Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current
You know that magnets can attract certain substances such as iron. So far, you have studied about electricity and magnetism separately. However, did you know that electricity and magnetism are closely related? Perform the following activity to understand this.
Activity
Aim: To see the magnetic effect of current passing through a wire (adult supervision required).
Materials needed: 1.5 V cell, two pieces of insulated wire, a small magnetic compass, and insulation/adhesive tape.
Method:
- Strip the insulation from the two ends of both the wires.
- Connect one end of one of the wires to the negative terminal of the cell. Secure the connection with the insulation/adhesive tape.
- Connect one end of the other wire to the positive terminal of the cell. Secure the connection with the insulation tape.
- Place the magnetic compass near the wire.
- Keep an eye on the needle of the magnetic compass and touch the free ends of the wires connected to the positive and negative terminals of the cell.
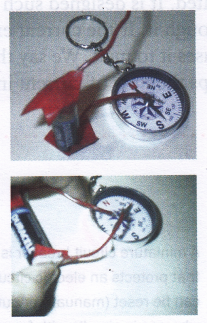 Observation: When the wire touches the positive terminal of the cell, the needle of the magnetic compass gets deflected (moves).
Observation: When the wire touches the positive terminal of the cell, the needle of the magnetic compass gets deflected (moves).
Conclusion: This is because when a current passes through the wire, it behaves like a magnet and therefore deflects the magnetic needle of the compass.
Note: Follow the precautions given on p. 182 while doing this activity.
We have seen in the above activity that a current-carrying conductor behaves like a magnet. As a result, it can deflect a magnetic needle.
Wrap a wire around a soft iron piece (known as the core). When an electric current is passed through the wire, the iron piece behaves like a magnet. A magnet made using such an arrangement is called an electromagnet. A solenoid is a device which can be used as an electromagnet. It is made of a long wire that has been wound many times (usually around a hollow metallic core) into a tightly packed coil, it has the shape of a long cylinder.
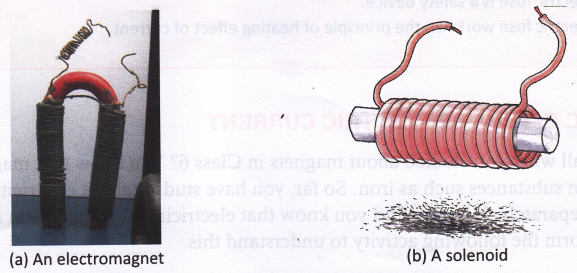
Fig. Applications of magnetic effect of current
People also ask
- Who discovered the magnet?
- How does a magnet work?
- What are the Different Types of Magnets?
- Is an electromagnet a temporary or a permanent magnet?
- What is the use of magnet?
- How does an electric bell work using electromagnets?
- What is the Magnetic Field?
- Factors Affecting the Magnitude of the Force on a Current-carrying Conductor
- What is magnetic force on a current carrying conductor?
- What factors affect the strength of an electromagnet?
- How does a current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field?
- Oersted Experiment on Magnetic Effect of Current
- How do you Determine the Direction of the Magnetic Field?
- What is the Meaning of Magnetic Force?
Activity
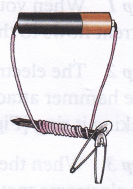
Aim: To make an electromagnet (adult supervision required) and show that it attracts iron.
Materials needed: 1.5 V cell, an iron nail, a safety pin, and a piece of wire (the one with a single thick wire).
Method:
- Take a piece of wire and strip the insulation from the two ends.
- Wind the wire around the iron nail.
- Connect the two ends of the wire to the two terminals of an electric cell. This is an electromagnet.
- Bring this close to a safety pin.

Observation: The safety pin gets attracted to the iron nail.
Conclusion: Passing an electric current in a coil wrapped around an iron piece makes the iron piece magnetic.
The strength of the electromagnet depends on the number of turns of the wire around the core and the amount of current passing through it. The more the number of turns, the more will be the magnetic effect. The iron nail attracts more number of safety pins when wrapped with a coil with more number of turns. What will happen if the current passing through the coil is switched off? The iron piece will lose its magnetic effect, i.e., it will stop behaving like a magnet and, thus, will not attract the safety pin.
Activity
Aim: To study the behaviour of an electromagnet when the current is switched off (adult supervision required).
Materials needed: An electromagnet, iron filings, wires, cardboard, and a pencil cell.
Method:
- Take an electromagnet. Connect the free ends of the wire to the terminals of a pencil cell.
- Take a cardboard and sprinkle some iron filings on it.
- Now bring the electromagnet near to the iron filings. Do the filings get attracted to the electromagnet?
- Now remove the pencil cell from the circuit.
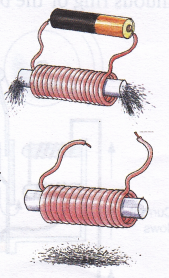
Observation: The filings fall down.
Conclusion: The electromagnet loses its magnetic effect when the source of electric current is removed.
