Kerala SSLC Chemistry Model Question Papers with Answers Paper 1 are part of Kerala SSLC Chemistry Previous Year Question Papers with Answers. Here we have given Kerala SSLC Chemistry Model Question Papers with Answers Paper 1.
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | SSLC Class 10 |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Category | Kerala SSLC Previous Question Papers |
Kerala SSLC Chemistry Model Question Papers with Answers Paper 1 Free Download English Medium
Time Allowed: 1 1/2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
Instructions
- First 15 minutes is cool-off time.
- Read all questions carefully.
- Questions with scores 1, 2, 3 and 4 are categorised separately.
- 5 questions are given in each category. Answer any 4 questions from each category.
- Answer each question by keeping time.
Answer any 4 questions from 1 to 5 (1 score each)
Question 1:
To which block of the periodic table does Lanthanoids belong?
Question 2:
What will be the molar volume of a gas at STP in litres?
Question 3:
Which substance is used to leach the ore in Aluminium extraction?
Question 4:
To which category of organic compounds does Ethylethanoate belong?
Question 5:
What is meant by denatured spirit?
Answer any 4 questions from 6 to 10 (2 scores each)
Question 6:
The third shell of an atom has 3 electrons :
a. Write down the subshell electronic configuration of the atom.
b. To which group of the periodic table does this element belong?
Question 7:
Fill up suitably:
| Element | Atomic mass | Amount taken in g | Number of Molecules | Number of Molecules | Volume at STP L |
| h2 | 1 | 4g | … (a) … | 4 x 6.022 x 10²³ | … (b) … |
| He | 4 | … (c) … | 5 x 6.022 x 10²³ | … (d) … | 112 L |
Question 8:
The order of reactivity of some elements are given in the box
![]()
a. Which element looses its lustre most easily on exposure to air?
b. Which is the element that cannot displace Hydrogen from dil.HCl?
Question 9:
Fill up the columns by choosing the appropriate ones from those given below
| Metal | Ore | Method of refining metals |
| Copper | … (a) … | … (b) … |
| Zinc | … (c) … | … (d) … |
(Distillation, Cuprite, Electrolytic refining, Bauxite, Calamine, Liquation)
Question 10:
Give reason for the following:
(a) Cement is not kept on moist surfaces.
(b) Concrete labourers wear gloves.
Answer any 4 questions from 11 to 15 (3 scores each)
Question 11:
Equation showing the burning of ethane in air is given below.
2 C2H6 + 5O2 → 4 CO2 + 6H2O
(a) How many mol. of Oxygen are required to bum 1 mol. of ethane completely?
(b) What will be the volume of C02 formed at STP on complete combustion of 150 g of ethane? (Atomic mass: H = 1, C = 12, 0=16)
Question 12:
Equal volumes of Con. HNO3 are taken in two test tubes. A piece of copper is added to one test tube and equal mass of copper powder to the other. Brown gas is found to evolve from the test tubes.
(a) In which test tube does the reaction proceed faster. Why?
(b) State any other method to increase the rate of the reaction.
Question 13:
N2O4(g)+ Heat → 2NO2(g)
(a) What will happen to the amount of NO, on increasing of temperature?
(b) State whether increase in pressure or decrease in pressure favours the forward reaction. Why?
Question 14:
(a) Complete the given flow chart related with the concentration of Aluminium ore
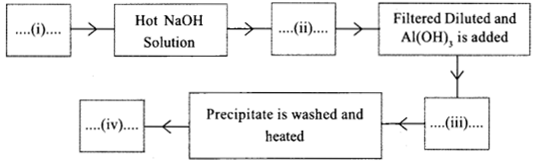
(b) The anode in Aluminium extraction is replaced frequently. Why?
Question 15:
(a) Which type of glass is used to make window panes? What are the materials used to make this glass?
(b) Which substance is added to glass to give it blue colour?
Answer any 4 questions from 16 to 20 (4 scores each)
Question 16:
Subshell electronic configurations of some elements are given. (Symbols are not real)
(A) [Ne] 3s23p5
(B) [Ar]4s1
(C) [Ar] 3d54s2
(D) [Ar] 3d104s24p5
(a) Which of these elements belongs to the same group?
(b) Which element has the lowest ionisation energy?
(c) Which is the element that always show +1 Oxidation State?
(d) Write down the subshell electronic Configuration of Cr4+ ion.
Question 17:
(a) Write down the structure of 2, 3 – Dimethylbutane.
(b) Write down the IUPAC name of its isomer with a single branch
(c) Write down the formula of Aldehyde functional group
(d) What is the IUPAC name of CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – C ≅ C – CH3
Question 18:
Examine the figure of the Galvanic cell given below:
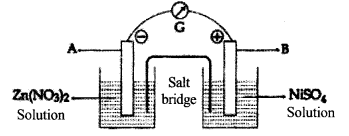
(a) What are A and B electrodes?
(b) From which metal to which metal do the electrons flow?
(c) Which metal acts as the cathode?
(d) Write down the equation for the redox reaction taking place in the cell.
Question 19:
Answer the following questions by choosing the suitable ones given in the box below :
(a) A pair of functional isomers
(b) Ether
(c) Vinegar
(d) A pair of position isomers
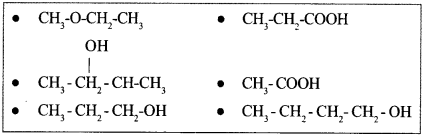
Question 20 :
(a) Complete the following equations:
(i) CH3 – CH2 – CH3 + Cl2 → + HCl
(ii) CH3 -CH = CH2 + Cl2 →
(b) Which type of reaction is represented by equation (ii) ?
(c) Write down the structural formula of Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC)
Answers
Answer 1:
f
Answer 2:
22.4
Answer 3:
Hot NaOH solution
Answer 4:
Ester
Answer 5:
For industrial purposes, ethanol is sometimes mixed with pisonous substances. The mix¬ture so obtained is called denatured spirit.
Answer 6:
a. 1s22s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
b. p
Answer 7:
a. 2 x 6.022 x 1023
b. 2 x 22.4 = 44.8
c. 20 g
d. 5 x 6.022 x 1023
Answer 8:
a. Na
b. Cu
Answer 9:
a. Cuprite
b. Electrolytic refining
c. Calamine
d. Distillation
Answer 10:
a. Cement combines with water and sets into a hardened mass (setting of cement)
b. Cement combines with water and sets into a hardened mass. It is an exothermic reaction. Hence a large amount of heat energy is liberated direct contact with the skin will lead to burning. To prevent this, workers wear gloves
Answer 11:
(Question error. 7O2 is suitable instead of 5O2 )
a. 3.5 mols If 7O2 is used
a. 2.5 mols If 5O2 is used
b. Molecular mass of C2H6 = 24+6 =30g
30g C2 H6 burn → 2 x 22.4 L CO2
150g C2 H6 burn → 5 x 2 x 22.4 LCO2
= 224 L CO2
Answer 12:
a. Test tube containing powdered copper. When solids are made into small pieces or powder, their surface area increases. As a result the number of molecules undergoing effective collisions also increases. Hence the rate of reaction increases.
b. Increase the temperature
Answer 13:
a. The amount NO2 will increase
b. According to Le-Cheltelier’s principle, if the pressure of a system of gaseous reacting species is altered, the system will try to nullify the effect of that change. The right side of the equation given has more gaseous moles than the left side. Decrease in pressure will favour the side with more gaseous moles. That is, the reaction proceeds faster towards the right side if the pressure is decreased
Answer 14:
a. i. Bauxite (Al2O3. 2H2O)
ii. Sodium aluminate (NaAlO2) solution
iii. Precipitate Al(OH)3
iv. Alumina (Al(O3)
b. Here, Oxygen is liberated at the Anode. It reacts with the carbon anode forming carbon dioxide. As a result, the anode gets consumed up. Hence Anode should be removed at regular intervals.
Answer 15:
a. Soda lime glass (Soda glass, Soft glass) Silicon dioxide (SiO2), Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
b. Cobalt oxide
Answer 16:
a. (A) [Ne] 3s2 3p5, (D) [Ar] 3d104s24p5
b. (B) [Ar] 4s1
c. (B) [Ar] 4s1
d. [Ar] 3d3
Answer 17:
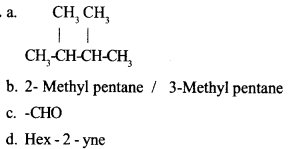
Answer 18:
a. A = Zinc (Zn) B Nickel (Ni)
b. From Zinc electrode to Nickel electrode
c. Nickel (Ni)
d. Zn → Zn2+ +2e
Ni2+ +2e → Ni
Zn+Ni2+ → Zn2+ + Ni
Answer 19:
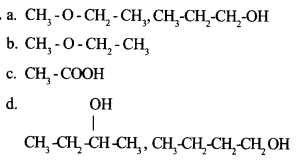
Answer 20:
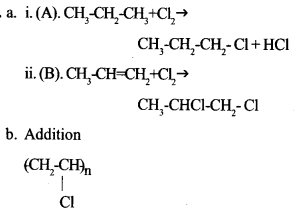
We hope the Kerala SSLC Chemistry Model Question Papers with Answers Paper 1 help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala SSLC Chemistry Model Question Papers with Answers Paper 1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
