ICSE Geography Previous Year Question Paper 2007 Solved for Class 10
ICSE Paper 2007
GEOGRAPHY
(Two hours)
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Attempt seven questions in all.
Part I is compulsory. All questions from Part I are to be attempted.
A total of five questions are to be attempted from Part II.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
To be supplied with this Paper : Survey of India Map Sheet No. 45D/7
and 20 cm of twine.
(ii) The extract of Survey of India Map Sheet No. 45D/7 must not be taken out of the examination hall. It must be handed over to the Supervising Examiner on completion of the Paper.
(iii) The Map given at the end of this question paper must be detached, and after marking must be fastened to your answer booklet.
(iv) All sub-sections of the questions attempted must be answered in the correct serial order.
(v) All working including rough work should be done on the same answer sheet which is used to answer the rest of the paper.
PART I [30 Marks]
Attempt all questions from this Part.
Question 1:
Study the extract of the Survey of India Map sheet No. 45D/7 and answer the following questions:
(a) Give the six figure grid reference of:
(i) A 364
(ii) The temple at Rempura. [2]
(b) Mention any two features seen in the map extract which show that the region has seasonal rainfall. [2]
(c) Calculate the distance in kilometres along the cart-track linking Juvol (923826) and Arniwada (944817). [2]
(d) Which is the chief form of irrigation shown in the map extract ? Give an evidence to justify your answer. [2]
(e) Give one reason to explain why the streams in grid square 9478 do not join a river.
Identify another grid square in the map extract that has similar streams. [2]
(f) What do the following represent:
(i) Black broken lines in 9575.
(ii) Black curved lines in 9879. [2]
(g) Identify two land forms shown by the contours in grid square 9876. [2]
(h) (i) What is the general direction of the Balaram Nadi ?
(ii) Which bank of the main river does the Balaram Nadi join ? [2]
(i) What is the main occupation of the people living in the area shown in the map extract ? Give one reason to support your answer. [2]
(j) What is meant by scale of a map ? What is the scale of the map extract provided to you ? [2]
Answer:
(a) (i) ∆364-957744
(ii) The temple at Rampura = 954806
(b) Two features seen in the map which show that the region has seasonal rainfall:
(i) Seasonal rivers and streams
(ii) Broken ground.
(c) Distance in cm = 4.8 [Scale (2 cm = 1 km)]
Distance in km = 4.8/2 = 2.4 km.
(d) Chief form of irrigation is perennial lined well which is evidence as many blue dots can be seen in the map.
(e) Streams in 9478 do not join a river because these are disappearing streams, which dry up or disappear into the sand.
Another grid square is 9575.
(f) (i) Black broken line in 9575 represents disappearing stream.
(ii) Black curved lines in 9879 represents broken ground.
(g) Two land forms shown by contours are
- Ridge
- Watershed
(h) (i) General direction of Balaram Nadi is from SE to NW.
(ii) Balaram Nadi joins on the left bank of the main river.
(i) The main occupation of the people is farming because most of the region is coloured yellow which represents agricultural land.
(j) Scale: It is the proportion between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the earth’s surface.
The scale of the map provided is 2 cm = 1 km.
Question 2:
On the outline map provided:
(a) Shade and label the country Nepal. [1]
(b) Shade and label an area of black soil in India. [1]
(c) Mark and label the Konkan Coast. [1]
(d) Shade and label one region of winter rainfall in India. [1]
(e) Shade and label the Sulaiman Ranges. [1]
(f) Label the River Yamuna. [1]
(g) Mark and name the port city of Bangladesh. [1]
(h) Label the River Tapti. [1]
(i) Shade and label the Vindhya Ranges. [1]
(j) Mark and name the capital of Bhutan. [1]
Answer:
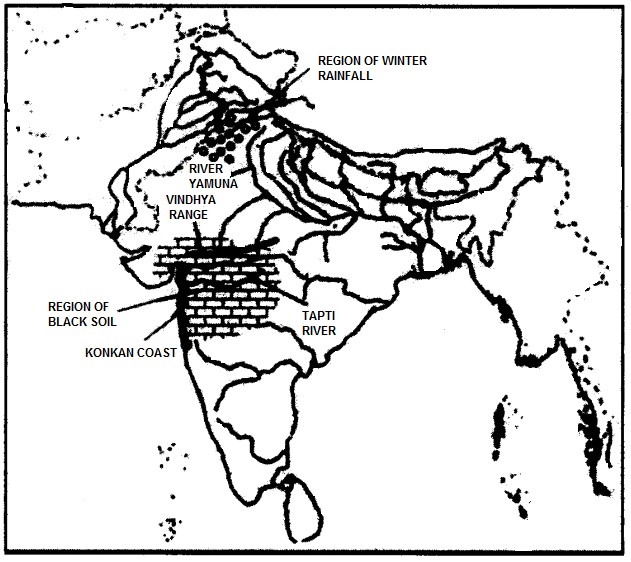
PART II [50 Marks]
Section-I
Attempt any three questions from this section.
Question 3:
(a) Name the source of the river Ganga. Where does this river enter the plains ? [2]
(b) What is a Delta ? Name two deltas in South Asia. [2]
(c) State three reasons for the importance of the Peninsular Plateau. [3]
(d) State three reasons why Myanmar and Afghanistan can be considered extensions of South Asia. [3]
Answer:
(a) Source of river Ganga is Gangotri glacier and the river enters the plains at Haridwar.
(b) The distributaries are also subdivided into mini distributaries due to deposition of sediments over a large area near its mouth at the sea. This deposition over a large area results in a triangular shaped formation which is called Delta.
Two Deltas in South Asia—(1) Ganga Brahamputra Delta, (2) Delta of Godawari.
(c) Three reasons for the importance of the peninsular plateau :
(i) The peninsular plateau has large deposits of metallic, non metallic and energy resources.
(ii) North western part of it has fertile black soil.
(iii) Rivers of western ghats are short and swift used for hydro-electricity.
(d) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
Question 4:
(a) Name the countries that have a land border with Bangladesh. [2]
(b) State two ways in which the rivers of Pakistan are useful to the people of the country. [2]
(c) Mention three differences between the Western Himalayas and Eastern Himalayas. [3]
(d) Define the following:
(i) Archipelago
(ii) Lagoon
(iii) A land-locked country. [3]
Answer:
(a) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(b) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(c) Three differences between the Western Himalayas and Eastern Himalayas are :
| Western Himalayas | Eastern Himalayas |
| 1. The Western Himalayas lie in Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. | 1. The Eastern Himalayas lie in West Bengal, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh and Bhutan. |
| 2. This part of the Himalayas is very high. | 2. This part of the Himalayas is of medium height. |
| 3. The major rivers of the Western Himalayas—Indus and Satluj—flow into the Arabian Sea. | 3. The major rivers of the Eastern Himalayas—Brahmaputra flows into the Bay of Bengal. |
| 4. The Western Himalayas get less rainfall. | 4. The Eastern Himalayas get more rainfall. |
(d) (i) Archipelago—A group of islands is called Archipelago eg. Indonesia etc.
(ii) Lagoon—A back water lake is called Lagoon. It is partly or completely separated from the open sea by a narrow strip of land.
(iii) A land locked country—A country which do not have opening to the sea and is surrounded by land in all sides is called land locked country eg. Nepal and Bhutan.
Question 5:
(a) Explain two factors that influence the climate of South Asia. [2]
(b) Which type of climate is experienced in the Northern Plains of India ? State one main characteristic of this type of climate. [2]
(c) Give a reason for each of the following :
(i) Most of Sri Lanka has the Equatorial type of climate.
(ii) Parts of Nepal experience the Arctic type of climate.
(iii) Western coastal plains receive more rainfall than the Eastern coastal plains. [3]
(d) Given below is the climatic data of a station. Study the table and answer the questions that follow :
| Months | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| Temp ° C | 13.7 | 16.6 | 21.6 | 25.5 | 33.2 | 33.5 | 30.8 | 29.8 | 29.2 | 25.5 | 16.9 | 15.2 |
| Rainfall in cms | 2.5 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 17.5 | 18.5 | 12.5 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.5 |
(i) Calculate the annual range of temperature.
(ii) What is the total rainfall experienced by the station ?
(iii) Which is the driest month ? [3]
Answer:
(a) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(b) Northern plains of India experiences continental types of climate. Its main characteristic is high range of temperature i.e. it is extremely hot in summer and extremely cold in winter.
(c) (i), (ii) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
Reasons:
(iii) Western coastal plains receive more rainfall because the Western ghats check the rain bearing S.W. Monsoon winds to cause heavy relief rainfall.
(d) (i) Annual range of temperature = 33.5 -13.7 = 19.8°C.
(ii) Total rainfall = 67.4 cm.
(iii) Driest month = November.
Question 6:
(a) Mention two important characteristics of laterite soil. [2]
(b) Name an area of black soil in India. Mention two crops grown in this soil. [2]
(c) How is’alluvial soil formed %Why is this soil agriculturally important ? [3]
(d) Name two important agents of erosion. For each, state one method of controlling the erosion caused. [3]
Answer:
(a) Two main characteristics of laterite soil are :
- It is red in colour with high content of iron oxides.
- High content of acidity and inability to retain moisture.
(b) Gujarat and Maharashtra are the regions of black soil.
Two crops grown on this soil are cotton and sugarcane.
(c) Alluvial soil is formed by the deposition of sediments brought down by the rivers. This soil is agriculturally important because it is more fertile. It is rich in humus, lime and potash.
(d) Two important agents of erosion are :
- Wind and
- Running water.
Erosion by wind can be controlled by planting shelter belts perpendicular to the wind direction.
Erosion by running water can be controlled by planting trees, making dams across the river etc.
Question 7:
(a) (i) Name the different types of iron ore found in India.
(ii) Mention one place in Nepal where iron ore is found. [2]
(b) Name an important coal producing State in India and a coal-mine located in that State. [2]
(c) Name two regions in Pakistan where petroleum is found. Which is the largest petroleum producing country in South Asia ? [3]
(d) Name an area of limestone in Sri Lanka. Mention two uses of limestone. [3]
Answer:
(a) (i) Different types of iron ore found in India are:
- Anthracite
- Bituminous
- Lignite
- Peat
(b) An important coal producing state is Jharkhand.
Coalmine—Bokaro
(c) Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
(d) Two uses of Limestone: Cement and Iron and Steel.
Section-II
Attempt any two questions from this Section.
Question 8:
(a) Mention two difference between subsistence agriculture and commercial agriculture. [2]
(b) State two geographical requirements for the growth of rubber. [2]
(c) In which season is wheat grown in northern India ? What are the rainfall and soil requirements of this crop ? [3]
(d) Explain why:
(i) Pulses are grown as rotation crops.
(ii) Millets are referred to as dry crops.
(iii) Tea plantations are found on hill slopes. [3]
Answer:
(a) Two differences between subsistence and commercial agriculture are:
(1) Subsistence agriculture is done with old primitive method where as commercial agriculture is practiced in scientific method.
(2) In subsistence agriculture crop is cultivated to fulfill farmers requirement and not for sale where as in commercial agriculture crops are meant for sale.
(b) Two geographical requirements for the growth of rubber are :
(i) It requires 200 to 300 cm of rainfall well distributed.
(ii) It requires temperature ranging between 20°C to 35°C.
(c) Wheat is grown in Rabi season in northern India.
Rainfall requirement 50 cm to 100 cm mainly in the winter season.
Soil requirement Black or Alluvial soil.
(d) (i) Pulses are grown as rotation crop because pulses are leguminous crop which changes atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates and restores the fertility of the soil.
(ii) Millets are referred to as dry crops, because they can also grow in regions of low rainfall and poor soils.
(iii) Tea plantations are found on hill slopes because tea plant cannot withstand standing water on its roots.
Question 9:
(a) Mention two steps taken by India and Bangladesh to solve the water sharing issues. [2]
(b) How do windmills generate electric power ? [2]
(c) Name two main minerals required for generating nuclear energy. Mention the nuclear power stations located in the States of Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. [3]
(d) (i) Mention two factors that favour the production of Hydel Power in the region around the Western Ghats.
(ii) State one advantage of electricity over coal. [3]
Answer: Answer has not given due to out of present syllabus.
Question 10:
(a) State two reasons for the concentration of the sugar industry in Uttar Pradesh. [2]
(b) Mention two ways in which the agro-based industries have affected the economy of India. [2]
(c) (i) Which is the largest jute producing State in India ? Name two centres of jute industry in that State.
(ii) Name two jute products. [3]
(d) State three main problems faced by the cotton textile industry in India. [3]
Answer:
(a) Two reasons for the concentration of sugar industry in Uttar Pradesh are :
(i) Availability of fertile alluvial soil which is rich in lime and potash for the growth of sugar cane.
(ii) It is densely populated and provides cheap labour and huge market.
(b) Agro based industries have affected the economy of India by:
(i) providing raw material for industries
(ii) They earn foreign exchange for the countries.
(c) (i) West Bengal is the largest jute producing state in India.
Two centres of jute industry are Kolkata and Rishra.
(ii) Jute products are gunny bags and carpets.
(d) Three problems faced by the cotton textile industry are:
(i) Shortage of raw material. India has still to face shortage of raw material and has to import it.
(ii) Obsolete Machinery
(iii) Competition in global market.
Question 11:
(a) Mention two reasons for the concentration of steel plants in the Chota-Nagpur Plateau region. [2]
(b) Name four petrochemical products. [2]
(c) What is the importance of the Heavy Engineering industry for the industrial development of India ? Name two Heavy Engineering industrial units in India. [3]
(d) (i) What are integrated steel plants ?
(ii) Name one integrated steel plant in the Public Sector. From where does this plant get its requirement of iron ore and coal ? [3]
Answer:
(a) Two reasons for the concentration of steel plants in the Chota Nagpur plateau region are : –
(i) Availability of iron ore and coal.
(ii) Cheap labour available from Bihar and Jharkhand.
(b) Four petrochemical products are :
(1) PVC pipes
(2) Polythene bags
(3) Synthetic fibre
(4) Plastic products.
(c) Heavy Engineering industry is important for industrial development of India because it not only provides machinery for industries but also equipments for transport, agriculture, mining, construction etc.
Two Heavy engineering industrial units :
(1) Ship building industries.
(2) Railway locomotive industries.
(d) (i) Integrated steel plants are the units in which all the processes from providing raw materials, to the conversion of steel rolling etc. are all done at one place.
(ii) Tata Iron and Steel Plant (TISCO). Its gets it iron ore from Mayurbhanj and coal from Jharia and Bokaro.
