ICSE Solutions for Class 7 History and Civics – The Constitution of India
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 7 History and Civics. You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 7 History & CivicsGeographyMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
Important Words
- The Constitution is a body of rules and regulations which defines the organization, powers and functions of the government as well as the rights and durties of the citizens.
- Sovereign means an independent country which is not subject to any outside authority. No external power can control or interfere in the internal affairs of the country or dictate its foreign policies.
- Amendment means any change in the Constitution of India.
- Socialism means fair distribution of the country’s wealth among all and providing equal opportunities to all, to bridge the gap between the rich and the poor.
- Secular state means a state which does not adopt a state religion and does not discriminate against anybody on the basis of religion.
- Democracy means a government of the people, for the people and by the people.
Time To Learn
A. Fill in the blanks:
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was the chairman of Drafting committee of the constitution.
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the chairman of the Constituent Assembly.
- The Constituent Assembly took about 2 years 11 months and 18 days to complete its work.
- The Preamble is an introduction to the Constitution.
- The constitution came into force in the year 1950.
B. Match the contents of Column A with those of Column B
Column A Column B

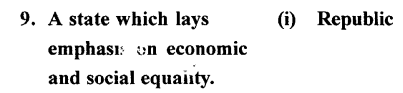
Answer:

III. Tick mark (✓) the cor (X) the wrong ones.
- Constitutiion is the supreme law of the land.
✓ - Before independence, our country was governed according to our Constitution.
X
After independence, our country was governed according to our Constitution. - Our country became a Sovereign Democractic Republic on 15 th August, 1947.
X
Our country became a Sovereign Democractic Republic on26th January, 1950. - In India, the son or daughter of the President succeeds him after his death.
X - In India, all religions are equally respected.
✓
- Elections to the Parliament and state legislatures are held every five years
✓
Answer the following:
Question 1.
What do you mean by the term ‘Constitution’? What does it contains?
Answer:
Constitution is a document which contains details of how to govern our country. It is a framework within which a government has to function. It defines the powers of different organs of the government and also enumerates the rights and duties of citizens.
Question 2.
Why is it necessary to have a Constitution for a country?
Answer:
Our Constitution explains our national goals like democracy, socialism, secularism, liberty, equality, fraternity etc. Thus our Constitution has an importance of its own and we must show our respect to it.
Question 3.
Name the body that framed the Constitution of India. Who was its chairman?
Answer:
Our constitution was framed by the Constituent Assembly! Dr Rajendra Prasad was its chairman.
Question 4.
Who represented the Anglo-Indians and the Parsees in the Constituent Assembly?
Answer:
Frank Anthony and Dr H. P. Modi represented the Anglo- Indians and Parsees respectively.
Question 5.
What is Preamble? Why is it important?
Answer:
The Preamble is an introduction of the things to come. The Preamble to our Constitution summarises its aims and objectives.The Preamble expresses a great deal of meaning in a few words. The Preamble indicates the nature and ideals of the state and also the ultimate source of our Constitution.
Question 6.
What are the main ideals contained in the Preamble to the Constitution of India?
Answer:
We, the people of India, having solemnly resolved to constitute India into a SOVEREIGN SOCIALIST SECULAR DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC and to secure to all its citizens.
JUSTICE, social, economic and political.
LIBERTY of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship.
EQUALITY of status and of opportunity; and to promote among them all.
FRATERNITY assuring the dignity of the individual and the unity and integrity of the Nation.
In our constituent assembly this twenty-sixth day of November, 1949, do hereby adopt, enact and give to ourselves this constitution.”
Question 7.
Define the following: (a) Sovereign State (b) Secular State (c) A Republic
Answer:
(a) Sovereign State: The Preamble declares India a Sovereign State. This means that India is completely free from external control and is the master of her destiny. No outside power can interfere in the internal affairs of the country.
(b) Secular State: The word ‘Secular’ in the Preamble implies that India does not have a state religion or official.
(c) A Republic: A ‘Republic’ is a state where the head of the state is an elected person and is elected for a definite period of time.
Question 8.
State the difference between a democracy and a republic.
Answer:
Democracy: Democracy is defined as a ‘Government of the people, by the people and for the people.’
Republic: A ‘Republic’ is a state where the head of the state is an elected person and is elected for a definite period of time.
Question 9.
Do you think Indian government is ‘of the people, by the people and for the people’?
Answer:
The Indian government is ‘of the people, by the people and for the people.’ The statement mentioned above is true as in India, after every five years, general elections are held and the people eleet their government.
Additional Questions
(The Constitution of India)
A. Fill in the blanks:
- The Constitution of India was framed by the constituent Assembly.
- The Preambles tells us about the source of the Constitution, the nature of the state and its main objectives of the Constitution.
- Socialism involves fair distribution of the country’s wealth among all sections of the people.
- The people of India eleet their own government because India is a Democratic country.
- The President of India has a fixed term of 5 years.
B. Match the following:


Answer:

C. Choose the correct answer:
1. India won freedom from British/French/Portuguese rule on 15 August 1947.
Ans. India won freedom from British rule on 15 August 1947.
2. The chairman of the Constituent Assembly of India was Dr Rajendra Prasad/B. R.Ambedkar/Maulana Azad.
Ans. The chairman of the Constituent Assembly of India was Dr Rajendra Prasad.
3. The source of the Indian Constitution is the President/the Prime Minister/the people of India.
Ans. The source of the Indian Constitution is the people of India.
4. A democractic/socialist/secular state does not have an official religion.
Ans. A secular state does not have’bn official religion.
5. A democracy can work only if there is a spirit of jealousy/ brotherhood/competition among the different sections of society.
Ans. A democracy can work only if there is a spirit of brotherhood among the different sections of society.
D. State whether the following are true or false:
- The Constitution of India was framed by the British government.
False. Correct: The Constitution of India was framed by the Constituent Assembly. - Sarojini Naidu was a member of the Constituent Assembly.
True. - The Preamble is the conclusion to the Constitution.
False. Correct: The Preamble is the introduction to the Constitution. - When the President of India dies, his/her son becomes the next President.
False. - All Indian citizens are equal in the eyes of the law.
True
E. Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
Question 1.
Define the term ‘constitution’.
Answer:
A Constitution is a statement which defines the powers and functions of the government as well as the rights and duties of the citizens. It is the fundamental law of that nation.
Question 2.
How do we know that the Constitution of India was not imposed on us by the British?
Answer:
Constitution of India was not imposed on us by the British. After we got independence in 1947, a constituent Assembly under the chairmanship of Dr. Rajendra Prasad was appointed to frame the constitution.
Question 3.
When did the Constitution of India come into force?
Answer:
The Constitution of India came into force on 26 January
Question 4.
What is a preamble.
Answer:
The Preamble is a kind of introductory statement which comes before the Constitution. It is not a law but it explains the hue spirit of the Indian Constitution.
Question 5.
Who gives the government of India the authority to govern the country?
Answer:
Our Constitution gives the government of India the authority to govern the country
F. Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of the following terms:
(a) Sovereign (b) Democratic (c) Republic
Answer:
(a) Sovereign: Means that India is an independent country.
No external power can control or interfere in its internal affairs.
(b) Democratic: A democratic government is a government of the people, for the people, by the people.
(c) Republic: A country where head of the state is elected by the people.
Question 2.
State the basic features of the following: (a) a socialist state (b) a secular state|
Answer:
(a) Socialist state: Is one where there is fair distribution of the country’s wealth among all sections of the people. It means providing equal opportunities to all in order to bridge the gap between the rich and the poor.
(b) Secular state: A secular state is one which:
- Does not have an official or state religion.
- Does not discriminate against anybody on grounds of religion.
- Does not favour or promote any particular religion.
- guarantees the freedom of every individual to profess, practise and propagate his or her own religion.
Question 3.
State the objectives of the Constitution with reference to: (a) Justice (b) Liberty (c) Equality
Answer:
(a) Justice: All citizens are equal in the eyes of law. Justice shall not be denied to anybody on the basis of place of birth, race, caste, creed, sex, status or religion. Every individual will get what is his or her due.
(b) Liberty: Every Indian citizen shall enjoy certain fundamental rights such as the freedom to think and express oneself and the freedom to follow the religion of our choice.
(c) Equality: All citizens are equal before law and will be protected equally by the laws of the land. The state shall not discriminate between people on the basis of place of birth, sex, caste, creed, race, religion or wealth.
Question 4.
Why did the farmers of the Constitution decide to promote fraternity among the people of India?
Answer:
A democracy can work only if there is a spirit of brotherhood and oneness among the different sections of society. When this feeling of being ‘one people’ is promoted and firmly established, social evils such as untouchability and communalism can be removed. Elarmony will prevail and the country can progress unitedly towards its goal of securing justice, liberty and equality for all its citizens.
G Picture study:
This is a picture of the Chairman of the Constituent Assembly of India which drafted the Indian Constitution.

Question 1.
Identify the person in the picture.
Answer:
Dr. Rajendra Prasad.
Question 2.
Name two other prominent members of the Constituent Assembly.
Answer:
- B.R Ambedkar
- MaulanaAzad
Question 3.
When was the first meeting of the Constituent Assembly held?
Answer:
9 Dec 1946.
Question 4.
When did the Constitution come into force?
Answer:
26 January 1950
Question 5.
What is the introduction to the Constitution called? What does it tell us about the source of the Constitution?
Answer:
The Preamble is an introduction to the Constitution. It helps us to understand the vision and the aspirations of the farmers of our Constitution. The Preamble tells us about the source of the Constitution, the nature of the state and its main objectives.
Question 6.
Mention the objectives stated in the introduction.
Answer:
Justice: All citizens are equal in the eyes of law. Justice shall not be denied to any body.
Liberty: Every Indian citizen shall enjoy certain fundamental rights such as the freedom to think and express oneself and the freedom to follow the religion of our choice.
Equality: All citizens are equal before law and will be protected equally by the laws of the land.|
Fraternity: A democracy can work only if there is a spirit of brotherhood and oneness among the different sections of society.
