ICSE Geography Previous Year Question Paper 2008 Solved for Class 10
ICSE Paper 2008
GEOGRAPHY
(Two hours)
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Attempt seven questions in all.
Part I is compulsory. All questions from Part I are to be attempted.
A total of five questions are to be attempted from Part II.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
To be supplied with this Paper : Survey of India Map Sheet No. 45D/10
and 20 cm of twine.
(ii) The extract of Survey of India Map Sheet No. 45D/10 must not be taken out of the examination hall. It must be handed over to the Supervising Examiner on completion of the Paper.
(iii) The Map given at the end of this question paper must be detached, and after marking must be fastened to your answer booklet.
(iv) All sub-sections of the questions attempted must be answered in the correct serial order.
(v) All working including rough work should be done on the same answer sheet which is used to answer the rest of the paper.
PART I [30 Marks]
Attempt all questions from this Part.
Question 1:
Study the extract of the Survey of India Map sheet No. 45D/10 and answer the following questions:
(a) What is the compass direction of Sunset Point from the settlement of Anadra ? [1]
(b) What is the pattern of drainage in grid square 2315? [1]
(c) Mention any two features seen in the map extract which indicate that the region has seasonal rainfall. [1]
(d) Calculate the distance in kilometres along the metalled road from the causeway in grid square 1715 to the distance stone marked 20 in grid square 1818. [1]
(e) What advantage does a Representative Fraction have over a verbal scale ? [1]
(f) Give the six figure grid reference of:
(i) Anjini Devi ka Mandir
(ii) A1327. [2]
(g) Name the three different kinds of roads in grid square 2411 and the one in grid square 2515. [2]
(h) Mention two occupations of the people living in the northern part of the region in the map extract. Give reasons to support your answer. [2]
(i) What is the difference between the slope in grid square 2115 and the one in 1811. Give a reason for your answer. [2]
(j) What is the purpose of:
(i) the fireline in grid square 2316
(ii) the pipeline in grid square 2209 ? [2]
(k) What do the following represent ?
(i) The red square in grid square 2514.
(ii) 4r in grid square 1612. [2]
(l) Abu is a popular holiday resort. Mention any three features seen in the map extract which attract holiday makers to Abu. [3]
Answer:
(a) Compass direction of sun set point from the settlement of Anadra is South-West.
(b) Pattern of Drainage in Grid Sq. 2315 is Radial.
(c) Any two features seen in the map extract which indicate that the region has seasonal rainfall are
(i) seasonal streams and rivers
(ii) Pressure of cause-way.
(d) The distance in kilometres from causeway to distance stone 20 is 3 km.
(e) The main advantage of the RF is that the ratio between any two points on the ground and on the map is presented in a fraction with a unit of measurement, which can be converted into any unit of measurement thus it can be used all over the world and also known as International Scale.
(f) Six fig. grid reference :
(i) Anjini Devi Ka Mandir = 229159.
(ii) ∆1327 = 217106.
(g) Three different kinds of roads in grid square 2411 are :
- Metalled road
- Pack track
- Gravelled road.
In square 2515 is foot path.
(h) In the northern part the main two occupations are :
(i) Agriculture as the region is coloured yellow. It has lot of perennial wells which supports the cultivation in this region.
(ii) Forestry as the region is coloured green due to presence of dense mixed jungle and open mixed jungle.
(i) (i) Gradual Slope : In 2115 Grid because the contours in such a slope are placed
wide apart as the change of elevation is gradual.
(ii) Steep Slope: In steep slope the contours are drawn close to one smother, contours are close to each other in 1811.
(j) (i) The purpose of fireline in grid square 2316 is to prevent spreading jungle fires,
(ii) The purpose of pipe line in square 2209 is to supply water to Abu from reservoir.
(k) (i) Red squares in grid square 2514 indicate temporary huts.
(ii) 4r in grid square 1612 is the relative height of an embankment i.e. 4 m.
(l) Abu is a popular holiday resort. Three features are :
- Dilwara temples are tourist attraction here.
- It is situated at height therefore it is a hill station in hot region.
- Lakes here like Nakhi and Alwar Taloa scenic beauty also attracts tourist here.
Question 2:
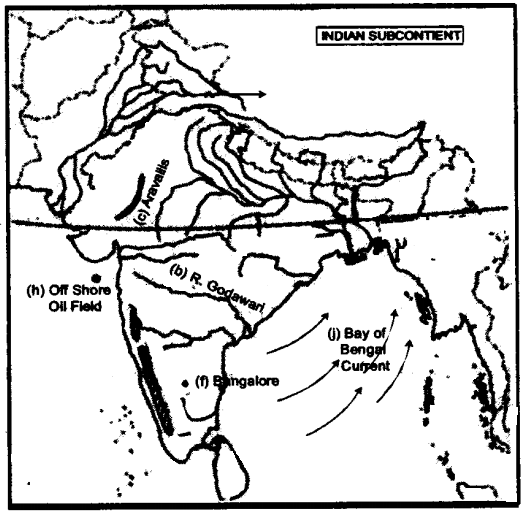
On the outline map of South Asia provided:
(a) Label the river Sutlej. [1]
(b) Label the river Godavari. [1]
(c) Mark with a bold line and name, the Aravali Range. [1]
(d) Mark and label the Khyber Pass. [1]
(e) Mark and name the largest commercial city of Pakistan. [1]
(f) Mark and label Bangaluru. [1]
(g) Shade and label an area oflaterite soil in North India. [1]
(h) Mark and name an off share oil field. [1]
(i) Mark and label the Tropic of Cancer. [1]
(j) Mark and name the winds which bring rain to Bangladesh in July and August. [1]
Answer:
PART II [50 Marks]
Attempt any five questions from this Part.
Question 3:
(a) Mention two favourable effects of the Himalayas on the economy of India. [2]
(b) Why is Pakistan often described as the ‘Gift of the Indus’ ? Give two reasons. [2]
(c) Mention three differences between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats. [3]
(d) Give three reasons why Bangladesh is one of the most densely populated countries in the world. [3]
Answer:
(a) Two favourable effects of the Himalayas on the economy of India are :
- There are many hill stations which encourage tourism in India. It also provides attraction for adventure seekers such as hiking, climbing, river rafting and skiing. All this earn foreign exchange.
- They give rise to fertile plains which are found by the rivers originating in l Himalayas. So most of people are engaged in agriculture.
- The Himalayas are covered by thick forests which are the source of numerous raw material for various industries which effects the economy of India.
(b) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(c) Three differences between eastern ghats and western ghats are:
| Western Ghats | Eastern Ghats |
| Western ghats are higher. | Eastern ghats are lower. |
| Western ghats are continuous. | Eastern ghats disappear between the delta of Krishna and Kaveri. |
| It has few passes like Pal ghat, Bhor ghat and Thai ghats. | It has no passes as it is a discontinuous range. |
| This strip gets rainfall mostly in summer and not in winter. | This strip gets rainfall both in summer and winter, especially in winter. |
(d) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
Question 4:
(a) What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of Pakistan ? [2]
(b) Mention two factors which are responsible for the slow growth of industry in Nepal. [2]
(c) Mention three benefits of the long coastline of India. [3]
(d) Give reasons for the following:
(i) The Deccan Plateau is a highly dissected one.
(ii) Most of the rivers in South India flow into the Bay of Bengal.
(iii) The Rann ofKutch is not cultivated. [3]
Answer:
(a) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(b) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(c) Three benefits of the long coastline of India are :
- Suitable sites for ports and harbours.
- Suitable coast for agriculture.
- Back waters and lagoons for fishing.
(d) (i) Deccan plateau is a highly dissected one because of many seasonal rivers flowing across the Deccan plateau.
(ii) Most of rivers in south India flow into the Bay of Bengal because the Deccan plateau flows towards the east i.e. towards Bay of Bengal.
(iii) Rann of Kutch is not cultivated because it is a marshy lowland covered with salty water.
Question 5:
(a) Mention two differences between the cyclonic rain in Bangladesh and the cyclonic rain in Pakistan. [2]
(b) Name the source of winter rain in Tamil Nadu. How does Tamil Nadu benefit from it ? [2]
(c) Give a reason for each of the following:
(i) Patna gets a heavier rainfall than Varanasi.
(ii) The Arabian Sea branch of the South West Monsoon does not shed any moisture in Western Rajasthan.
(iii) India has varied climatic conditions. [3]
(d) Study the climatic data provided below and answer the questions that follow :
| Station | Months | J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| A | Temperature in degree C | 24.4 | 25.4 | 26.7 | 29.3 | 30.0 | 29.9 | 29.8 | 27.8 | 26.9 | 25.3 | 25.1 | 24.8 |
| Rain fall in cms | 01 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 3.8 | 26.6 | 29.6 | 30.5 | 26.5 | 11.9 | 1.1 | 0.2 | |
| B | Temperature in degree C | 8.1 | 83 | 15.6 | 20.1 | 25.2 | 24.3 | 24.1 | 22.7 | 20.6 | 18.4 | 14.1 | 9.6 |
| Rainfall in cms | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 3.2 | 7.7 | 10.3 | 5.8 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
(i) Calculate the annual range of temperature of Station A Suggest a reason why the range is a small one.
(ii) Which of the two Stations has the lower temperature ? Why ?
(iii) Calculate the annual rainfall of Station B. [3]
Answer:
(a) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(b) The source of winter rain in Tamil Nadu is N.E. Monsoons which pick up moisture from Bay of Bengal and shed in Tamil Nadu. This rain is beneficial for Rice and Coffee.
(c) (i) Patna gets heavier rainfall than Varanasi because as the S.W. Monsoon Bay of Bengal current advances towards N.W. amount of rainfall decreases.
(ii) The Arabian sea branch of the South West Monsoon does not shed any moisture in western Rajasthan as Aravallis are parallel to the direction of the winds.
(iii) India has varied climatic conditions because of large latitudinal and longitudinal extent. Distance from the sea and altitude.
(d) (i) Annual range of temperature of station A is 5.6°C which is low because of the station is close to the sea.
(ii) Station B has the lower organization because it is situated at greater altitude.
(iii) Annual rainfall of station B is 31.8 cm.
Question 6:
(a) Explain the formation of Laterite soil. Why is Laterite soil not suitable for cultivation ? [2]
(b) Give one difference between the following:
(i) Khadar soil and Bangar soil.
(ii) Sheet erosion and Wind erosion. [2]
(c) Mention two characteristics of Black soil. Why is this soil agriculturally important ? [3]
(d) Give reason as to why :
(i) Red soil is red in colour.
(ii) Large tracts in Maharashtra are covered with black soil.
(iii) Man is largely responsible for soil erosion. [3]
Answer:
(a) Laterite Soil is formed by leaching in the regions of alternate wet and dry spells. Disadvantage—It is acidic is nature and cannot retain moisture.
(b) (i)
| Bhangar | Khadar |
| (1) It belongs to Old alluvium. | It belongs to New alluvium. |
| (2) It is less fertile. | It is more fertile. |
| (3) It is non porous, claying and loamy. | It is calcareous clay. |
| (4) It is found in the lower areas of valley bottom. | They are found 30 m above flood level of the rivers. |
(ii)
| Sheet erosion | Wind erosion |
| (1) It mainly occurs on hill slopes. | (1) It occurs in desert areas. |
| (2) Agent of denudation is running water. | (2) Agent of denudation is wind. |
(c) Two characteristics of black soil are:
(i) It is moisture retentive.
(ii) It is rich in iron, potash, lime, calcium etc.
Imortance: It is deep, fine grained and in moisture retentive. These qualities of soil are important for agriculturally.
(d) (i) Red soil is red in colour because it is rich in Iron Oxide.
(ii) Large tracts in Maharashtra are covered with black soil because this region is made up of lava traps.
(iii) Man is largely responsible for soil erosion because man has cleared the forest for his habitation, adopted wrong methods of farming, over grazing by animals etc.
Question 7:
(a) Name two states with large deposits of coal. Name the coalfields in the states that you have named. [2]
(b) What is lignite ? Name one place in India where it is mined. [2]
(c) (i) Mention two uses of mineral oil.
(ii) Name an old and a new mineral oil producing area. [3]
(d) (i) Mention two reasons why minerals are important ?
(ii) Name one area in Orissa and one area in Chattisgarh where iron ore is mined. [3]
Answer:
(a) Two states with large deposits of coal are:
| States | Coal fields |
| (i) West Bengal (ii) Jharkhand | Raniganj. Jharia, Kampura, Ramgarh, Bokaro. |
(b) Lignite is a lower grade coal and contains about 60% carbon. Its colour varies from dark to black brown. In India it is mined at Neyveli in Tamil Nadu.
(c) (i) Two uses of mineral oil are :
- It is used as locomotive power.
- It is an important raw material for petrochemical products.
(ii) Old oil producing area—Digboi in Assam.
New oil producing area—Khambhat Basin and Krishna Kaveri Basin.
(d) (i) Two reasons why minerals are important are :
- Minerals are power resources for the countries.
- Minerals based industries like iron and steel etc. depend on them.
(ii) In Orrisa, iron ore is mined in Sundergarh and Mayurbhanj.
In Chattishgarh, iron ore is mined in Baster and Durg.
Question 8:
(a) (i) When are kharif crops (1) sown and (2) harvested ?
(ii) Name a cash crop which is also a kharif crop. [2]
(b) India is the largest producer of tea. State the climatic factors necessary for its growth. [2]
(c) Explain the following methods of propagation and name the crop associated with each :
(i) bud grafting
(ii) ratoon cropping [3]
(d) (i) What are the geographical conditions necessary for the cultivation of groundnuts ?
(ii) What climatic condition adversely affects the groundnut crop ?
(iii) Name two non-edible oilseeds grown. [3]
Answer:
(a) (i) Kharif crops are sown after monsoons in June, July and harvested in Oct. and Nov.
(ii) A cash crop which is also a Kharif crop — cotton.
(b) Climatic factors necessary for tea are:
Temperature required is between 15° to 35°C (under shade), but 25°C is most suitable.
Rainfall should be between 150 cm to 250 cm, well distributed throughout the year.
(c) (i) Bud grafting—It is associated with rubber crop. This method is done by the
insertion of a strip of bark containing a bud from high yielding clones under a bark of a young seedling about 5 cm high till they become united in 3 to 4 weeks. The old seedling stem is then sawn off above the grafted bud, which then grows to form a new rubber plant.
(ii) Ratoon cropping—It is associated with sugarcane. It is a process by which the cane is cut close to the ground where the sugar content is concentrated. After the crop has been cut the stem begins to grow again and produces a second crop called ratoon.
(d) (i) Geographical conditions necessary for the cultivation of ground nuts :
- It requires a tropical or sub-tropical climate.
- Rainfall should be between 50 to 75 cm and temperature should be 20°C to 25°C.
- Dry, light and sandy soils ideal.
(ii) This crop is highly susceptible to prolonged drought, continuous rains, stagnant water and frost.
(iii) Two non edible oil seeds grown—castor and linseed.
Question 9:
(a) What are two advantages of natural gas ? [2]
(b) Mention two reasons to explain the increasing use of bio-gas. [2]
(c) Give three reasons to explain why it is easier to harness rivers in South India for power than rivers in North India. [3]
(d) (i) What does NTPC stand for ? Mention one of its functions.
(ii) Name any two coal based thermal power stations in Uttar Pradesh. [3]
Answer:
Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
Question 10:
(a) Mention two reasons why the sugar industry has developed in Maharashtra. [2]
(b) Give two reasons for the importance of the silk industry in India. [2]
(c) Give three factors that favour the cotton industry in Kolkata. [3]
(d) (i) Explain why sugar-cane must be crushed within 24 hours of harvesting.
(ii) Name four sugar milling centres in the northern plains. [3]
Answer:
(a) Two reasons why sugar industry has developed in Maharashtra are:
(i) Geographical conditions are suitable for the cultivation of sugarcane.
(ii) Sugar industry is better organized and farms are close to the mills.
(b) Importance of silk industry in India because:
(i) It is labour intensive industry provides employment to people in rural areas.
(ii) India is fourth largest producer of silk in the world.
(c) Three factors that favour cotton industry in Kolkata are:
(i) Being close to Jharia and Raniganj coal fields. It has sufficient power supply.
(ii) It has a port facility for import and export.
(iii) It has humid climate which facilitates the spinning of yam of finer cotton.
(d) (i) Sugarcane must be crushed within 24 hrs of harvesting because the sucrose content starts decreasing.
(ii) Four sugar milling centres in Northern plains—Gorakhpur, Saharanpur, Lucknow and Munger.
Question 11:
(a) Mention two reasons for the importance of the Electronic industry in India’s development. [2]
(b) What is a petrochemical industry ? Mention two reasons why petrochemical products are replacing traditional raw materials. [2]
(c) (i) Mention two characteristics of a mini steel plant.
(ii) From where does the integrated steel plant at Jamshedpur get its iron ore and coal ? [3]
(d) Name the following:
(i) A shipbuilding yard on the west coast of India.
(ii) A centre where diesel locomotives are manufactured.
(iii) The foreign collaborator of the iron and steel plant at Rourkela. [3]
Answer:
(a) Two reasons for the importance of electronic industry in India’s development are :
(i) It has largely contributed to space technology, communication, information technology and software industry. Indian software is in great demand in the world.
(ii) It has helped medical sciences and defence to develop with electronic apparatus.
(b) Petrochemical industry derives chemicals and compounds from petroleum products. These chemicals are used for manufacturing a large variety of articles such as synthetic fibre, synthetic rubber, plastics, drugs etc.
Two reasons :
- Petrochemical products are cheaper as compared to traditional raw materials.
- Its raw materials are easily available.
(c) (i) Two characteristics of a mini steel plant are :
- They use cheaply available scrap iron.
- They use electric furnaces therefore cause no pollution.
(ii) Jamshedpur plant get its iron ore from Singhbhum and Mayurbhanj. It get its coal from Jharia and Raniganj.
(d) (i) Cochin (The Cochin Shipyard)
(ii) Varanasi
