ICSE Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2013 Solved for Class 10
ICSE Paper 2013 BIOLOGY
SECTION-I (40 Marks)
(Attempt all questions from this Section)
Question 1:
(a) Name the following :
(i) The cell body of a nerve cell.
(ii) The waxy layer on the epidermis of the leaf meant to reduce transpiration.
(iii) A non-biodegradable pesticide.
(iv) The physical expression of genes in an individual.
(v) Knot-like mass of blood capillaries inside the bowman’s capsule. [5]
(b) State the exact location of the following :
(i) Chloroplast
(ii) Incus
(iii) Corpus callosum
(iv) Guard cells
(v) Pulmonary semilunar value [5]
(c) Given below are six sets with four terms each. In each set a term is an odd one and cannot be grouped in the same category to which the other three belong. Identify the odd one in each set and name the category to which the remaining three belong. The first one has been done as an example :
Example : Fructose, Sucrose, Glucose, Calcium.
Odd term: Calcium Category: Carbohydrates
(i) Carbonic acid, Acetip acid, benzoic acid, boric acid.
(ii) Saliva, bile, sweat, tears.
(iii) Cretinism, Myxedema, Simple goitre, Acromegaly.
(iv) Sneezing, coughing, blinking,hyping.
(v) Semicircular canals, Cochlea, tympanum, utriculus. [5]
(d) Match the items in Column A with that which is most appropriate in Column B. Rewrite the matching pair. [5]
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Testis | (a) Kidney |
| (2) Poliomyelitis | (b) Water vapour |
| (3) Transpiration | (c) Prostate gland |
| (4) Clotting of blood | (d) Iron |
| (5) Uriniferous tubule | (e) Uterus |
| (f) Gonad | |
| (g) Salk’s vaccine | |
| (h) Water droplet | |
| (i) Calcium | |
| (j) TAB vaccine |
(e) Choose the correct answer from the four options given below :
(i) The cell component visible only during cell division :
(A) Mitochondria (B) Chloroplast (C) Chromosome (D) Chromatin
(ii) Pulse wave is mainly caused by the :
(A) Systole of atria (B) Diastole of atria (C) Systole of the left ventricle (D) Systole of the right ventricle
(iii) The recessive gene is one that expresses itself in :
(A) Heterozygous condition (B) Homozygous condition (C) F2 generation (D) Y-linked inheritance
(iv) A gland which secretes both hormone and enzyme is the :
(A) Pituitary (B) Pancreas (C) Thyroid (D) Adrenal
(v) The ventral root ganglion of the spinal cord contains cell bodies of the :
(A) Motor neuron (B) Sensory neuron (C) Intermediate neuron (D) Association neuron [5]
(f) Given below is an example of certain structures and their special functional activities:
For example : Eye and uision. On, a similar pattern complete the following :
(i) Neutrophils:
(ii) Ureter:
(iii) Neurotransmitters:
(iv) Iris of the eye :
(v) Placenta:
(g) The figure given below represents an experiment to demonstrate a particular aspect of photosynthesis. The alphabet ‘A’ represents a certain condition inside the flask. [5]
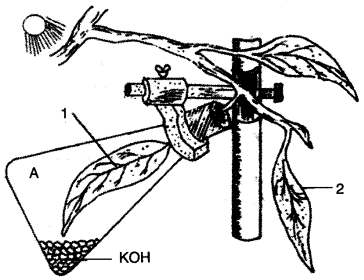 (i) What is the aim of the experiment ?
(i) What is the aim of the experiment ?
(ii) Identify the special condition inside the flask.
(iii) Name an alternative chemical that can be used instead of KOH.
(iv) In what manner do the leaves 1 and 2 differ at the end of the starch test ?
(h) Given below are five groups of terms. In each group arrange and rewrite the terms in the correct order so as to be in a logical sequence. [5]
For example : Implantation, Parturition, Ovulation, Gestation, Fertilization. Answer: Ovulation, Fertilization, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition.
(i) Spongy cells, Upper epidermis, Stoma, Palisade tissue, Substomatal space.
(ii) Spinal cord, Motor neuron, Receptor, Effector, Sensory neuron.
(iii) Endodermis, Cortex, Soil water, Xylem, Root hair.
(iv) Metaphase, Telophase, Prophase, Anaphase, Cytokinesis.
(v) Intestine, Liver, Intestinal artery, Hepatic Vein, Hepatic Portal Vein.
Answers:
(a) (i) Cyton
(ii) Cuticle
(iii) DDT
(iv) Phenotype
(v) Glomerulus
(b) (i) Choroplast: They are found in plant cells along the inner margin of cell, membrane and green parts.
(ii) Incus: Found in middle ear between malleus and stapes.
(iii) Corpus Callosum: Found between two lobes of cerebrum i.e., cerebral hemispheres.
(iv) Guard cells: They are important constituents of stomata and found connected to adjacent epidemal cells.
(v) Pulmonary semilumar valves: At the base of the pulmonary trunk these valves are found.
(c) (i)
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Food Preservatives | Boric acid |
| (ii) Lysozyme containing secretion | Bile |
| (iii) Disorders of thyroid gland | Acromegaly |
| (iv) Unconditioned reflexes | Typing |
| (v) Parts of inner ear | Tympanum |
(d)
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Testis | (f) Gonad |
| (ii) Poliomyelitis | (g) Salk’s Vaccine |
| (iii) Transpiration | (b) Water vapour |
| (iv) Clotting of blood | (i) Calcium |
| (v) Uriniferous tubule | (a) Kidney |
(e) (i) (C) Chromosome
(ii) (C) Systole of the left ventricle
(iii) (B) Homozygous condition
(iv) (B) Pancreas
(v) (D) Association neurons
(f) (i) Neutrophils: Phagocytosis
(ii) Ureter: Carries urine from Kidney to urinary bladder.
(iii) Neurotransmitters: Conduction of nerve impulse.
(iv) Iris of eye: Regulates amount of light entering the eye.
(v) Placenta: Connects foetus with mother.
(g) (i) The aim of the experiment is to show that C02 is necessary for photosynthesis.
(ii) The leaf inside the flask do not turn blue black when tested with iodine.
(iii) NaOH (Sodium hydroxide) can be used as an alternative.
(iv) ) Leaf 1 does not turned blue black while leaf 2 turned blue black at the end of starch test,
(h) (i) Upper epidermis, Palisade tissue, Spongy cells, Substomatal space, Stoma.
(ii) Receptor, Sensory neuron, spinal cord, Motor neuron, effector.
(iii) Soil water, Root hair, Cortex, Endodermis, Xylem.
(iv) Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis.
(v) Intestinal artery, Intestine, Hepatic Portal Vein, Liver, Hepatic Veins.
SECTION-II (40 Marks)
(Attempt any Four questions from this Section.)
Question 2:
(a) Given below is a diagram of the lateral section of a testis of a man. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
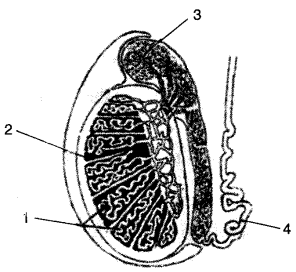 (i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 4 of the diagram.
(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 4 of the diagram.
(ii) State the functions of the parts labelled 1 and 3.
(iii) What is the significance of the testes being located in the scrotal sac outside the abdomen ?
(iv) What is the role played by-the inguinal canal ?
(v) What is semen ? [5]
(b) Give the biological I technical terms for the following :
(i) Chemical found in the blood which act against antigens.
(ii) A constituent that causes pollution.
(iii) The onset of menstruation in a young girl.
(iv) Structure which connects the placenta with the foetus.
(v) The fluid present between the layers of meninges.
(vi) Permanently open structures seen on the bark of an old woody stem.
(vii) The biological process which is the starting point of the food chain.
(viii) The change in an organism resulting due to stimulus.
(ix) An Antiseptic substance present in tears.
(x) A solution in which the relative concentration of water molecules and the
solute on either side of the cell membrane is the same. [5]
Answer:
(a) (i) (1) Seminiferous tubules.
(2) Testicular lobes
(3) Epidydymes
(4) Sperm duct/Vas deferens
(ii) Functions of Part 1 (Seminiferous tubules): The cells of seminiferous tubules keep on dividing and produce sperms by the process called spermatogenesis.
Function of Part 3 (Epidydymes):
(i) It helps in transportation of sperms from seminiferous tubules into vas deferens.
(ii) It also helps the sperm to attain maturity.
(iii) Testis are located in scrotal sac because it provides 2-3 °C less temperture than the body temperature, which is required for maturation of sperms.
(iv) Inguinal canals facilitates the movement of testis from abdominal cavity into scrotal sac or vice-versa.
(v) Semen is an alkaline combination of sperms and seminal fluid.
(b) (i) Immunoglobulins
(ii) Pollutant
(iii) Menarche
(iv) Umbillical cord
(v) Cerebrospinal fluid
(vi) Lenticles
(vii) Photosynthesis
(viii) Reflex action
(ix) Lysozyme
(x) Isotonic
Question 3:
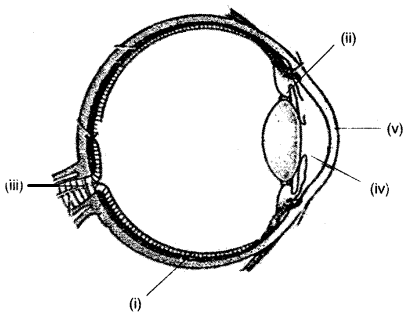
(a) Draw a diagram of the human eye as seen in a vertical section and label the parts which suits the following descriptions relating to the:
(i) photosensitive layer of the eye.
(ii) strucutre which is responsible for holding the eye lens in its position.
(iii) structure which maintains the shape of the eye ball and the area of no vision.
(iv) anterior chamber seen in front of the eye lens.
(v) outer most transparent layer seen in front of the eye ball. [5]
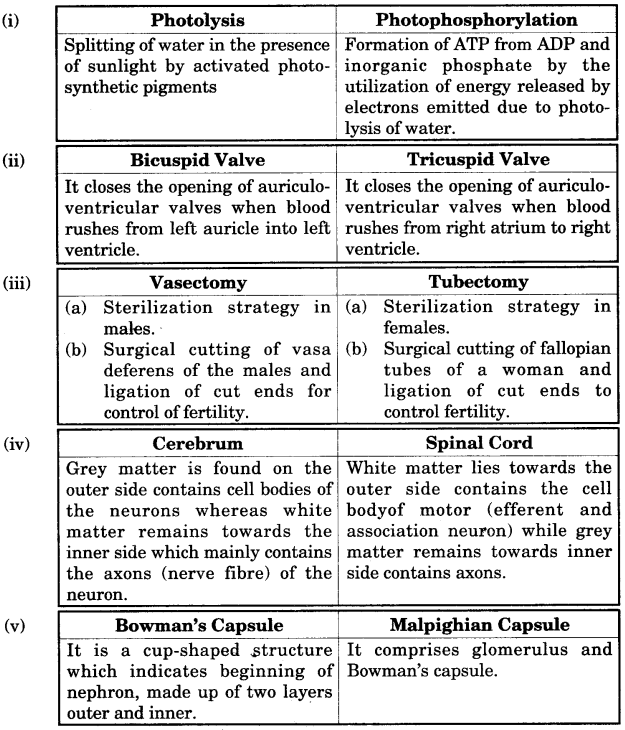
(b) Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of what is mentioned in brackets :
(i) Photolysis and Photophosphorylation. (Definition)
(ii) Bicuspid valve and Tricuspid valve. (Function).
(iii) Vasectomy and Tubectomy. (Explain)
(iv) Cerebrum and Spinal cord. (Arrangement of nerve cells)
(v) Bowman’s capsule and Malpighian capsule. (Parts included) [5]
Answer:
(a)
(b)
Question 4:
(a) Given below is a schematic diagram showing Mendel’s Experiment on sweet pea plants having axial flowers with round seeds (AARR) and Terminal flowers with wrinkled seeds (aarr). Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
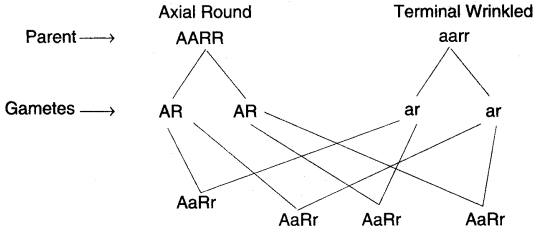 (i) Give the phenotype of F1 progeny.
(i) Give the phenotype of F1 progeny.
(ii) Give the phenotypes of F2 progeny produced upon by the self-pollination of progeny.
(iii) Give the phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny.
(iv) Name and explain the law induced by Mendel on the basis of the above observation. [5]
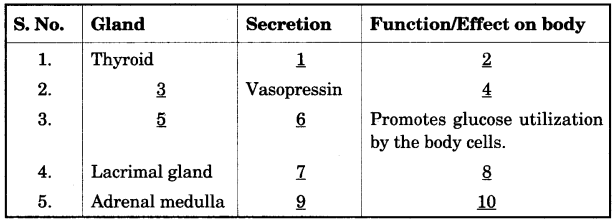
(b) Complete the following table by filling in the blanks from 1 to 10 with appropriate terms. [5]
 Answer:
Answer:
(a) (i) F1 progeny is Axial Round.
(ii) F2 progeny are Axial Round, Axial Wrinkled, Terminal Round and Terminal Wrinkled.
(iii) Phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
(iv) Above observation are based on Law of Independent Assortment. This law states that factors or genes controlling different characters assort independently without influencing each other during the formation of gametes.
(b)
Question 5:
(a) The diagram given below represents the human heart in one phase of its functional activities. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
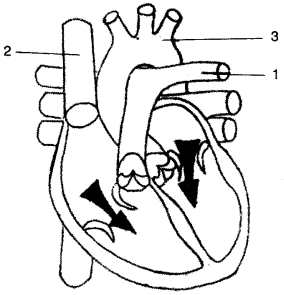 (i) Name the phase.
(i) Name the phase.
(ii) Label the parts 1, 2, and 3
(iii) Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase ? Give a reason to support your answer.
(iv) Draw well labelled diagrams of part 1 and 2 to show the structural differences between them. [5]
(b) Give biological reasons for the following :
(i) The wall of the ventricle is thicker than the auricles.
(ii) The renal cortex has a dotted appearance.
(iii) Wooden frames of doors get jammed during the monsoon season.
(iv) Throat infections can lead to ear infections.
(v) The hand automatically shows the direction to turn a cycle without thinking. [5]
Answer: (a) (i) Arial systole is the phase.
(ii) 1. Aorta, 2. Pulmonary Artery, 3. Superior Vena Cava
(iii) Upper chambers i.e., both the atria are contracting in this phase because blood is flowing downwards (towards the ventricles).
(iv)
(b) (i) The wall of the ventricles are thicker than the walls of atria due to different muscular development related to their different functions. Ventricles, particularly left venticle has to pump the blood into aorta under a high pressure, against force of gravity. As such they are adapted to withstand greater pressure.
(ii) Renal cortex has a dotted appearance as it is dark in colour and nephrons are highly coiled in this region.
(iii) Wooden frames of doors and windows get jammed due to process of imbibition. In this process, water is adsorbed or absorbed by surface attraction. Wood have a strong affinity for water (hydrophillic). Thus, they absorb or imbibe water or moisture from their surroundings and swell up.
(iv) The anterior wall of middle ear contains an opening that leads directly into Eustachian tube. This tube connects the middle ear to throat. Hence the passage for infection is common and it may lead to ear infection.
(v) It occurs due to conditioned reflexes. These reflexes are learned responses to stimuli acquired individually during the life of an organism.
Question 6:
(a) The figure given below shows the epidermal cells of an onion bulb. This cell was then transferred to a drop of sugar solution.
 (i) Draw a well labelled diagram of the epidermal cell as it would appear after immersion in a strong sugar solution.
(i) Draw a well labelled diagram of the epidermal cell as it would appear after immersion in a strong sugar solution.
(ii) What scientific term is used for the changes as shown in (i) above ?
(iii) What should be done to restore the cell back to its original condition ?
(iv) Give the scientific term for the recovery of the cell as a result of the step taken in (iii) above.
(v) Define the term osmosis. [5]
(b) Briefly explain the following terms :
(i) Genes.
(ii) Cytokinesis in plant cells.
(iii) Guttation.
(iv) Diabetes insipidus.
(v) Disinfectants. [5]
Answer:
(a) (i)
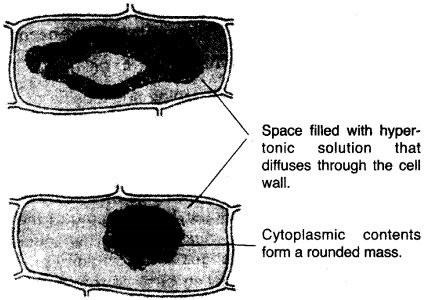
(ii) Plasmolysis is technical term used for the above change.
(iii) To restore the cell back to its original condition, it must be placed in hypotonic solution immediately after it gets plasmolysed.
(iv) Deplasmolysis is technical term used for recovery of the cell as a result of the step taken in (iii) above.
(v) Osmosis: It is the movement of water molecules from the region of its lower concentration to the region of higher concentration through semipermeable membrane.
(b) (i) Genes: Genes are units of heredity that determine particular traits (e.g., colour of hair, blood group, colour of eye etc.)
(ii) Cytokinesis in plant cells: Cells in multicellular plants do not have centrioles. The division of cytoplasm occurs by the formation of a new cell wall in the equatorial regien at the end of anaphase. In telophase, new cellulose particles are gradually deposited in the equatorial zone. The particles extend on either side, from the centre towards the periphery (centrifugal) until it completely divides the cell. These particles fuse together to form a delicate plate membrane.
(iii) Guttation: The loss of water in the form of water droplets along the margins of leaves through hydathodes.
It takes place due to increased hydrostatic pressure that builds up within the cells. The wall pressure that develops in fully turgid parenchymatous cells force the water out.
(iv) Diapedes insipidus: The condition occurs due to lesser secretion of vasopressin (Anti-diuretic hormone) from the posterior lobe of pituitary gland. The disease is characterized by excretion of large amounts of urine and subsequent dehydration and thirst. No sugar or albumin is present in the urine. A person with severe diabetes insipidus may die due to dehydration if deprived of water for few days.
(v) Disinfectants: These are powerful chemical substances used for destroy¬ing microbes in spots, places for sterilizing operation theatres and surgical instruments. They are not applied on the body due to their strong corrosive nature eg. Cresol, Phenol, Lysol, DDT etc.
Question 7:
(a) (i) Draw a well labelled diagram to show the anaphase stage of mitosis in a plant cell having four chromosomes.
(ii) State any two harmful effects of acid rain.
(iii) Expand the following biological abbreviations :
(1) NADP (2) ACT [5]
(b) (i) List any two major activities of the Red Cross.
(ii) Write any two major reasons for the population explosion in the world.
(iii) Write the names of four nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule. [5]
Answer:
(a) (i)

(ii) Harmful effects of acid rain: It has following effects :
(a) Acid rain corrodes buildings and metal structures.
(b) Acid rains also makes soil acidic which becomes unsuitable for cultivation. It also causes damage to plants.
(iii) (1) NADP: Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (2) ACT: Adrenocorticotropin.
(b) (i) Activities of Red Gross: These are as follows :
(a) It aims at providing social and medical care during war, and natural calamities such as famine^ drought, flood, earthquake etc.
(b) To arrange for ambulance during emergencies and lookafter maternal and child welfare centres.
(ii) Reasons for population explosion in the world: The reasons are as follows :
(a) Better health care at all age groups and fewer deaths due to better medical aids.
(b) Large scale immunization against communicable diseases.
(c) Balanced and improved nutrition specially for growing children.
(d) More children reach the reproductive age.
(iii) Nitrogenous bases of DNA molecules are: