What causes ions to form ionic bonds?
- An ionic bond is formed when a metal combines with a non-metal to produce a compound.
- The compound formed is called an ionic compound.
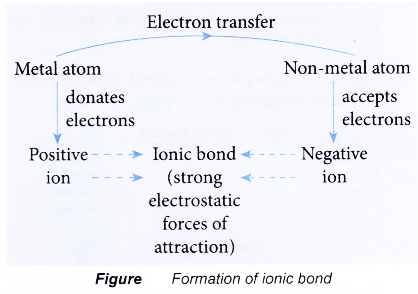
Metal + Non-metal → Ionic compound - The ionic bond is formed through the transfer of electrons from the metal atoms to the non-metal atoms.
- The metal atoms lose their valence electrons to achieve a stable noble gas electron arrangement. Thus, positively-charged ions are formed.
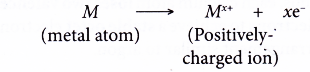
- The non-metal atoms accept the electrons donated by the metal atoms to achieve a stable noble gas electron arrangement. Thus, negatively-charged ions are formed.
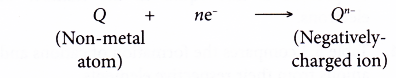
- The positively-charged ions and negatively-charged ions are then attracted to each other by strong electrostatic forces which are closely-packed in an orderly manner in a crystal lattice, forming an ionic compound.
- The strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely-charged ions is called ionic bond.
- Figure shows a chart that summarises the formation of an ionic bond from a metal atom and non-metal atom.
- Examples of ionic compounds:

People also ask
- Chemical Bonding and Compound Formation
- Chemical Bonding
- What is Covalent Bond?
- How is covalent bond is formed?
- Describe how to write a formula for a covalent compound
- Explain the formation of ionic bonds with examples
- Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
- How do you write the formula for ionic compounds?
- How do you Name an Ionic Compound?
Formation of Ions
- In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Hence, the atom is neutral.
- An ion is a charged particle formed when an atom loses or accepts electrons.
- An ion is a charged particle because the number of protons is not equal to the number of electrons.
- Table compares the formation of cations and anions from their respective elements.
Formation of cations:
- An atom that loses electrons from its valence shell forms a positive ion called cation.
- The cation is positively-charged because it has more protons than electrons.
- Metals form positive ions (cations) by donating electrons.
Formation of anions:
- An atom that accepts electrons into its valence shell forms a negative ion called anion.
- The anion is negatively-charged because it has more electrons than protons.
- Non-metals form negative ions (anions) by accepting electrons.
Figure shows how a neutral atom becomes an ion by donating or accepting electrons.
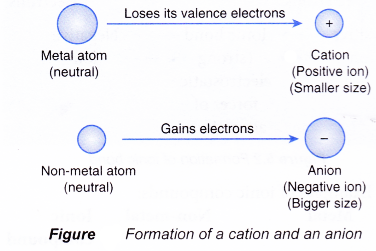
How positive and negative ions are formed?
Formation of Cations (Positive Ions)
- Metals from Group 1, 2 and 13 of the Periodic Table, form cations (positively-charged ions) by donating their valence electrons.
- Metals are generally more electropositive.
- (a) This means that metals readily lose their valence electrons to achieve stable duplet or octet electron arrangements similar to noble gases.
(b) By doing so, cations (positively-charged ions) are formed.
Formation of cations by Group 1 elements:
- Metal atoms of Group 1 elements have one valence electron.
- It is easier for each of these atoms to lose one electron than to gain seven electrons to achieve stable duplet or octet electron arrangements.
- As a result, a Group 1 metal atom loses one valence electron to form a cation with a charge of +1.
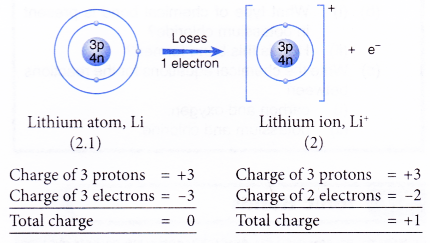
- Example: Lithium
- A lithium atom has an electron arrangement of 2.1.
- It has one valence electron.
- In bond formation, each lithium atom loses one valence electron to achieve a stable duplet electron arrangement similar to helium (noble gas).
- Hence, a lithium ion, Li+ is formed.

- The figure below shows the formation of a lithium ion from a lithium atom:
Formation of cations by Group 2 elements:
- Metal atoms of Group 2 elements have two valence electrons.
- It is easier for each of these atoms to lose two electrons than to gain six electrons to achieve stable noble gas electron arrangement.
- As a result, a Group 2 metal atom loses two valence electrons to form a cation with a charge of +2.
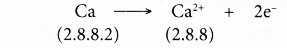
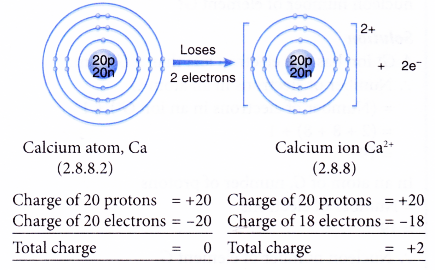
- Example: Calcium
- A calcium atom has an electron arrangement of 2.8.8.2.
- It has two valence electrons.
- Thus, each calcium atom loses two valence electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement similar to argon.
- Hence, a calcium ion, Ca2+ is formed.
- The figure below shows the formation of a calcium ion from a calcium atom:
Formation of cations by Group 13 elements:
- Metal atoms of Group 13 elements have three valence electrons.
- In order to achieve a stable noble gas electron arrangement, each of the Group 13 metal atoms loses all the three valence electrons to form a cation with a charge of +3.
- Example: Aluminium
- An aluminium atom has an electron arrangement of 2.8.3.
- It has three valence electrons.
- Thus, each aluminium atom loses three valence electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement similar to neon.
- Hence, an aluminium ion, Al3+ is formed.
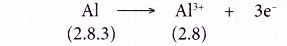
- The figure below shows the formation of an aluminium ion from an aluminum atom:
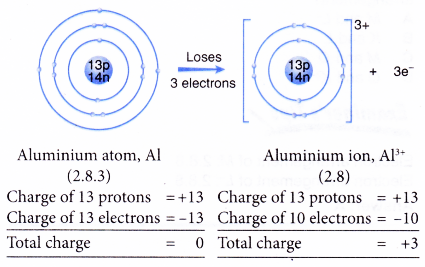
Changes in the number of subatomic particles during the formation of cations:
- Below is a list of four important facts regarding the formation of a cation from an atom.
When an atom of a metal changes to a cation,- the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus remains unchanged.
- only the number of electrons decreases.
- the electron arrangement changes to achieve a stable noble gas electron arrangement.
- the number of protons (total positive charge) is more than the number of electrons (total negative charge) in the cation formed.
- In general, a metal atom X loses n electrons (all its valence electrons) to form a positive ion (cation) with a charge of +n.
Method to determine the charge of a positive ion:
- A particle is positively-charged if the number of protons (total positive charge) is more than the number of electrons (total negative charge).
- The charge can be calculated as below:

Formation of Anions (Negative Ions)
- Non-metals, from Group 15, 16 and 17 of the Periodic Table, form anions (negatively-charged ions) by accepting electrons into their valence shells.
- Non-metals are generally more electronegative.
- (a) This means that non-metals readily accept electrons into their valence shells to achieve stable octet electron arrangements (similar to those of noble gases).
(b) By doing so, anions (negatively-charged ions) are formed.
Formation of anions by Group 15 elements:
- Non-metal atoms of Group 15 elements have five valence electrons.
- It is easier for each of these atoms to accept three electrons than to lose five electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement.
- As a result, a Group 15 non-metal atom accepts three electrons into its valence shell to form an anion with a charge of -3.
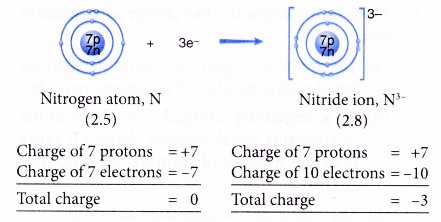
- Example: Nitrogen
- A nitrogen atom has an electron arrangement of 2.5.
- It has five valence electrons.
- In bond formation, each nitrogen atom gains three electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to neon).
- Hence, a nitride ion, N3- is formed.
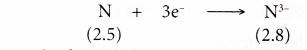
- The figure below shows the formation of a nitride ion from a nitrogen atom:
Formation of anions by Group 16 elements:
- Non-metal atoms of Group 16 elements have six valence electrons.
- It is easier for each of these atoms to accept two electrons than to lose six electrons to achieve a stable noble gas electron arrangement.
- Hence, a Group 16 non-metal atom accepts two electrons into its valence shell to form an anion with a charge of -2.
- Example: Sulphur
- A sulphur atom has an electron arrangement of 2.8.6.
- It has six valence electrons.
- Hence, each sulphur atom accepts two electrons into its valence shell to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to argon).
- Thus, a sulphide ion, S2- is formed.
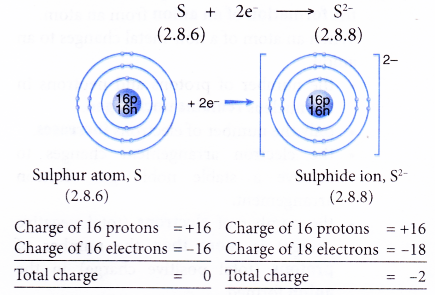
Formation of anions by Group 17 elements:
- Non-metal atoms of Group 17 elements have seven valence electrons.
- It is easier for each of these atoms to accept one electron than to lose seven electrons to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement.
- Hence, a Group 17 non-metal atom accepts one electron into its valence shell to form an anion with a charge of -1.
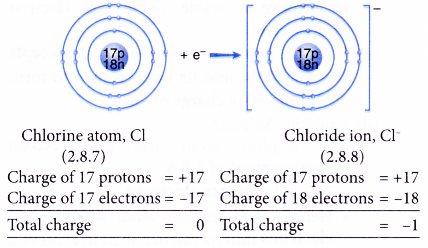
- Example: Chlorine
- A chlorine atom has an electron arrangement of 2.8.7.
- It has seven valence electrons.
- In bond formation, each chlorine atom accepts one electron into the valence shell to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement (similar to argon).
- Thus, a chloride ion, Cl– is formed.
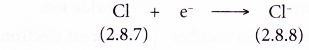
- The figure below shows the formation of a chloride ion from a chlorine atom:
Changes in the number of subatomic particles during the formation of anions:
- Below is a list of four important facts about the formation of an anion from an atom. When an atom of a non-metal changes to an anion,
- the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus remains unchanged.
- only the number of electrons increases.
- the electron arrangement changes to achieve a stable noble gas electron arrangement.
- the number of electrons (total negative charge) is more than the number of protons (total positive charge) in the anion formed.
- In general, a non-metal atom, Y, accepts m electrons into the valence shell to achieve a stable noble gas electron arrangement. As a result, a negative ion (anion) with a charge of -m is formed.
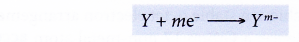
Method to determine the charge of a negative ion
- The charge of a negative ion can be determined based on the number of subatomic particles.
- In a negatively-charged ion, the number of electrons (total negative charge) is more than the number of protons (total positive charge)
- The charge can be calculated as below:
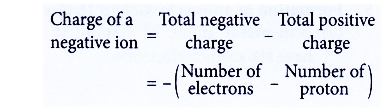
Ion Formation Examples
1. An ion of an element, Y, has the following number of subatomic particles:
25 protons, 30 neutrons, 23 electrons
(a) Is this ion positively or negatively-charged? Explain your answer.
(b) Calculate the charge of this ion.
(c) Write the formula of this ion.
Solution:

2. Element W has a nucleon number of 27. It has 14 neutrons. It forms an ion with the formula W3+.
(a) What is the number of protons and electrons in an ion of W3+?
(b) Write the electron arrangement of a W3+ ion. Solution
Solution:

3. An element, G, forms an ion with the formula G+. An atom of G has 20 neutrons. The electron arrangement of an ion of G+ is 2.8.8. What is the nucleon number of element G?
Solution:

4. Element J has a proton number of 16 and a nucleon number of 32. Atom J forms a negative ion, Jn-.
(a) Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in a Jn- ion.
(b) What is the value of n?
Solution:

5. An ion of element M has the following number of subatomic particles:
15 protons, 16 neutrons, 18 electrons
(a) What is the charge of this ion?
(b) Write the formula of this ion.
Solution:

6. Atom R has a nucleon number of 19. It forms an ion with the formula R–. A R– ion has an electron arrangement of 2.8. What is the number of neutrons in an atom of R?
Solution:

7. Element D forms a D2+ ion.
The electron arrangement of D2+ ion is 2.8.8.
(a) Where is element D located in the Periodic Table?
(b) What is the proton number of element D?
Solution:


8. Element G is placed in Group 16 and Period 2 of the Periodic Table. When atom G forms an ion, its electron arrangement will be changed.
(a) Is the ion formed by element G positively or negatively charged?
(b) What is the formula of the ion formed by element G?
(c) Write the electron arrangement of the ion formed by element G.
Solution:

