ICSE Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2008 Solved for Class 10
ICSE Paper 2008 BIOLOGY
SECTION-I (40 Marks)
(Attempt all questions from this Section)
Question 1:
(a) Name the following:
(i) A membrane that disappears during late prophase.
(ii) A fluid that occupies the larger cavity of the eyeball behind the lens.
(iii) The ground substance present in a chloroplast.
(iv) A specific part of a chromosome that determines hereditary characteristics.
(v) A neurotransmitter stored at the terminal end of the axon. [5]
(b) The following paragraph is related to absorption of water from the soil.
Copy and complete the following paragraph by selecting the correct word from those given in the box. You may use the term only once.
Exosmosis, Hypertonic, Osmosis, Isotonic, Hypotonic, Cortical, Endosmosis
Water enters the root hair from the soil by the process of ……… .This is because the solution in the soil is ……… whereas the cell sap in the root hair cell is ……… . The water then passes through the cells by cell to cell ………. and reaches the xylem of the root. [5]
(c) Given below are sets of 5 terms each. Without changing the first term, rearrange the remaining four so as to be in logical sequence as per the directions given in brackets for each. One has been done for you as an example.
Example: Pathogen, active immunity, produces antibodies, lymphocytes, antigen, (defence mechanism of the body)
Answer : Pathogen —> antigen —> lymphocytes —> produces antibodies —> active immunity.
(i) Destarched plant, iodine added, washed in water, a leaf boiled in alcohol, placed in sunlight. (testing for presence of starch)
(ii) Interphase, Anaphase, Prophase, Telophase, Metaphase (sequential stages in Karyokinesis).
(iii) Seminiferous tubule, peris, urethra, epidodymis, vas deferens. (course of passage of sperms in man).
(iv) Pinna, cochlea, tympanum, ear ossicles, auditory canal (route through which vibrations of sound enter the ear).
(v) Soil water, xylem, cortex, enaodermis, root hair (coduction of water) [5]
(d) State whether the following statements are True or False. If False rewrite the correct form of the statement by only changing the last word of the statement.
(i) The alpha cells dfthe pancreas secrete insulin.
(ii) Duplicated chromosomes remain attached at a point termed centrosome.
(iii) The number of pairs ofautosomes in man is 22.
(iv) Penicillin obtained from si fungus is an example of an antibody.
(v) Plants that manufacture their own food are termed heterotrophs. [5]
(e) Given below is an example of a particular structure and its special functional activity, e.g., Glomerulous and ultra filtration.
On a similar pattern complete the following:
(i) Corpus luteum and ………. .
(ii) Iris of the eye and ………. .
(iii) Seminal vesicle and ………. .
(iv) Phloem and ………. .
(v) Eustachian tube and ………. . [5]
(f) Given alongside is an experimental set up to study a particular process:
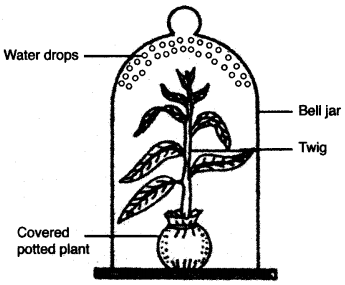 (i) Name the process being studied.
(i) Name the process being studied.
(ii) Explain the process named in (i) above.
(iii) Why is the pot covered with a plastic sheet ?
(iv) Mention one way in which this process is beneficial to the plant.
(v) Suggest a suitable control for this experiment. [5]
(g) Given below are incomplete explanations of certain biological processes I terms where a key word has been left out. Rewrite the completed explanation by inserting the key word in the space indicated by ‘^’.
(i) Birth rate is the number of ‘^’ birth per thousand of the population per year.
(ii) Photolysis is the splitting of water molecules into hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions in the presence of ‘^’ and light.
(iii) Vaccine is a preparation consisting of ‘^’ microbes which help to build immunity in the human body.
(iv) Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from its region of high concentration to its region of low concentration through a ‘^’ membrane.
(v) Antiseptics are chemical substances applied to the ‘^’ to destroy or prevent the growth and multiplication of harmful microbes. [5]
(h) Briefly explain the following terms :
(i) Destarched plant
(ii) Phenotype
(iii) Death rate
(iv) Power of accommodation of the eye.
(v) Natural immunity [5]
Answer:
(a) (i) Nuclear Membrane
(ii) Vitreous humour
(iii) Stroma.
(iv) Genes
(v) Acetylcholine
(b) Water enters the root hair from the soil by the process of Endosmosis. This is because the solution in the soil is hypotonic whereas the cell sap in the root hair cell is hypertonic. The water then passes through the cortical cells by cell to cell osmosis and reaches the xylem of the root.
(c) (i) Destarched plant —> washed in water —> a leaf boiled in alcohol —> placed in sunlight —> Iodine added.
(ii) Interphase —> Prophase —> Metaphase —> Anaphase —> Telophase.
(iii) Seminiferous tubule —> Epididymis —> Vas deferens —> Urethra —> Penis.
(iv) Pinna —> auditory canal tympanum —> ear ossicles —> cochlea.
(v) Soil water Root hair —> Cortex —> Endodermis Xylem.
(d) (i) The alpha cells of the pancreas secrete glucagon.
(ii) Duplicated chromosomes remain attached at a point termed centromere.
(iii) True.
(iv) Penicillin obtained from a fungus is an example of an antibiotic.
(v) Plants that manufacture their own food are termed autotrophs.
(e) (i) Corpus luteum and secretion of progesterone.
(ii) Iris of the eye and regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
(iii) Seminal vesicle and semen.
(iv) Phloem and photosynthesis.
(v) Eustachian tube and balancing the air pressure on either side of the eardrum.
(f) (i) Transpiration.
(ii) ‘Loss of water as water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is called as transpiration’.
(iii) Covering the pot with a plastic sheet would prevent the escape of water vapour from the pot.
(iv) Transpiration helps in the ascent of sap by producing a suction force acting from the top of a plant.
(v) A similar empty plastic sheet with its mouth tied, with no potted plant kept in sunlight will show no drops of water.
(g) (i) Birth rate is the number of ‘live’ per thousand of the population per year.
(ii) Photolysis is the splitting of water molecules into hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions in the presence of‘chlorophyll and light.
(iii) Vaccine is a preparation consisting of ‘killed or weakened’ microbes which help to build immunity in the human body.
(iv) Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from its region of higher concentration to its region of low concentration through a ‘semipermeable membrane’.
(v) Antiseptics are chemical substances applied to the ‘body’ to destroy or prevent the growth and multiplication of harmful microbes.
(h) (i) Destarched Plant: A plant from the leaves of which starch has been removed. This can be done by placing the plant in the dark for 24 to 48 hours.
(ii) Phenotype: The expressed character whieh Is genetically controlled.
Example : Tall pea plants (genotype TT or Tt), dwarf pea plant (genotype tt). So this expressed tallness or dwarfness is called as phenotype.
(iii) Death Rate: This is also called as mortality It is the number of death per 1000 of population per year.
(iv) Power of Accommodation of the eye: The process of focussing the eye at different distances is called as power of accommodation of the eye.
(v) Natural Immunity: This is also called as native or innate immunity. This immunity is by virtue of genetic constitutional make up Tt is there in the body without any external stimulation of a previous infection.
SECTION—II (40 Marks)
(Attempt any four questions from this Section)
Question 2:
(a) Given below is a diagrammatic representation of the internal structure of an organelle found in a plant cell Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
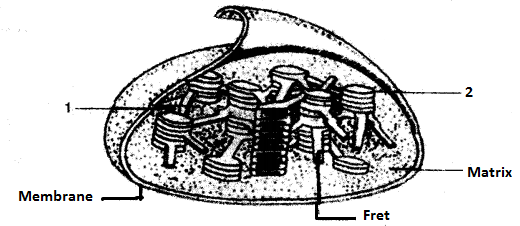 (i) Identify the organelle.
(i) Identify the organelle.
(ii) Name the physiological process occurring in this organelle.
(iii) Mention one way in which, this process is beneficial to man.
(iv) Name the phases of the process occurring in the part labelled 1 and 2.
(v) A chemical substance ‘NADP’ play s an active part in one of the phases. Give the expanded form of NADP and state its role in the above process.
(vi) Represent the physiological process mentioned in (ii) above in the form of a chemical question. [5]
(b) Give the technical / biological term for the following:
(i) Onset of menstruation in a young girl around the age of 13 years.
(ii) Eye defect occurring in old people whereby they are unable to see near objects.
(iii) The mucous membrane lining the uterus
(iv) The process of conversion of ADP to ATP during the first phase of photosynthesis.
(v) The point of contact between two neurons.
(vi) Protective membranes covering the human brain and spinal cord.
(vii) Respiratory openings found OP the stem of woody plants.
(viii) The process by which white blood cells engulf harmful microbes.
(ix) The process of mixing of two different substances molecules.
(x) Exudation of sap firm injured parts of a plant. [5]
Answer:
(a) (i) Chloroplast.
(ii) Photosynthesis.
(iii) It is a process supporting all life on earth. All animals including man, ultimately depend on plants for food as every food chains have just one starting point, i.e., plants the producers.
(iv) The process occurring in the part labelled ‘1’ is ‘dark reaction or biosynthetic reaction or Calvin cycle’.
The process occurring in the part labelled ‘2’ is ‘Light Reaction or Photochemical reaction or Hill reaction’.
tv) The expanded form of NADP is Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleocide phosphate.
NADP is reduced to NADPH by accepting one electron. Now this NADPH in the dark reaction transfers its hydrogen through a series of chemical reactions to combine with CO2 to produce C6H12O6 by using energy from ATP.
(vi)
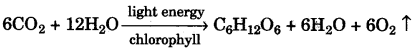
(b) (i) Onset of menstruation in a young girl around the age of 13 years ‘Menarche’.
(ii) Eye defect occurring in old people whereby they are unable to see near objects Presbyopia.
(iii) The mucous membrane lining the uterus Endometrium
(iv) The process of conversion of ADP to ATP during the first, phase of photosynthesis Photophosphorylation.
(v) The point of contact between two neurons ‘Synapse’.
(vi) Protective membranes covering the human brain and spinal cord ‘Meninges’.
(vii) Respiratory openings found on the stem of woody plants ‘Lenticels’.
(viii) Harmful microbes ‘Phagocytosis’.
(ix) The process of mixing of two different substances/molecules ‘Diffusion’.
(x) Exudation of sap from injured part of a plant ‘Bleeding’.
Question 3:
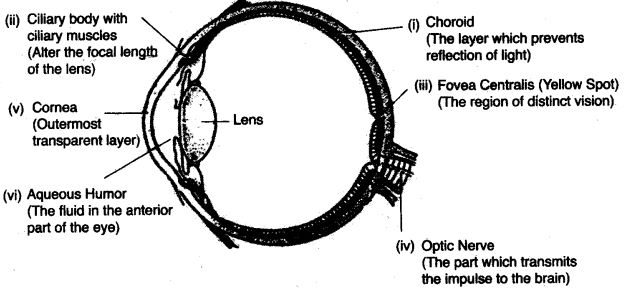
(a) Draw a diagram of the human eye as seen in a vertical sect ion a nd label the part which suits the following functions/descriptions :
(i) The layer which prevents reflection of light.
(ii) The structure that alters the focal length of the lens.
(iii) The region of distinct vision.
(iv) The part which transmits the impulse to the brain.
(v) The outermost transparent layer in front of the eye lens.
(vi) The fluid present in the aiitermf part of the eye in front of the eye lens. [5]
(b) Complete the following table by filling in the blanks 1 to 10 which the appropriate terms: [5]
Answer:
(a)
(b)
Question 4:
(a) Given below are diagrams shqwing different stages in the process of fertilization of an egg in the female reproductive tract:
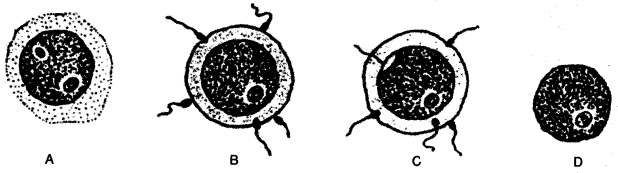 (i) Use the alphabets given below each diagram to show the correct order in the process of fertilization.
(i) Use the alphabets given below each diagram to show the correct order in the process of fertilization.
(ii) Where in the female reproductive system does this process normally take place ?
(iii) What is the biological term for the product of fusion ?
(iv) What is the chromosome number of (1) the egg (2) the fused product ?
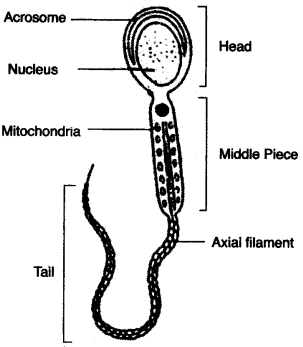
(v) Draw a neat labelled diagram of a mature human sperm. [5]
(b) Differentiate between the following on the basis of what is given in brackets :
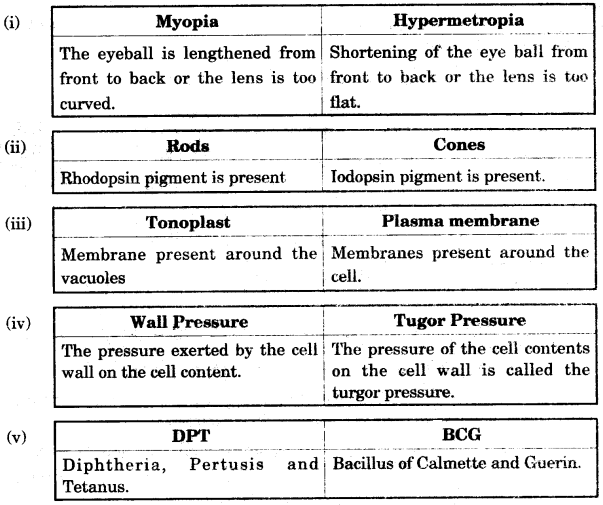
(i) Myopia and Hypermetropia (Condition of eyeball)
(ii) Rods and Cones (Pigment Present)
(iii) Tonoplast and Plasma membrane (Location)
(iv) Wall pressure and Turgor pressure (Explain briefly)
(v) DPT and BCG (Expanded form of the vaccine). [5]
Answer:
(a) (i) Correct order in the process of fertilization is D —> B —> C —> A.
(ii) In human fertilization takes place in fallopian tube.
(iii) The biological term for the product of fusion is ‘Zygote’.
(iv) The chromosome number of the egg is n and the chromosome number of the fused product is 2n.
(v)
(b)
Question 5:
(a) The diagram given below depicts the cross section of the spinal cord Study the same and then answer the Questions that follow:
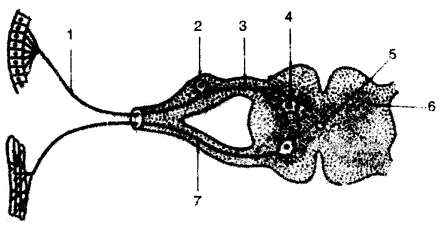 (i) Name the process that is being depicted.
(i) Name the process that is being depicted.
(ii) Name the parts labelled 2, 5, and 6.
(iii) Name the cells in contact with the part labelled ‘1’.
(iv) What is the function of the parts labelled 3, 4 and 7 ? What is the technical term given to the pathway represented by 3, 4, and 7 ?
(v) How does the arrangement of cells in the spinal cord differ from that in the brain ? [5]
(b) (i) Mention any three functions of the Red Cross.
(ii) Name any two microbes that cause diseases in man. In each case give an example of a disease caused by them.
(iii) Mention three reasons why the growth of population has not been appreciably checked in India. [5]
Answer: (a) (i ) The process’depicted by this diagram is ‘Reflex Action’.
(ii) Part 2 — Dorsal Root Ganglion
Part 5 — Central Canal.
Part 6 — Gray Matter.
(iii) The cells in contact with the part labelled ‘1’ is Receptor cells.
(iv) Functions of the parts labelled 3, 4 and 7 are as follows :
Part 3 — Afferent (Sensory) nerve fibre carry the stimulus from receptor organ to the spinal cord.
Part 4 — (Synapse) point between sensory and motor neuron. It is a place where incoming sensory impulse generates an outgoing motor impulse.
Part 7 — ( Effect neuron) : It carries away the impulse generated by the association neuron in the centre to the effector organ (muscle or gland).
Technical term given to the pathway represented by 3, 4 and 7 is ‘Reflex Arc’.
(v) In spinal cord, the gray matter lies on the inner side and the white matter lies on the outer side This arrangement is just reversed in the brain.
(b) (i) Three Functions of Red Cross:
(1) To extend relief and help to the victims of any calamity such as flood, fire, famine and earthquake etc.
(2) To produce and supply blood for the needy victims of war or other calamities.
(3) To extend all possible first aid in any accident.
(ii) Two microbes and diseases caused by them :
(1) Plasmodium — Malaria.
(2) HIV Virus —AIDS.
(iii) Illiteracy, Traditional beliefs, Mortality rate, religious and social culture and desire for a male child are some of the reasons, why the growth of population has not been appreciably checked in India.
Question 6:
(a) Given alongside are diagrams of plant cells as seen under the microscope after having been placed in two different solutions:
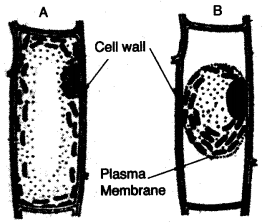 (i) What is the technical term for the condition of:
(i) What is the technical term for the condition of:
1. Cell A
2. Cell B?
(ii) From the solutions given in brackets (water, strong sugar solution, 1% salt solution) name the solution into which :
1. Cell A
2. Cell B was placed before being viewed under the microscope.
(iii) Under what conditions in the soil will the root hair cell resemble :
1. Cell A
2. CellB ?
(iv) Name the pressure responsible for the movement of water from the root hair cell to the xylem of the root. How is it set up ?
(v) Name the pressure that helps in the movement of water up the xylem of the root. [5]
(b) (i) Explain the following terms :
1. Mutation 2. Homologous chromosomes 3. Alleles
(ii) Give the dihybrid ratio. Narhe and state the law which explains the same.
(iii) Mention three main reasons for the sharp rise in ‘Human population’ in the world. [5]
Answer:
(a) (i) The technical term for the condition of cell A is Turgid cell and for the condition of cell B is plasmolysed cell or flaccid cell.
(ii) Cell A was placed in water solution where as cell B was placed in strong sugar solution before being viewed under the microscope.
(iii) The root hair cell will resemble with cell A in the condition when the field is over flooded. The root hair cell will resemble with cell B in the case of excessive application of fertilizers in the fields.
(iv) Root Pressure is responsible for the movement of water from the root hair cell to the xylem of the root. Root pressure is built up due to cell to cell osmosis in the root tissues. As one turgid cell presses the next cell, the force of the flow of water increases inward. When the water reaches the xylem vessels, it enters the pores of their thick walls with considerable force.
(v) Cell to cell difference of osmotic pressure helps and turgor pressure in the movement of water up the xylem of the root.
(b) (i) (1) Mutation: Sudden changes in one or more genes in the progeny, which normally may not have existed in the parents, grand parents or even great grand parents.
Example: Albinism (total loss of skin pigment).
(2) Homologous Chromosomes: A pair of corresponding chromosomes of the same Size and shape, one from each parents.
(3) Alleles: Allele is the alternative form of a gene occupying the same position on a chromosome and affecting the same characteristic but in two alternative ways.
Example : The free and attached ear lobe alleles of the ear lobe character.
(ii) Dihybrid Ratio: The dihybrid ratio is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
Mendel’s 3rd law i.e., ‘Law of Independent Assortment’ explains the dihybrid ratio. This law states that when there are two pairs of contrasting characters, the distribution of the members of one pair into the gametes is independent of the distribution of the other pair.
(iii) The three main reasons for the sharp rise in human population in the world are as follows:
(1) Better health care: There are more health care centres, hospitals and practicing doctors available for help to all age groups.
(2) Food shortages minimized: Due to green revolution, more food is produced and stored. There are very few starvation deaths.
(3) Large scale immunization: There has been large scale immunization against fatal diseases, to protect the infants from death.
Question 7:
(a) (i) Draw a diagram of the nucleds of a cell, having chromosome number 6, as it would appear in the Metaphase stage of Mitosis and label the following parts in the diagram:
1. Aster
2. Achromatic spindle
3. Chromatid
4. Centromere.
(ii) Mention the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis with reference to :
1. No. of daughter cells formed at the end of the division.
2. The chromosome number of the daughter cells formed. [5]
(b) Account for the following briefly:
(i) The pituitary gland is known as the ‘Master gland’.
(ii) Animals owe their existence to Chlorophyll.
(iii) Twins may or may not be identical.
(iv) Herbaceous plants growing in well watered soils are found to wilt on a hot day.
(v) Throat infections can lead to ear infections. [5]
Answer:
(a) (i)
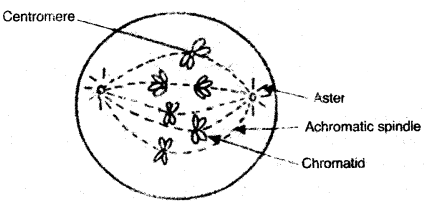
(ii)

(b) (i) Pituitary gland is popularly known as ‘Master gland’ as it seems to control all other endocrine gland.
(ii) Animals owe their existence to chlorophyll as animals are hetrotrophs. Animals derive their food from plant and plants can prepare their food with the help of chlorophyll by the process of photosynthesis.
(iii) Twins may not be identical as in the case of fraternal twins which are produced from two eggs. In this two eggs are released from ovaries at a time and both may get fertilized to produce two individuals.
(iv) Herbaceous plants growing in well watered soils are found to wilt on a hot day. It is due to the fact that in such cases the rate of transpiration during day time exceeds the rate’of-absorption of water by the roots. The cells therefore lose turgidity. In the evening or during night, the stomata are constricted and the temperature is not high; therefore there is no loss of water through transpiration and the turgidity of the leaves is re-acquired and they stand out erect.
(v) Throat infection can lead to ear infection as both throat and ear are connected with each other by Eustachian tube.
