What are the Main Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom
Kingdom : Plantae of Plant Kingdom
Division : Thallophyta (Algae)
The plants in this divisions are commonly called algae. The terms “Algae ” was coined by C. Linnaeus which means ‘sea weeds’. The division is characterized by the following :
- The division comprises of most primitive and simple plants not differentiated into true roots, true stem and true leaves. Therefore, they are thalloid (thallus-like) and placed under the division-thallophyta.
- They are predominatly aquatic, occur both in marine (sea water) as well as fresh water habitats. However, some are terrestrial and grow in moist places.
- Algal cells possess photosynthesis. Thus, the algae are photoautotrophs.
- Some algae have additional accessory pigments of other colours (such as red, brown, yellow, etc.) and accordingly they have beeen classified into different groups. such as green algae, red algae, brown algae etc.).
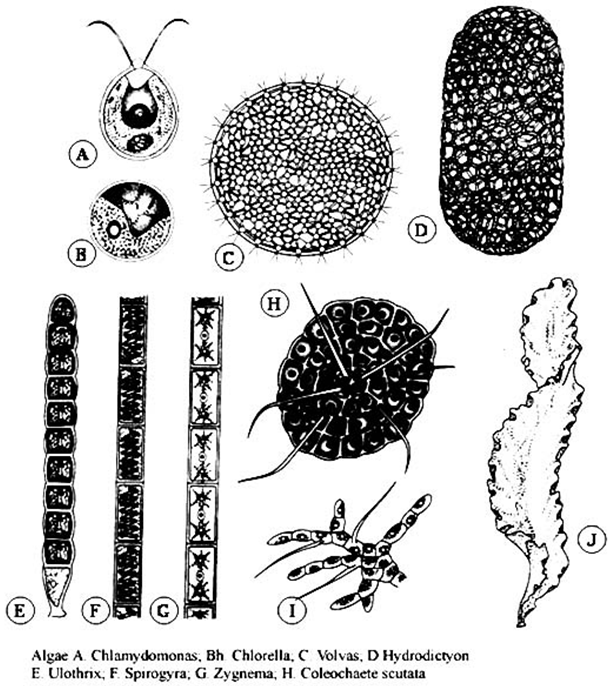
- The plants are thalloid (figure). The plant body may be unicellular (Chlamydomonas, Chlorella), colonial (Volvox, Hydrodictyon), filamentous unbranched (Spirogyra, Ulothrix), filamentous branched (Chara, Cladophora), heterotrichous (Ectocarpus) or foliaceous (Laminaria, Ulva, Fucus, Sargassum).
- The reproductive organs are unicellular non-jacketed gametangia. The contents of reproductive structure are completely converted into spores or gametes.
- After fertilization, embryo is not formed.
 Division : Bryophyta
Division : Bryophyta
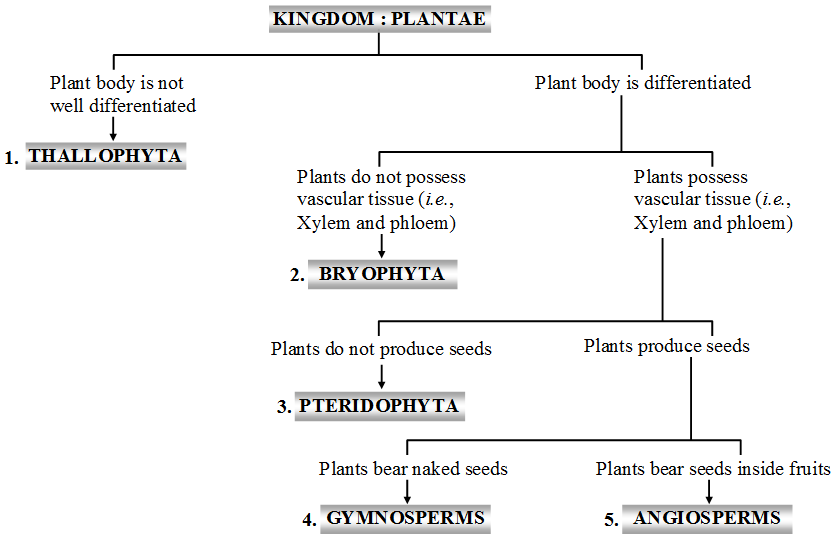
- The division Bryophyta (Greek word Bryon = moss ; phyton = plant) includes the simplest and most primitive non-vascular land plants having an embryo stage in their life cycle.
- The plants are essentially terrestrial but require water at every step in the life cycle. They usually grow in moist and shady places – on the sides of ditches, ponds, pools, lakes; on the banks of streams; damp soil; wet hills and many other similar habitats. They are called amphibians of the plant kingdom.
- The main plant body is gametophyte (haploid body responsible to produce gametes). It is flat, green thallus and lacks true leaves and roots. Plants are fixed by means of hair-like rhizoids.
- The vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) are completely absent.
- Sex organs are multicellular. The male sex organs are antheridia and female sex organs are archegonia.
- An embryo is formed upon fertilization. Sporophyte lives as a parasite over gametophyte.
- Examples (figure) Liverworts (Riccia, Marchantia), hornworts (Anthoceros) and Mosses (Funaria, Polytrichum.
 Division Pteridophyta :
Division Pteridophyta :
- They are found mainly in shady or damp places.
- The plant body is made up of root, stem and leaves.
- They have well developed vascular system.
- These plants have no flowers and do not produce seeds.
- Sex organs are multicellular and jacketed by sterile cells.
- Club mosses – Selaginella, Lycopodium (“ground pine”); horsetails – Equisetum; and ferns – Marsilea.
Gymnosperm :
- The seeds produced by these plants are naked and are not enclosed within fruits.
- Cycadae, e.g. Cycas etc.
- Coniferae, e.g. Pinus, Ginkgo, etc.
pteridophytes | gymnosperms |
| 1 Vascular tissue are present but secondary growth is absent. | Vascular tissues are present and secondary growth is present. |
| 2 Ovule and seeds are not formed. | Ovule and seeds are formed. |
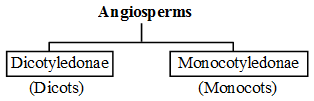
Angiospermae :
- Angiosperms are highly evolved plants and they produce seeds that are enclosed within the fruit.
- The reproductive organs are aggregated in a flower.
 Dicotyledonse :
Dicotyledonse :
- The seeds produced by these plants have embryos with two fleshy leaves, the cotyledons.
- Their leaves have reticulate venation, with a network of veins.
- The root system has a prominent tap root.
Examples : Pea (Pisum sativum), potato (Solanum tuberosum), sunflower (Helianthus annuus), rose (Rosa indica), banyan (Ficus religiosa), neem (Melia indica), apple (Malus silvestris).
 Monocotyledonse :
Monocotyledonse :
- The seeds of these plants have only one cotyledon.
- Their leaves have parallel venation.
- The root system consists of similar fibrous roots.
- The vascular bundles are scattered and closed (i.e. lack cambium). Secondary growth does not occur.
Examples : Maize (Zea mays), Wheat (Triticum vulgare), rice (Oryza sativa), onion (Allium cepa), sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum), barley (Hordeum vulgare), banana (Pandanus), Coconut and grasses.
monocots | dicots |
1 Parallel venation is present in leaf. | Reticulate venation is present in leaf. |
| 2 Embryo consists of only one cotyledon. | Embryo consists of two cotyledons. |
3. Example – Maize | Example – Pea |
