Intuitive Idea of Probability
The theory of probability was developed towards the end of the 18th century and its history suggests that it developed with the study of games and chance, such as rolling a dice, drawing a card, flipping a coin etc. ‘probability’ thus suggest that there is an uncertainty about the happening of events.
Probability is the chance that something will happen – how likely it is that some event will happen.

Sometimes you can measure a probability with a number: “10% chance of rain”, or you can use words such as impossible, unlikely, possible, even chance, likely and certain.
We use ratios to show how likely, or unlikely, an outcome might be.
This ratio is called the probability.
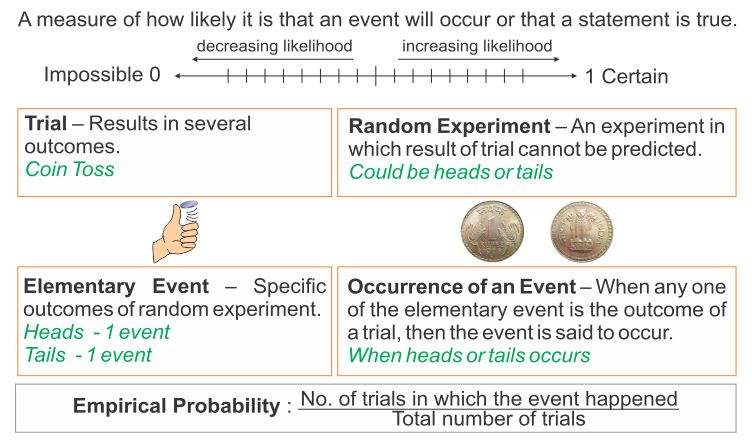
For example, the probability of getting heads on the toss of a penny is the ratio . Heads is one of two possible outcomes when a penny is tossed.
Our ratio for probability can be thought of as:
![]()
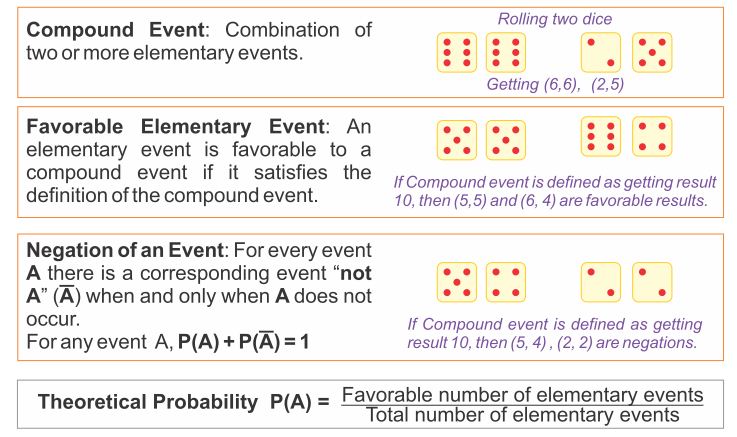
Ratios are most often expressed in the form of a fraction. Fractions, however, can also be expressed as decimals or percents. So probabilities may be expressed as fractions, decimals or percents.
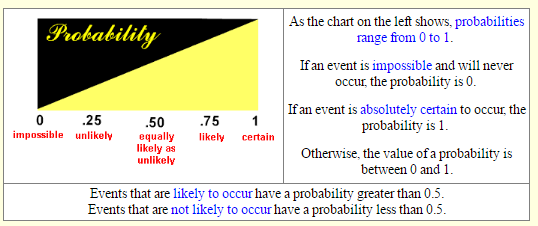
While probability was originally developed to deal with gaming techniques, it is used today in a wide range of applications. Even common sayings reflect the concept of probability:
Someone may say “Don’t hold your breath” when you are waiting for something to happen. What is the person implying about the probability that the event will occur in the near future?
ANSWER: This statement implies that you may die holding your breath waiting for this event to occur.
Obviously, the probability of the event occurring in the near future, is extremely low, if not impossible.
Example:
A fair die is rolled, and the outcome noted. Determine whether each of the following outcomes is: certain to happen, certain not to happen, likely to happen, likely to not happen.

