ICSE Physical Education Previous Year Question Paper 2017 Solved for Class 10
General Instruction:
- Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
- You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
- This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
- The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
- Note. Attempt all questions from Section A and two questions from Section B.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
Section – A [50 Marks]
(Attempt all questions from this Section)
Question 1.
(a) What do you mean by a balanced diet ? (2)
(b) What is Coronary Thrombosis ? (2)
(c) Mention any three causes of Insomnia. (3)
(d) List any three harmful effects of tobacco consumption. (3)
Answers:
(a) Balanced Diet: Balanced diet is that diet which contains all the important nutrients (macro and micro) in correct proportion for efficient working of the body. In other words, it is intake of appropriate type and adequate amount of food to supply energy and to support growth and development of an individual. Balanced diet contains all nutrients (macro and micro) in sufficient quantity and it fulfils the needs of body. Components of balanced diet are
(a) Energy Yielding Food
(b) Body Building Food
(c) Defensive Food
(b) It is the most common Coronary Artery Disease and named as Heart Attack. Heart attack is actually a defect in which there is reduction in functional ability of the heart. Heart attack does not mean heart has been hit. It is actually failure of heart to continue activity. It is one of the most serious health problems as this is the cause of 30% of mortality rate in adults. This is mostly common with those who have sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits.
(c) Insomnia: Insomnia, the inability to get to sleep or sleep well at night. It’s the most common sleep complaint.
- Emotional excitement or anxiety.
- Insufficient exercise, sedentary life.
- Studying late at night, high noise or sound, bright light.
- Inability to relax mind from stresses of life, worry or depression. .
- Constipation and poor dietary habits, excess coffee or tea.
(d) 1. Tobacco as Poison : Nicotine is a brain poison found in tobacco. It is one of the most deadly poisons known to man. Half a drop of pure nicotine can be lethal to kill a person. There is no antidote for this poison. .
2. Wrong Habit: Usually people start this habit to relieve tension (wrong concept). A small amount of nicotine with the first puff subdues tension. Soon after, it again stimulates the person for another puff. Thus, a smoker is caught in its vicious circle and becomes a slave to this habit.
3. Causes of Lung and Jaw Cancer: Intake of tobacco brings ‘tar’ (carbon compound) along with the smoke. This tar has a strong sticking effect, thus it gets attached to the lining of trachea and lungs, causing great risk of lung cancer. Chewing of tobacco also has similar carcinogenic effect and causes jaw cancer.
4. Increases Blood Pressure: Medical researches reveal that a single puff of cigarette can contract the smallest capillary. It increases the heart rate up to 20 beats per minute, thus extra pressure is exerted over heart and blood vessels. Therefore, the chances of heart problem increase.
5. Decrease in Body Temperature: When nicotine enters the body, it reduces the blood flow. This reduces the skin temperature by 3 to 4 degree.
Question 2.
(a) What do you mean by obesity? (2)
(b) List any four preventive measures against communicable diseases. (2)
(c) How should we provide first aid to a drowning victim? (3)
(d) List any three preventive steps to treat Arthritis. (3)
Answers:
(a) Obesity means excessive accumulation of fats in the body and tendency of an individual to become fatty due to this. It is a health problem in which the body gains lot of weight, i.e., overweight of body (abnormal). In this problem, the non-consumed (extra) fats of the body get deposited under the skin. This deposition of fats takes place especially in areas like the abdomen, chest, shoulder, buttocks and legs. Sometimes the excess of fats can also be noticed on neck, chin and cheeks. The obesity level can be calculated by the formula of “Body Mass Index” (BMI).
(b) Prevention of spread of communicable diseases is called prophylaxis. Preventive measures are:
- Health education.
- Isolation of patients from healthy persons.
- Proper sanitation and proper disposal of excreta.
- Eradication of vectors (flies, mosquitoes, etc.)
- Sterilization of articles used by the patients.
(c) When a person is drowned in the water, his lungs and stomach are filled with water. In such state, the victim may die in 5 minutes. In such condition :
- Pull the victim out from water and make him to lie down with face down, i.e., pro-line position.
- Loosen his clothes. Press his chest firmly from the back so that water in mouth, lungs and stomach should come out.
- Slightly raise the legs higher at inclined position and repeat it till water is removed from chest.
- Artificial Respiration (AR) should be continued if the victim does not start breathing, (v) The victim should be kept at rest for half horn till victim gets up himself. Then make him to vomit out the water by self.
- Regular yogic asana cure it permanently.
Question 3.
(a) What is congenital disease? (2)
(b) What is meant by Drug Abuse ? (2)
(c) Give any three preventive steps to avoid a heart attack. (3)
(d) What three preventive measures would you take to check the spread of Bronchitis? (3)
Answers:
(a) These are also known as hereditary diseases. These diseases are present right from the birth. They are caused either due to genetic disorder or environmental factors during development, e.g. hemophilia, colour-blindness, sickle-cell anemia, albinism, etc. They are passed on from generation to generation.
(b) Non-prescribed drugs are known as Drug Abuse. These drugs are not recommended by physician or doctor. They are not taken for curing certain disease. They are self-taken for their addictive effect. Person takes these drugs as a habit under the influence of bad company; to remove tensions, loneliness, etc. But once a person starts taking drugs, he or she cannot stop using it, thus becoming slave to drugs.
(c) Preventive and treatment steps:
1. Immediate Treatment: Recently new medicines and researches have been made for the treatment of heart attack such as Clot Buster, Streptokinase and Urokinase, etc. These medicines dissolve the abnormal clot within coronary arteries/veins. Aspirin is also helpful.
2. Permanent Treatment: Regular exercises with low to medium intensity pace for half to one hour. Slow jogging or brisk walk is also other alternative. Practicing yogic asana and pranayama is also very helpful for heart victims. Diet is important part for heart patients. It should be low in fats with lot of fibrous food.
(d) Preventive and treatment steps:
- Inhalation of moist steam is the best treatment.
- Penicillin or some other antibiotic medicine.
- Taking cough syrup/drops or medicine to relieve cough.
- Hot pack over chest or hot water gargles also relieve cough.
- If cough continues for long duration then consult a doctor.
Question 4.
(a) What is a Thomas splint ? (2)
(b) Why should we avoid heavy meal at night? (2)
(c) Mention any three symptoms of bone injury. (3)
(d) Give any three preventive measures of poisoning. (3)
Answers:
(a) Thomas splint is an easy way to provide the support to injured elbow. In this, a cloth piece is rotated around the neck up to elbow so that it gives support to injured elbow, moreover it prevents further movement and does not damage the injured elbow further.
(b) During night our physical activity is less, thus less energy is required. The energy from heavy meal during night is useless and it gets deposited in form of adipose tissues i.e., it increases the fat percentage in the body.
(c) Symptoms of bone injury:
- Severe pain around fracture or around the joint / bone.
- The joint / bone will look deformed and swelling around the affected part.
- The joint / bone will appear fixed with no movement being possible.
- Local temperature rises.
- Fracture part is deformed.
(d) Prevention from poisoning:
- Keeping medicines, disinfectants, household cleaners, etc., out of the reach of children.
- Bottles containing harmful substances and poison should be labelled with red pen and block letters.
- While purchasing and consuming medicines, the expiry date should be checked.
- Drugs should be poured from the opposite side of label to prevent the destruction of label.
- Harmful and dangerous drugs should be kept under lock and key.
Question 5.
(a) Mention any four preventive steps to minimize sports accidents. (2)
(b) What do you mean by the term dislocation? (2)
(c) What three points should be kept in mind in order to take care of our eyes ? (3)
(d) Name the causal agents for the following diseases : (3)
(i) Rabies
(ii) Pneumonia
(iii) Ring worm
Answers:
(a) 1. Proper Warming-up : Proper warming-tip (general and specific) is a must for player
before participating in any physical activity. It tones-up body muscles and prepares the player psychologically for the coming activity. Thus, it prevents them from accidents or injuries. .
2. Medical Check before Activity: Player should be properly medically checked up before physical activity related to previous injury disease, physical fitness level, etc. They must be fit to participate in the activity.
3. Proper Concentration: Player should play with full alertness and proper concentration over the activity. Player should not have any stress or tension; moreover, must be mentally ready for the activity.
4. Safety Guards and Check Equipments: Player should check his equipments and their condition. Player should use good quality equipments along with safety guards. Player should wear proper dress or kit along with proper shoes (according to surface as per activity needs).
5. Regular Conditioning and Proper Skill: Regular conditioning improves various abilities of player like proper skill action, develops specific physical components, strengthens weak muscles and joints, etc.
(b) Dislocation : It is an injury of joint in which the adjoining bones are displaced from their original position. It may be associated with sprain or fracture. Dislocation is mainly caused due to direct or indirect impact over the joint. It may be simple dislocation, fractured dislocation or complicated dislocation.
(c) Eyes being a delicate sense organ, special care should be given to the eyes. Following precautionary measures can keep eyes in proper condition:
- People, especially children, should get their eyes regularly checked up. Immediate treatment should be taken if any ailment is discovered.
- During reading, the page of a book should be at least at a distance of 1 ‘A feet at an angle of 45° to 70°. The horizontal light should be provided sufficiently but not immediately in front of eyes. Look away from the computer screen.
- Eyes should be protected from dust, smoke, bright light, etc., by using good quality goggles or sunglasses.
- Precautions should be taken while handling sharp articles like blade, knife, etc. Use safety eyewear.
- Entry of any foreign body in the eye or any injury made to the eye should be taken seriously. The patient should be taken to the eye specialist immediately.
(d) The main causes of:
(i) Rabies : Rabies virus is a neurotropic virus. This disease is caused by the Rabicilus virus (found in wild carnivorous animals like wolf, jackals, etc.). Sometimes it is also caused by diseased dog bite. It is not a communicable disease but still a very dangerous disease.
(ii) Pneumonia : It is caused by various types of germs such as Diplococcus pneumonia, Staphylococcus, Pneumococcal which enter into lungs and affect its fimctioning. It is caused due to exposure to cold or dry places or by the infected sputum of the patient
(iii) Ring worm : It is a contagious disease of skin, hair and nails. On infection, ring-like discoloured patches appear on the skin which is covered by scales and vesicles. It is transmitted by contact with the infected persons or using the articles used by the patients. It can be prevented by personal cleanliness and avoiding the use of articles and clothes used by the patient.
Section – B [50 Marks]
(Attempt two questions from this Section)
You must attempt one question on each of the two games of your choice.
CRICKET
Question 6.
(a) Explain the following: (8)
(i)A dot ball
(ii) A runner
(iii) An appeal
(iv) A wide ball
(b) (i) Mention any three instances when umpire calls for a No ball. (9)
(ii) When is a batsman considered to be out stumped ?
(iii) List three different types of strokes played by the batsman in front of the wicket?
(c) Explain the following terms: (8)
(i) Clean bowled
(ii) Hit wicket
(iii) Handling the ball
(iv) Runout
Answers:
(a) (i) Dot Ball: A good length ball (bowled by bowler) on which batsman cannot score runs.
(ii) Runner : A supplement player to the batsman who runs for the batsman, in case of injury, illness while playing.
(iii) Appeal: It is a request or shouts by fielding players in anticipation of batsman to be given out by the umpire.
(iv) Wide Ball: When the bowler bowls the ball out of the batsman’s reach, towards the . sideward of wickets.
(b) (i) No Ball: When the bowler commits some non-legal action to bowl.
1. When bowler crosses the popping/ bowling crease during bowling.
2. When ball is released from side and not over the head by bowler.
3. When the bowler’s back foot is touching or outside the return crease.
4. A full toss – a ball which does not bounce – from a seam bowler reaches the batsman at waist height.
5. If the bowler changes the arm with which he bowls without notifying the umpire.
(ii) Stump out: If a batsman misses the ball and the wicketkeeper breaks the wicket when he
outside the crease.
(iii) Sweep : In this, the batsman hits the ball to deep angle while kneeling down.
Lofted Hit : A hit by the batsman, on which ball is lifted up in air.
Drive : It is hitting the ball in front field.
Hook-Shot : It is hitting the high raised ball with force towards the leg side.
Pull-Shot : It is hitting the ball forcefully with good back lift and follow-through action of bat goes towards the on side of field.
(c) (i) If the ball partially or completely destroys the wicket even if it touches the bat.
(ii) A bowler gets three wickets in three successive balls, i.e., the bowler dismisses three batsmen on three consecutive balls.
(iii) If the batsman touches the ball with his hand.
(iv) If the batsman runs towards wicket but does not get therein time to place his bat between the edge of the popping crease and an opponent breaks the wicket then the batsman is run out.
Question 7.
(a) Explain the following:
(i) Bodyline bowling
(ii) Declaration
(iii) Power play
(iv) Straight drive
(b) (i) What is meant by obstructing the field ?
(ii) What is meant by the term LBW?
(iii) Write any three duties of the umpire.
(c) (i) Write down any four ‘off side’ fielding positions in cricket.
(ii) What are the signals for the following :
1. Short run
2. Power play
3. Bye
4. Free hit
Answers:
(a) (i) Bodyline bowling: A type of negative bowling in which the ball is aimed at hitting the body of the batsman.
(ii ) Declaration : A process in which the captain of the batting side may call the batsman off the field irrespective of the scores and discontinue their innings.
(iii) Power Play: A Power play is the name for the fielding restrictions in limited-over’s and Twenty-20 cricket. Mandatory Power play (1-10 over’s); the first 10 over’s of an innings will be a mandatoiy power play (i.e. in One Day format). During the mandatory.
Power-play, only two fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle. Between over’s 11- and 40, a maximum of four fielders are allowed outside the 30-yard circle. In the final 10 over’s (41-50), a maximum of five fielders will be allowed to field outside the 30-yard circle. It is mounting pressure over batsman by placing close fielding positions (9 players .inside the 30 yard circle). It can be in three stages on request by captain.
(iv) Straight Drive: An over pitched ball is hit straight with full control of bat.
(b) (i) A batsman can be given out for obstructing the field if he willfully attempts to obstruct or distract the fielding side by word or action. The following three circumstances where this applies, but the law is not limited to these circumstances.
(ii) When the batsman’s leg or any part of his body prevents the ball from touching the wicket is given out for Leg-Before-Wicket(LBW).
(iii) They are the officials in ground responsible for administrating and imposing the rules and regulations of the game.
Duties of Umpires:
- Umpire signals and declares the batsmen out
- Short-run
- End of over
- Boundary; beginning
- End of power play ; no ball ; wide ball ; leg bye, bye ;time-out, time-over; obstruction; break.
(c) 1. Slips 2. Cover 3. Long off 4. Point 5. Mid off
- It is signaled by Leg Umpire by folding the arm sideward.
- The power play is signaled by moving the arm in a clockwise fashion from the ground to above your head.
- Umpire signals this by raising one arm to sideward.
- The umpires will signal a free hit by (after the normal No Ball signal) extending one arm straight upwards and moving it in a circular motion.
Football
Question 8.
(a) (i) What is a penalty arc and why is it important? (8)
(ii)What do you mean by the term indirect free-kick ?
(iii)Write down the procedure to restart the game when the ball passes over the touch line.
(iv) Write down the procedure to restart the game when the ball is last touched by the defending player and passes over the goal line.
(b)(i) State any three instances when the opposite team is awarded an indirect free kick for an offence committed by the goal keeper. (9)
(ii) Name the tool kit carried by the referee to conduct a football match.
(iii) State any three fouls when the referee shows a yellow card to a player during the game.
(c) (i)Explain in detail the procedure followed during Tie-breaker in the game of Football. (8)
(ii) State the following:
- Duration of the football match (men and women)
- Substitution allowed in a match.
- Officials for conducting a football match.
- Duration of extra time
Answers:
(a) (i) Penalty arc marked from 10 yards away from Penalty Point. It touches rectangular area of penalty area. It restrains the players to enter this area during Penalty Kick.
(ii) Indirect Free-Kick: An indirect free-kick is awarded to the opponent if a goalkeeper commits any of the following offences inside his own penalty area: takes more than four steps while controlling the ball with his hands, before releasing it from his possession; touches the ball again with his hands after it has been released from his possession without touching another player; touches the ball with his hand after it has been deliberately kicked to him by a teammate; touches the ball with his hand after he has received it directly from a throw-in by a teammate.
(iii) Goal-Kick: When ball passes over the goal line without goal scoring by the attacking player, then ball is kicked by placing from the penalty area.
(iv) Corner-Kick: It is also known as flag kick. Comer-kick is awarded when a defender puts the ball out of the play behind his team’s goal line. An attacking player then tries to send the ball in front of the goal for another attacker to head or make a short pass to a teammate to convert it into goal. It is taken from comer-arc or quarter-yard circle.
(b) (i) If a goalkeeper commits any of the following offences inside his own penalty area :
- Takes more than four steps while controlling the ball with his hands, before releasing it from his possession;
- Touches the ball again with his hands after it has been released from his possession without touching another player.
- Touches the ball with his hand after it has been deliberately kicked to him by a teammate;
- Touches the ball with his hand after he has received it directly from a throw-in by a teammate.
(ii) It includes Cap, Whistles, Penalty/Foul Cards (Red, Yellow), Pocket Diary, Stop Watch/ Timer Watch, Flags, Bags, Coin, Down Indicators, Rule book etc.
(iii) Warning (Yellow Card):
- The players receive a warning if they regularly break the rules,
- Do not respect the Referee’s decision,
- Delay the start of play, are argumentative or show un-sportsman conduct,
- Goalkeeper keeps the possession of the ball for more than six seconds,.
(c) (i) Tie-Breaker Rule:
1. Extra Time: During a knockout tournament, if there is a tie at the end of regulation time, then the teams play for 30 minutes extra time of two halves of 15 minutes each. In this duration, if any team scores the goal, wins the match. Earlier there was golden goal period in which the team who scored the goal first won the game but now it is said as silver goal period.
2. Penalty Shoot-outs: If there is still a tie after the overtime period, a penalty shootout takes place. The referee decides which goal will be used for the penalty kicks; the team to kick first is determined by a toss. Each team chooses 5 players to take the kicks in turn. The team that has the most goals after 5 kicks wins the game.
3. Sudden-Death: If the teams are still tied after 5 kicks each, the teams keep taking penalty kicks until one team wins. The goal is scored when ball crosses the goal line (may be on surface or in air).
(ii) 1. Duration of Match is 2 halves of 45 minutes for Men and 40 minutes for Women.
2. Substitution: A maximum of three substitutes may be used in any match played in an official competition organized under the auspices of FIFA.
3. Officials of Match are : 1 Match Referee, 2 Assistant Referees or Linesmen, 1 Commissioner, 1 Injury Timekeeper (depending upon tournament).
4. Extra Time: During a knockout tournament, if there is a tie at the end of regulation time, then the teams play for 30 minutes extra time of two halves of 15 minutes each. In this duration, if any team scores the goal, wins the match. Earlier there was golden goal period in which the team who scored the goal first won the game but • now it is said as silver goal period.
Question 9.
(a)(i) What do you mean by the term Red Card? (8)
(ii) Explain the term ‘Sudden death’.
(iii) What is the distance between the goal posts and the height of the cross bar from the ground?
(iv) Give the measurement of the goal area in football.
(b) (i) List any three duties to be performed by the captain of the team. (9)
(ii) Mention any three duties of the referee before the match.
(iii) State any three duties of the fourth official.
(c) Explain the following: (8)
(i) Trapping
(ii) Tackling
(iii) Dribbling
(iv) Kicking
Answers:
(a) (i) Expulsion (Red Card): Player is expelled if he commits a serious foul; as violent; strikes, charges; kicks or attempts to kick; trips on opponent, holds opponent; handles the ball intentionally; uses abusive language, offensive or insulting language; receives a second yellow card during the game.
(ii) Sudden death: If the teams are tied after 5 kicks, i. e., after penalty shootouts; then each team keeps taking penalty kicks until one team wins. The goal is scored when ball crosses the goal line (may be on surface or in air).
(iii) Goalpost Dimension is 8 yards. (7.3 meters) x 8 ft. (2.44 meters) with 5 inches cylindrical thickness of post.
(iv) It is marked at front of goal post, with 6 yards to both sides of goal post and 6 yards at front. The dimensions of this rectangular goal area is 20 yards by 6 yards.
(b) (i) Duties of a Captain:
- He represents the team to decide the toss, make strategies of the team in the field.
- He decides the team members and their position.
- He guides the team actions in the playing field like which player to take throw-in, comer-kick, penalty-kick, etc.
- Captain encourages team members to play better, checks the conduct of team members in the playing field.
(ii) Duties of Match Referee : Match Referee is an official responsible for the conduct of game under rules and regulations. His or her duties before the match are :
- To check the equipments used in game like Football, Stopwatch, Penalty cards etc.
- To check the dimensions of the playfield.
- To check the players equipments like shoes (studs), Shin Guard, Stocking, T-shirt with Number etc.
(iii) The fourth official serves as a replacement official in the event that one of the other officials (referee or assistant referees) cannot continue officiating; usually through injury. In situations where an Assistant Referee is unable to continue, the fourth official replaces that Assistant Referee.
(c) (i) Trapping: It is controlling the lifted ball before it could bounce or control the ball in air, so that it should fall near the body range. It is trapped by chest, thigh (upper leg), under the foot, etc.
(ii) Tackling: It is taking the ball possession from the opponent with sliding. Many times • trapping the ball with head, chest, foot is also done for the possession of the ball.
(iii) Dribbling: It is faking to the opponent in such a way that the control of ball is kept. Player controls the movement of the ball with the feet whereas upper body gives the dodging movement.
(iv) Kicking: It is the most common skill used to hit the ball with power. It reaches long and away to the desired position. It is performed in various ways like kicking with inside; outside of foot; instep-kick; punt-kick; scissor kick; banana or chip-kick; roll back-kick, etc. It can be used during free-kick, goal-kick, comer-kick, penalty-kick or when situation suits.
Handball
Question 10.
(a) Write the following: (8)
(i) Duration of the game (men and women)
(ii) Duration of the extra time and timeout .
(iii) Weight of the ball (men and women)
(iv) Circumference of the ball (men and women)
(b) (i) How is a goal scored? (9)
(ii) How does a player advance with the ball?
(iii) List any three occasions when the clock is stopped during the game?
(c) (i) What are the dimensions of the playing area? (8)
(ii) Where is the penalty line marked on the field?
(iii) What is the shape of the handball and what material is used in the construction of a handball?
(iv) What do you understand by the term Fake?
Answers:
(a) (i) Duration of game has 2 halves of 30 minutes for Men and 25 minutes for Women with 5 to 10 minute break in each half.
(ii) Extra time has 2 halves of 5 minutes each with 1 minute break in-between.
(iii) Weight of ball is 450 g ± 25 grams for Men and 350 g ± 25 grams for Women. .
(iv) Circumference of the ball is 60 centimeters for Men and 55 centimeters for Women. 1
(b) (i) When ball crosses the goal line completely under the goal-post, provided that no violation ;
of the rules has been committed by the thrower, a teammate or a team official before or dining the throw. Referee raises one hand and blows the short whistle twice. ;
(ii) Dribble : It is a skill of controlling and advancing with the ball . It is preventing ‘ opponents to gain the possession of the ball by bouncing, dodging, faking with the ball and advancing with the ball.
(iii) 1. Timekeeper stops the game clock during time-out and inform the end of time-out
to Referee.
2. He stops or starts the game clock in between (by the indication of Referee).
3. He notes the duration of 2-minute suspended player and sends him for play accordingly.
(c) (i) The dimensions of the playfield have rectangular shape with 40 meters length and 20 meters breadth. It should have 1 to 2 meters free zone area on all its sides.
(ii) Penalty line is marked parallel at the distance of 7 meters at the front of goal post.
(iii) The playfield have rectangular shape with 40 meters length and 20 meters breadth. Handball is an indoor game played on hard leveled wooden surface.
(iv) Fake : A skill to deceive opponent in wrong direction and thus making free space to
move ahead.
Question 11.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of a handball court giving all its measurements. (8)
(b) (i) List three duties of a Recorder. (9)
(ii) When is a comer throw awarded?
(iii) What is the utility of the goal area?
(c) Define the following terms : (8)
(i) A double-dribble
(ii) A line cut
(iii) A goal-throw
(iv) An over time
Answers:
(a)
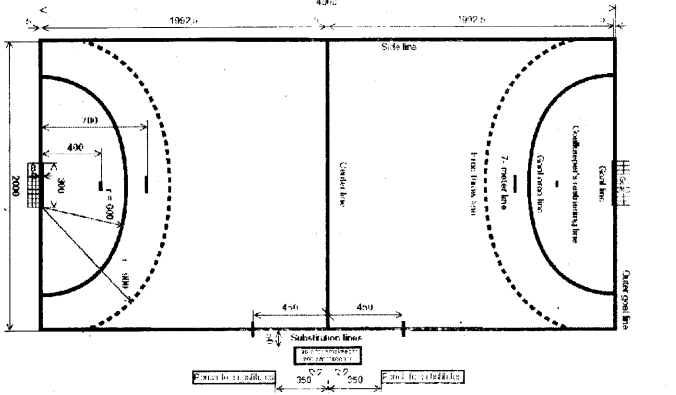
(b) (i) Recorder sits over the official table.
- He fills the score sheet carefully.
- He notes down the players, fouls, suspension, warning cards, etc. over the score sheet.
- He notes down the player scoring the goal.
- He checks the changing player.
(ii) A comer throw is given to an attacking player while the ball is played over goal line by a defending player or either side of the goal. Corner throw is thrown by attacking player from the comer of court. It is done by throwing the ball by using either hand.
(iii) Goal Area: The arc around the goal post at 6 meters which is restricted for all players except goalkeeper. Only goalkeeper is permitted inside the own goal area. Goalkeeper can touch the ball with any body part inside the goal area. Only goalkeeper is permitted to leave the goal area without permission.
(c) (i) Double-Dribble: If player uses both hands simultaneously while dribbling, it is a fault.
(ii) Line Cut: During attempt for goal if a player cuts or crosses the goal line, this is a violation.
(iii) Goal-Throw: During play if ball goes out from the end lines (goal line) by the opponent, then goalkeeper starts the game by goal throw. This is also known as goalkeeper throw.
(iv) Overtime is played, following a 5-minute break, if a game is tied at the end of the regular . playing time and a winner has to be determined. The overtime period consists of 2 halves of 5 minutes, with a 1 -minute half-time break.
Hockey
Question 12.
(a) Explain the following: (8)
(i) Carried
(ii) Back stick
(iii) A comer
(iv) A penalty stroke
(b) (i) List three offences by defenders which are penalized with a penalty comer against them. (9)
(ii) List any six instances when a referee blows the whistle for a foul.
(c) (i) What is the procedure for taking a penalty comer? (8)
(ii) What signal shall the umpire give for the following?
- Goal scored
- Dangerous play
- Obstruction
- Penalty comer
Answers:
(a) (i) Carried : When ball touches the leg or feet of the player, it is a violation.
(ii) Back stick: A player when uses backside of stick while dribbling. It is also a violation.
(iii) Penalty Corner: Apenalty comer is awarded for an offence by a defender in the circle which does not prevent the probable scoring of a goal; for an intentional offence in the circle by a defender against an opponent who does not have possession of the ball or an opportunity to play the ball; for an intentional offence by a defender outside the circle but within the 23 metres area they are defending; for intentionally playing the ball over the back-line by a defender.
(iv) Penalty Stroke: It is also known as 7-yard push. It is given when some serious offence is committed by the defending team in their shooting circle which probably has interrupted the goal scoring. Time stops during penalty stroke. Only goalkeeper and the player taking stroke is permitted inside shooting circle. At the whistle player pushes or scoops or flicks the ball towards the goal scoring whereas goalkeeper defends it. It is done from the penalty spot 7 yards in front of goalpost.
(b) (i) 1. A penalty comer is awarded for an offence by a defender in the circle which does not prevent the probable scoring of a goal.
2. For an intentional offence in the circle by a defender against an opponent who does not have possession of the ball.
3. For intentionally playing the ball over the back-line by a defender.
(ii) The Umpire blows the whistle during the game when:
- Start and end of each half
- Fouls committed by players
- Goal has been scored
- Penalty comer
- Penalty stroke
(c) (i) Penalty Corner Procedure : When serious foul is committed (intentional or
unintentional), dangerous play, misconduct, argument with Umpire by player. It is taken from end line (10 yards away from goalpost) with push and while remaining attacker stops the ball outside the D to continue. Only five defenders are allowed inside the shooting circle during penalty comer.
(ii) 1. A goal is scored when the ball is played within the circle by an attacker and does not travel outside the circle before passing completely over the goal-line and under the cross-bar..
2. Dangerous Play: It is any action which is dangerous to the player or could lead to a dangerous situation due to raised ball, tackling from wrong position, etc.
3. Obstruction : It is hindrance to opponent against the rules.
4. A penalty comer is awarded for an offence by a defender in the circle which does not prevent the probable scoring of a goal; for an intentional offence in the circle by a defender against an opponent who does not have possession of the ball or an opportunity to play the ball; for an intentional offence by a defender outside the circle but within the 23 metres area they are defending; for intentionally playing the ball over the back-line by a defender.
Question 13.
(a) Write down the following:
(i) Height of the corner flag post
(ii) Duration of the game (men and women)
(iii) Dimensions of the goalposts.
(iv) Weight of the ball and weight of the stick.
(b) (i) When is a player awarded a push ini What minimum distance should be observed by the player of the opposite team during a push in? (9)
(ii) When is a goal considered to have been scored in a match?
(iii) Write any three duties of the referee.
(c) Draw a neat diagram of the hockey field with its measurement. (8)
Answer:
(i) Four flags are placed at four comers and two are placed at a distance of 1 meter from the sideline over the centre line. The height of flag post should be 4 to 5 feet.
(ii) Duration of the game has 2 halves of 3 5 minutes for Men and 30 minutes for Women.
(iii) Dimension of goalpost has 12 Feets (3-66 meters) by 7 Feets (2-14 meters) of 5 centimeters thick wood.
(iv) Weight of ball is 5!4 Ounces (156 grams).
Weight of stick is between 16 to 32 Ounces.
(b) (i) When ball goes outside from the end line (intentional) by the defending players. It is
awarded to the attacking team after the ball goes over the end line (not between the goalposts) from the stick of the defender. The ball is placed five yards away from the sideline over the end line.
(ii) A goal is scored when the ball is played within the circle by an attacker and does not travel outside the circle before passing completely over the goal-line and under the cross-bar.
(iii) Two Umpires are there (one in each half).
- They judge fair play in their half and give decisions.
- They ensure the time of play (start and end of each half).
- They signal fouls and enforce penalties.
- They conduct Long comer, Penalty comer, Penalty stroke.
- They signal goal; restart game after a goal or restart after the suspension of play.
(c)
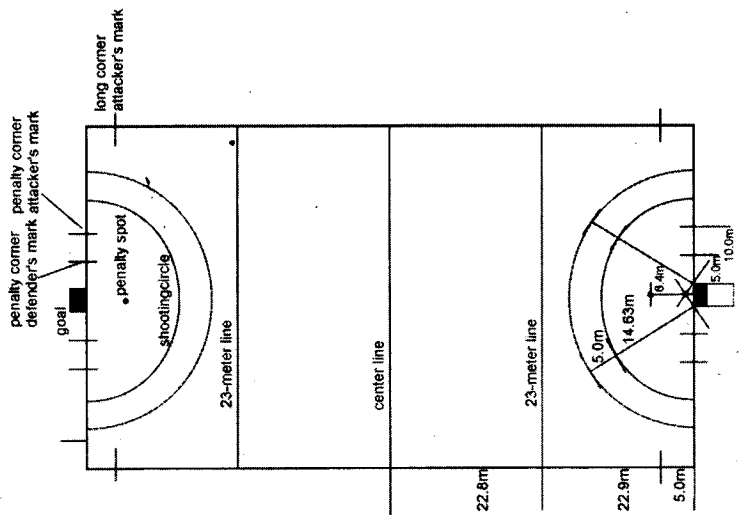
Basketball
Question 14.
(a)(i) Name the types of the time-outs. (8)
(ii) What do you mean by pivot-foot ?
(iii) Name any four fundamental skills in Basketball.
(iv) Write any two duties of the time keeper.
(b) (i)What is the duration of the game ? How is this time divided ? (9)
(ii) List any six player fouls which are noted over the score sheet by the table official.
(c) (i) Write the procedure to start the game (8)
(ii) List any four technical equipments used by the table officials.
Answers:
(a) (i) Charged Timeout: It is an interruption of game requested by coach. It lasts not more than one minute. It can be taken one time in I, II and III quarters; and two times in IV quarter.
(ii) Pivot-Foot: It is a restricted motion with ball. A player rotates around keeping one foot stationary. It is changing the direction of body while one foot maintains the contact with floor.
(iii) Passing : Chest-pass, bounce-pass, long-pass, one-hand pass, one-hand side-pass and underhand pass.
Dribbling : Low-dribble, high-dribble, behind the back-dribble, under the leg-dribble.
Shooting : Jump-shot, set-shot, hook-shot, lay-up-shot, dunk-shot and tip-in shot.
Defence : Zone defence, man-to-man defence, match-up defence (blocking, screening), press defence.
(iv) Duties of Timekeeper:
- He shall note when each quarter is to start and notify this to Referee more than three minutes before this time.
- He shall keep record of play and stoppage of time.
- He shall indicate with bell the expiry of playing time in each quarter or extra time.
- Timekeeper shall start timeout watch for charged timeout.
(b) (i) Playing Time: The playing time period is of 40 minute duration which is extended into four quarters. The rest period in-between I to II and III to IV quarters is 2 minute whereas, in half (between II to in quarter) it is 5 minute to 10 minute, i.e., 10 -2; 10 – 5/ 10; 10 – 2; 10. The game clock starts when the ball reaches the highest point on a toss, . during a jump ball is tapped by the first player.
(ii) The main fouls are:
Personal Foul’: It is a player’s foul which involves illegal contact with the opposing player whether the ball is live or dead. A player is eliminated from the match if he commits 5 personal fouls. They are further penalized with throw-in or free-throws if their team has committed more than four fouls in each quarter. These fouls are charging, illegal blocking, guarding from behind, holding or pushing opponent, illegal-screening, etc.
Unsportsmanlike Foul: This foul is also known as intentional foul. It is a personal foul of a player, with or without the ball. It has been deliberately committed against opponent like intentionally hitting the opponent player who is going for scoring basket. This is a serious foul in which opponent gets two freethrows along side pass from centre-line.
Technical Foul: When a player or coach performs unsportsmanlike act or misconduct or violent act deliberately. In this foul opponent gets two free-throws along with throw- in from centre.
Multiple Foul: When two players are involved in the foul at almost the same time. Throw in taken from sideline is taken in alternate manner.
Team Fouls: These are total fouls of team. If the team fouls exceed more than four fouls in each quarter then opponent team is awarded with two free-throws on each foul.
(c) (i) Jump-Ball: A jump-ball is a technique of starting the game in the beginning, from the circles. It takes place when official tosses the ball between the two opposing players. With new rules only one time the jump-ball is done and next time it is done with throw-in.
- Two or three standard specified basketballs
- One game clock for overall game duration of playing time; one stopwatch for small breaks inbetween the playing time.
- One 24-Second alarm device
- Alarm or bell or whistle
- Two team foul indicators
- Number markers and two free-throw flags; one to five number personal foul cards;
- Throw-in indicator (Jump-ball replacement)
- Score sheet; scoreboard.
Question 15.
(a) (i) Write any two conditions when a team forfeits the right of play. (8)
(ii) Give the signals for the following:
- Jump ball
- Charged time out
- Technical foal
- Double foul
- Travelling
- TiIne in
(b) (i) State any three violations when opponents gain the possession of the ball. (9)
(ii) What is cenfre circle ? What are its dimensions?
(iii) What is front pavot?
(c) Write down the following; ‘ (8)
(i) ‘24’second rule
(ii) ‘8’second rule
(iii) ‘5’second rule (iv) ‘3’second rule
Answers:
(a) (i).
- Team did not reported as per given time. ;
- If team has less than 5 players.
(ii) 1. It is indicated by Thumbs up followed by point finger in direction of alternating possession arrow.
2. It is indicated by forming T by index finger showing.
3. It is indicated by form T, palm showing.
4. It is indicated by wave clenched fists on both hands. „
5. It is indicated by rotate fists. ?
6. It is indicated by chop with hand. ’
(b) 1. Travelling: Illegal movement of the ball like running without bounce or passing while running.
2. Caring: A player with ball dribbles the ball with the shifting palm rather than the finger.
3. Double-Dribble : A player while dribbling the ball cannot use both hands simultaneously for dribble. He can use both hands only while receiving or while ‘ passing the ball.
4. Out of Bound: Ball hits the boundary line or it bounces out of playfield. ;
5. Back-Court: If ball is passed from the front court to the rear court to own teammate.
(ii) It is marked circle at the center of playfield for the jump ball. The radius of center circle is 1-80 meter.
(iii) Front Pivot: It is a restricted motion with ball. A player rotates around keeping one foot stationary. It is changing the direction of body while one foot maintains the contact with floor.
(c) (i) ‘24’ Second Rule : Whenever team gains possession of ball, they are supposed to attempt the basket within 24 seconds.
(ii) ‘8’ Second Rule : After the score or due to foul or any other reason if team gets the possession of ball they are supposed to move the ball in the front of court (from the rear half of court) within ‘8’ seconds. (Earlier it was 10 second rule).
(iii) ‘5’ Second Rule : A player cannot hold the ball (without bounce) for more than ‘5’ seconds.
(iv) ‘3’ Second Rule: Any offensive player cannot stay inside the opponents restricted area consecutively for more than ‘3’ seconds, (apart from attempts, rebounds or tries for making basket).
Volleyball
Question 16.
(a) Define the following terms:
(i) A double touch
(ii) Ball out of play
(iii) A disqualification
(iv) Service
(b) (i) Enumerate any three duties of each of the following :
1. A line judge
2. A scorer
3. A coach
(c) (i) Mention any three breach which are punishable. (8)
(ii) Explain legal and illegal substitution in volleyball.
Answers:
(a) (i) Double Touch : A player hits the ball twice in succession or the ball contacts various parts of his/her body in succession.
(ii) Ball out of Play t When ball is out of play at the moment of a fault, which is whistled by one of the Referees.
(iii) A team member who is sanctioned by disqualification must leave the Competition Control Area for the rest of the match with no other consequences. It is indicated by yellow + red card (jointly)
(iv) It is a skill to start the game. The server delivers it over the net, and it is done behind the service line.
(b) (i) If only two line judges are used, they stand at the comers of the court closest to the right hand of each referee, diagonally at 1 to 2 meter from the comer.
Duties of line judge :
- The ball “in” and “out” whenever the ball lands near their line(s),
- The touches of “out” balls by the team receiving the ball,
- The ball touching the antenna, the serv ed ball crossing the net outside the crossing space, etc.
- The foot faults of the server,
- Any contact with the antenna on their side of the court by any player during his/ her action of playing the ball or interfering with the play,
(ii) The scorer performs his/her functions seated at the scorer’s table on the opposite side of the court facing the first referee.
- He/She keeps the score sheet according to the rales, co-operating with the second referee.
- Registers the data of the match and teams, including the name and number of the Libero player, according to the procedures in force, and obtains the signatures of the captains and the coaches ;
- Records the starting line-up of each team from the line-up sheet;
(iii) Duties of coach:
Throughout the match, the coach conducts the play of his/her team from outside the playing court.
- He/She selects the starting line-ups.
- Coach requests for timeouts.
- Requests for substitution.
- The coach records or checks the names and numbers of his/her players on the score sheet, and then signs it.
(c) (i) 1. Penalty: The first rude conduct in the match by any team member is penalized with a point and service to the opponent.
2. Expulsion: A team member who is sanctioned by expulsion shall not play for the rest of the set and must remain seated in the penalty area with no other consequences.
3. Disqualification : A team member who is sanctioned by disqualification must leave the Competition Control Area for the rest of the match with no other consequences.
(ii) A substitute player may enter the game in place of a player of the starting line-up, but only once per set, and he/she can only be substituted by the same starting player. A substitution is illegal, if it exceeds the limitations indicated in Rule.
Question 17.
(a) (i) When and by whom was the game volleyball invented? (8)
(ii) List down the equipment used by a volleyball player.
(iii) Define the terms:
- Positional fault
- Rotational fault
(b) (i)Explain how a set and a match is won by a team. (9)
(ii) What is delay ? What are the various ways which a game may be delayed ?
(iii) How many legal interruptions are allowed in a game? Who grants the legal interruption?
(c) Briefly explain the following terms: (8)
(i) Service zone
(ii) Substitution zone
(iii) An attack line
(iv) A substitution
Answers:
(a) (i) The game of volleyball, originally called “mintonette,” was invented in 1895 by William G Morgan after the invention of basketball.
(ii) A standard spherical volleyballs, Proper kit with uniformity except the Libro, Proper shoes, Net, Antenna, Team bench etc.
(iii) 1. Positional fault: During service the players must stay in their positions, i.e., diagonally opposite player must be in the same manner as in beginning. Otherwise, positional fault is given to opponent.
2. Rotational fault: A fault in which a wrong positional player performs the service.
(b) (i) A set is won by the team which first scores 25 points (except the deciding 5th set) with minimum lead of two points. To win a match, team has to win three sets. In case of 2-2 tie of sets, the deciding 5th set is played to 15 points with a minimum lead of 2 points.
(ii) During substitution, time out, ball goes away, injury to player, improper request to Umpire. Like delaying a substitution, requesting an illegal substitution, repeating an improper request, delaying the game by a team member.
(iii) Regular game interruptions are Time-outs and Substitutions. An interruption is the time between one completed rally and the 1st Referee’s whistle for the next service. Regular game interruptions may be requested by the coach, and/or by the game captain.
(c) (i) Service-zone : The service zone is a 9 m wide area behind each end line. It is an area behind the backline which is used for performing service.
(ii) Substitution zone: The substitution zone is limited by the extension of both attack lines up to the scorer’s table.
(iii) Attack line: On each court, an attack line, whose rear edge is drawn 3 m back from the axis of the centre line, marks the front zone.
(iv) Substitution : Replacement of one or more players from the listed substitution apart from libero. The coach of the team requests for substitution to the assistant referee. An area 3 m away towards sideline (substitution area) is allowed to move for substitution. When Referee signals for substitution, the player should move out and substitute player should enter.
