. Detergents are usually made from synthetic resources such as petroleum fractions.
- They were developed during the Second World War in response to a shortage of animal fats and vegetable oils.
- Detergents are usually sodium salts of sulphonic acid.
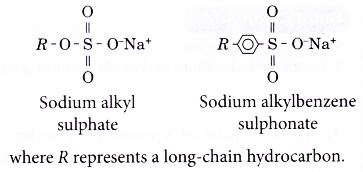
- The general formulae for two common detergents are:
People also ask
- What is saponification in soap making?
- Explain the cleansing action of soap and detergent
- How are soaps and detergents different?
- What are the Advantages of Synthetic Detergents over Soap?
- Types of food additives and their functions
- What are the different types of medicine?
- The Existence of Chemicals
Preparation of detergents
- During the preparation of detergents, a long- chain hydrocarbon obtained from petroleum fractions is converted into an organic acid through a series of steps.
- The organic acid is then neutralised with sodium hydroxide solution to produce a neutral salt which is a detergent.
Preparation of sodium alkyl sulphate:
Step 1: Formation of an organic acid
A long-chain alcohol reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid to form alkyl sulphonic acid.

Step 2: Neutralisation
The resulting acid is then converted to a sodium salt by a reaction with sodium hydroxide.

Preparation of sodium alkylbenzene sulphonate:
Step 1: Formation of an organic acid
A long-chain alkene reacts with benzene to form alkylbenzene.
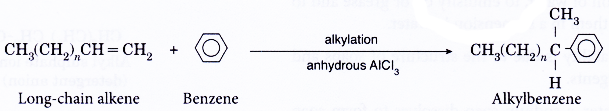
The alkylbenzene formed is then reacted with concentrated sulphuric acid to form alkylbenzene sulphonic acid.

Step 2: Neutralisation
The alkylbenzene sulphonic acid is then converted to a sodium salt by a reaction with sodium hydroxide.

The additives in detergents
- Detergents generally contain a number of additives.
- Additives are added to a detergent to enhance its cleaning efficiency and to meet the needs of consumers.
- The additives in a detergent and their respective functions are shown in Table.
| Additive | Example | Function |
| Biological enzyme | Amylases, proteases, cellulases and lipases | To remove protein stains such as blood. |
| Whitening agent | Sodium perborate | To convert stains into colourless substances. |
| Optical whitener | Fluorescent dyes | To add brightness and whiteness to white fabrics. |
| Builder | Sodium tripolyphosphate | To enhance the cleaning efficiency of a detergent by softening the water. |
| Suspension agent | Carboxymethylcellulose | To prevent the dirt particles removed from redepositing onto cleaned fabrics. |
| Filler | Sodium sulphate, sodium silicate | To add to the bulk of the detergent and enable it to be poured easily. |
| Foam control agent | Silicones | To control foaming in a detergent. |
| Fragrance | – | To add fragrance to both the detergent and the fabrics. |
