Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
The Properties of a Gas
- A student explores the properties of some air in a round bottom flask as shown in Figure. He noted the temperature, θ1, and pressure, P1, of the air.
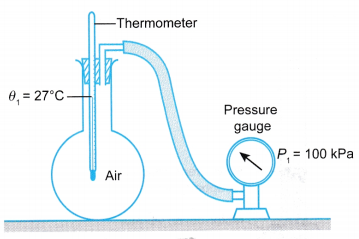
- When the flask was immersed in hot water as shown in Figure, he found that the temperature and pressure of the air increased to θ2 and P2 respectively.
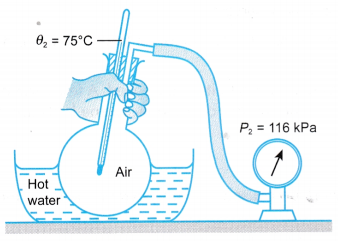
- This activity shows that the air has temperature and pressure.
- The air occupies the whole space in the flask. Therefore, the volume of the air is equal to the volume of the flask.
- A gas has three properties that are related to each other: pressure, temperature and volume.
People also ask
What is the Charles Law?
What is the Boyle’s law?
What is the Pressure Law?
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
- The kinetic theory makes the following assumptions for a gas in a closed container:
(a) The gas consists of a large number of identical molecules. The number of molecules is constant, therefore the mass of the gas is constant.
(b) The molecules are in continuous random motion.
(c) The molecules collide with the walls of the container and with one another.
(d) The average kinetic energy of the molecules is proportional to the temperature of the gas. - The behaviour of the gas depends on the three properties of the gas: volume, temperature and pressure.
- The volume, temperature and pressure of a gas can be explained using the kinetic theory of gases as shown in Table.
Property of a gas Explanation based on the kinetic theory Volume The molecules are moving freely in random motion.
Therefore the molecules fill up the whole space in the container.
The volume of the gas is equal to the volume of the container.Temperature The molecules are in continuous random motion.
The molecules have an average kinetic energy which is proportional to the temperature.
The higher the temperature, the faster the motion of the molecules.Pressure The molecules are in continuous random motion.
The molecules collide with the walls of the container and bounce back.
For each molecule, there is a change of momentum and force is exerted on the wall.
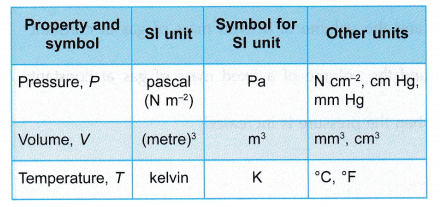
The total force per unit area is the pressure of the gas. - Table gives a summary of the units for pressure, volume and temperature of a gas.
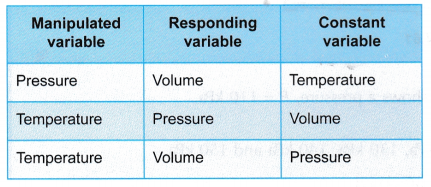
- The relationship between pressure, volume and temperature can be investigated in three ways as shown in Figure.
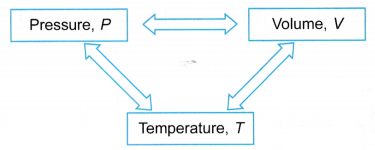
- The relationship between two properties are investigated while the third is kept constant, as shown in Table.
Activity
Aim: To study the behaviour of the molecules of a gas using a model.
Apparatus: An electrically operated kinetic theory model as shown in Figure.
Method:
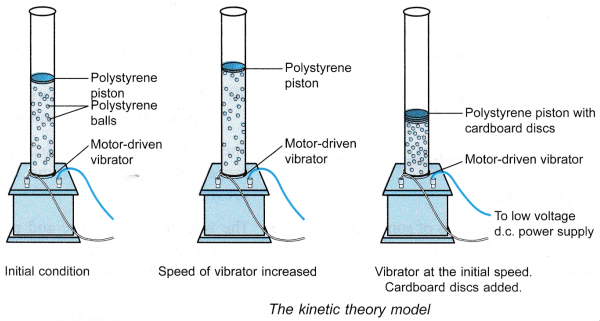
- The kinetic theory model is switched on.
- The motion of the polystyrene balls and the polystyrene piston is observed.
- The voltage of the d.c. power supply is slowly increased. The changes to the motion of the polystyrene balls and the position of the piston are observed.
- The voltage of the d.c. power supply is reduced so that the vibrator returns to its initial speed. A few cardboard discs are dropped onto the polystyrene piston. The changes to the motion of the polystyrene balls and the position of the piston are observed.
Observation:
- When the kinetic theory model was switched on, the vibrator caused the polystyrene balls to move continuously in random motion.
- The polystyrene balls continuously strike the walls of the cylinder and also the polystyrene piston.
- The polystyrene piston floats to a certain position above the moving polystyrene balls.
- When the voltage of the d.c. power supply was increased, the balls moved faster. The piston is pushed to a higher position.
- The piston moved to a lower position when the cardboard discs were dropped onto them.
Discussion:
- The kinetic theory model is used to simulate the motion of the molecules of a gas. The polystyrene balls represent the molecules of a gas. An electric motor drives a vibrator which sets the balls into motion. The speed of the motor can be changed by adjusting the voltage.
- The kinetic theory model shows that
(a) the molecules of a gas are in continuous random motion,
(b) the molecules exert a pressure on the walls of the container,
(c) the molecules of a gas occupy the whole space of the container. The volume of the gas is equal to the volume of the container. - When the temperature of a gas is increased, the gas expands.
- Increasing the pressure on a gas causes its volume to decrease.
