ICSE Commercial Studies Previous Year Question Paper 2017 Solved for Class 10
- Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
- You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
- This time is to be spent in reading the Question Paper.
- The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
- Attempt all questions from Section A and any four questions from Section B.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
Section – A (40 Marks)
(Attempt all questions from this Section)
Question 1.
Distinguish between :
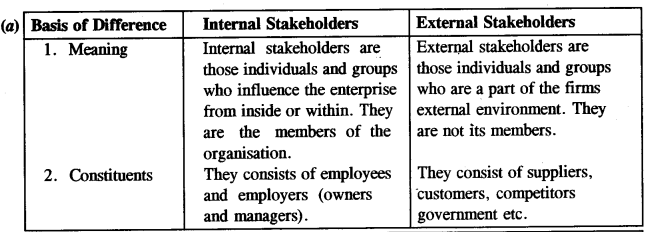
(a) Internal and External stakeholders [2]
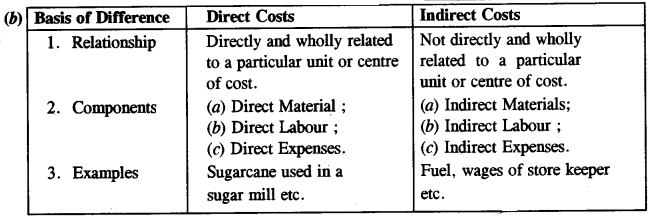
(b) Direct Costs and Indirect Costs [2]
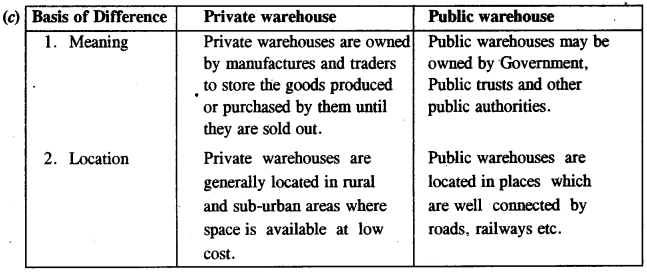
(c) Private warehouse and Public warehouse [2]
(d) Recruitment and Selection [2]
(e) Overdraft and Cash credit [2]
Answer:


Question 2.
(a) What is Survey Method of Marketing Research ? Give one reason why it is mosdy used. [2]
(b) Why should ‘Non-Trading Organisations’ maintain books of accounts ? Name the accounts prepared by them. [2]
(c) Give any four examples of Public awareness programmes organized for a better environment. [2]
(d) State any two expectations of the Associates from a business enterprise. [2]
(e) What do you mean by ‘Semantic barrier’ ? [2]
Answer:
(a) Survey Method : Survey method involves getting answers to specific questions from the entire market or a representative sample of it. A Survey is a detailed enquiry to collect information from either the entire universe or a part of it. Survey method involves the preparation and use of questionnaire (a list of questions) and therefore, it is also known as ‘QUESTIONNAIRE METHOD’. Survey is the most widely used method of collecting data due to it provides both quantitative as well as qualitative information and can be used to obtain both facts and opinions.
(b) Non-Profit Organisations need to prepare certain financial statements to know to be surplus or deficit during the year and financial position at the end of the year.
Non – Trading Organisations prepare the following accounts and statements :
- Receipts and Payments Accounts
- Income and Expenditure Accounts and
- Balance Sheet.
(c) Examples of Public awareness programmes organized for a better environment are as follows :
- Chipko Andolan (Movement)
- Beej Bachao Andolan (Save the seeds movement)
- Ganga Action Plan
- Ralegan Siddhi
(d) Expectations of Associates from a business enterprise are as follows :
- They expect fair trade practices regarding price, quality and service.
- They expect an atmosphere of healthy competition and ethical behaviour.
- They expect coordination among competitors to ensure the growth of the entire industry.
(e) Semantic Barrier : Semantics is the science of meaning. The same words and symbols may carry different meanings to different people. Communication breaks down when the sender and the receiver of the message use words and symbols in different senses. Sometimes, the language used by the sender may not be understood by the receiver.
Question 3.
(a) What are convenience products ? Give any two examples.
(b) What is semi-variable cost ? Give one example.
(c) What is meant by ‘Revenue Expenditure’ ?
(d) What is Direct Mail advertising ? Give any two advantages of it.
(e) State two disadvantages of internal recruitment.
Answer:
(a) Convenience Goods : These are the products which consumers purchases frequently and with minimum efforts. Bread, butter, milk, toothpaste, soaps, newspaper etc., are the examples of convenience goods.
(b) Semi – Variable Costs : The costs which vary with every increase or decrease in the volume of production but do not vary proportionately are called as semi-variable costs. Such costs contain fixed and variable elements. Because of the variable element, they fluctuate with volume and because of fixed element they do not change in direct proportion to output. Depreciation, repairs etc, are the examples of the semi-variable costs.
(c) Revenue Expenditure : Revenue expenditure means the expenditure the benefit of which is exhausted within the current year. Such expenditure is of a recurring nature and does not result in the acquisition of permanent assets. These expenditure are incurred for meeting day to day requirement of the business enterprise. All expenses incurred on day- to-day administration of a firm and the effect of which is completely exhausted within the current accounting are called revenue expenditure. Examples of revenue expenditure are ; rent; salaries ; wages etc.
(d) Direct Mail Advertising : In this medium, a mailing list of potential customers is prepared. The message is sent directly to individual customers through mail in the form of circular letters, booklets, leaflets, folders and catalogues which containing detailed information about the product are sent by post to these buyers.
Advantages of Direct Mail’Advertising are :
- It is the most selective medium as the message is sent to selected persons directly.
- It has a personal touch since the message is addressed to a particular person.
- It ensures secrecy in advertising since the competitors do not get the information contained in the message.
(e) Disadvantages of internal recruitment are :
1. Limited Choice : Internal recruitment restricts the choice of management. The existing employees may not be suitable for higher positions. Competent and deserving candidates from outside do not get the opportunity to be considered for these posts.
2. Inbreeding : When all higher level vacancies are filled in by promoting present employees, new ideas and fresh thinking may not enter the organisation.
Question 4.
Mention any two qualities of a good salesman. [2]
(a) Mention any two qualities of a good salesman. [2]
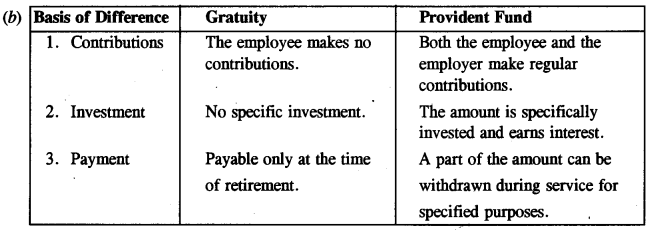
(b) Distinguish between Gratuity and Provident Fund. [2]
(c) What is a bonded warehouse ? [2]
(d) What do you mean by Mural advertising ? [2]
(e) Mention any two main advantages of group life insurance to employees and employers. [2]
Answer:
(a) Qualities of a good salesman are :
1. Knowledgeable : A good salesman should possess knowledge about his organisation, product, market, customer and competitor. He should have knowledge about the customer related to his habits, tastes, preferences and time of buying so that the repeated sales can be made.
2. Communication Skills : Communication skills is an asset for the salesman. He should be able to speak freely, clearly and in a well-pitched voice. He must be a person who has a natural ability for conversation.
(c) Bonded Warehouse : A Bonded warehouse is established under a bond with the customs authorities for storage of duitable goods till the payment of import duty. The owner of a bonded warehouse gives on undertaking not to release the goods until the customs duty is paid. Bonded warehouse are located in port towns and are licensed by the Government. These warehouses operate under the vigilance of customs officials.
(d) Mural Advertising : Mural advertising is also known as Outdoor advertising. This is the oldest medium of advertising and continues to be popular in spite of new media. It consists of the use of posters, billboards, electric displays etc. Poster? are pasted on walls at important public places to convey the message to the people passing by such places. Sign boards or painted boards are displayed on buses, railways, carriages and public vehicles. Loudspeakers, travelling announcers, sky writings, handbills etc., are examples of outdoor advertising or mural advertising.
(e) Advantages of Group Life Insurance to employees and employers are as follows :
- Group life insurance is economical for employees as they have to pay low premium in comparison with individual life policies.
- Group life insurance is also economical and convenient for the employer as he can meet his obligation out of money received from insurance company in case of an employee’s death.
SECTION – B [40 Marks]
(Attempt any four questions from this Section)
Question 5.
(a) Explain any five measures taken to overcome barriers of communication. [5]
(b) Explain expectations of the Government from a business organisation. [5]
Answer :
(a) Following are the measures taken to overcome the barriers of communication :
- Well Drafted Message : The message to be transmitted must be clear and concise. It is very essential to know the audience for whom the message is meant. The message should be adequate and appropriate for the purpose of communication.
- Proper language : The message should be expressed in simple and easily understood language. The words and symbols used to convey the message should match the reference and understanding of the receiver. This will help to minimise the semantic barrier.
- Consistency : Communication should be consistent with the goals and policies of the organisation. There should be no contradiction between words and actions.
- Gestures and tone : Words in the message must be reinforced through appropriate gestures or facial expressions. The tone used should take into account the physical environment and human conditions.
- Feedback : Communication is complete when the response or reaction of the receiver becomes known to the sender. Therefore, the receiver should be encouraged to express his reactions. The feedback should be analysed and used to improve future communications.
(b) Every Stakeholder group expects something from a business organisation. The expectations of Government are as follows :
- They expect to follow the laws and regulations of the country.
- They expect to pay all taxes honesty, regularly and in time.
- They expect to avoid corrupting public servants.
- They expect to make proper use of scarce resources.
- They expect to assists in solving national problems, like poverty, unemployment, unbalanced regional growth etc.
- They expect to avoid monopoly and concentration of economic power.
Question 6.
(a) ‘Advertisement is a social waste.’ In this context explain the demerits of advertisement. [5]
(b) What is ‘standardization’ of products ? List any three benefits of standardization. [5]
Answer:
(a) Although advertising has a lot of benefits, it has been criticised on the following grounds :
1. Higher Prices : Advertising increases prices of products to consumers because the expenses incurred on advertisements are passed on to consumers. However, advertising may not increase prices if it leads to large scale production.
2. Creation of Monopoly : Big firms spend huge amount of money on advertising. Small firms cannot compete with them and ultimately fail. As a result, big firms become monopolies and use their monopoly power to exploit consumers.
3. Wastage of Resources : Money spent on advertising is sheer waste because it does not add to the utility of products and services. Most of the advertisements are either ignored or escape the attention of consumers. Advertisements do not create new demand but only shift demand from one product to another.
4. Misleads the Consumer : It is said that advertising is often deceptive and misrepresents • facts to the consumer. Exaggerated or tall claims and flowery language are used to dupe unwary consumers. They are induced or defrauded through bogus testimonials and false comparisons to buy goods of doubtful value.
5. Undermines Social Values : Modem advertising exerts such a corrupting influence on cultural and social life that it is not only wasteful but immoral. Many advertisements are highly objectionable and socially undesirable as they encourage social evils like drinking and smoking. To some extent advertising spoils the landscape and diverts attention of drivers. Some advertisements may really be in poor taste but majority of them help to improve social standards.
(b) Standardization Of Products : Standardization refers to the process of setting up basic measures or standards to which the products must conform and taking steps to ensure that the goods actually produced adhere to these standards. In standardization, the product contains certain desirable qualities like durability, safety, utility and special features such as design, weight, colour and size. Standardization facilitates the purchasing and selling of the products. Goods are sold by description. In India, ISI mark issued by die Bureau of Indian Standard guarantees the quality of the product.
Benefits of Standardization are :
- They facilitate buying and selling of goods by sample or description. When goods are of standardised quality, customers do not insist on detailed inspection.
- Standardised goods sell better and fetch a better price to the seller because customers have more faith in them.
- Standardised goods enjoy a wider market.
- Standardisation help in raising finance because standardised products enjoy a ready market and they are readily accepted as a collateral security for granting loans.
Question 7.
(a) Explain any two methods of ‘Off-the-job training’. [5]
(b) Explain any five functions of the Central Bank of India. [5]
Answer:
(a) Off-the-Job Training: When an employee is trained outside the job, it is called off-the-job
training.
Various methods of off-the-job training are :
(i) Internship Training : This is a joint programme of training in which business houses collaborate with technical institutions Internship training involves a balance between theory and practice. The trainees are given theoretical instructions in technical institutions. After completing theoretical learning, they receive practical training in factories and offices. This method is used in medical, accountancy and legal professions. It is very useful for technical and professional jobs which require advanced theoretical knowledge and practical experience on the job. But it is very time-consuming.
(ii) Vestibule Training : It is the most common off-the-job training method. Vestibule means a room between the outer door and the interior of a building. Workers are trained in a classroom or hall within the plant. A large number of workers are trained under the guidance of expert trainers. Special instructors teach the theoretical and practical aspects of the job. Same machines and equipment are used in the vestibule which are employed at the workplace. Vestibule method permits greater emphasis on teaching the best method of work.
Trainees get accustomed to the work routine and can overcome initial nervousness before working on the actual job. Training does not hamper actual work of production and trainees can better concentrate on learning. But vestibule training is very expensive.
(b) Functions of the Central Bank of India are :
(i) Issue of Currency Notes : The central bank has monopoly over issuing currency notes in the country. In order to inspire public confidence in paper currency, the central bank keeps reserves of gold, silver, etc., for issuing currency notes. Central bank is given monopoly of note issue in order to maintain uniformity in currency, to avoid over-issue and to lend prestige to the currency system.
(ii) Banker to the Government : The central bank acts as a banker, agent and advisor to the Government. As a banker, it receives and makes payments on behalf of the Government. The central bank serves as the Government’s agent in financial matters. It advises the Government in matters relating to monetary and banking policies. It manages the national debt and issue of Government securities. It also represents the Government in international conferences on monetary and banking matters.
(iii) Banker’s Bank : The central bank acts as the bank for all commercial banks in the country. When a commercial bank needs funds it can obtain loans and re discount its bills with the central bank. Therefore, central bank is called ‘Lender of last resort’. Commercial banks are required to keep a cash reserve with the central bank so as to control credit in the country. The central bank advises commercial banks on matters relating to their business.
(iv) Credit Control : The central bank exercises both qualitative and quantitative control over credit granting capacity of commercial banks in order to maintain stability in prices and foreign exchange. In the absence of such control, commercial banks may lend too much or too little. They may lend to wrong parties or for unproductive purposes. They may also charge very high rates of interest.
(v) Custodian of Foreign Currency Reserves : The central bank is the sole custodian of gold, foreign exchange and all other reserves of the country. It manages these reserves judiciously so as to overcome difficulties in balance of payments and to stabilise the exchange rates.
(vi) Maintenance of Exchange Rate : The central bank monitors the exchange rate of the home currency in relation to foreign currencies. It tries to maintain stability in the exchange rate in order to promote the country’s foreign trade and to encourage the flow of foreign investment. The central bank buys and sells foreign currencies in order to maintain a stable exchange rate.
Question 8.
(a) Explain any five principles of Insurance. [5]
(b) Explain any five importance of warehousing. [5]
Answer:
(a) Principles of Insurance are as follows :
1. Utmost Good Faith (uberrimae fedie) : The contract of insurance are based on the principle of utmost good faith. It implies that both the parties to the contract must disclose all material information truly and correctly. Misrepresentation or failure to reveal material information gives the aggrieved party the right to regard the contract as void.
2. Insurable Interest : Every insured person must have the insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. There can be no insurance if there is no insurable interest. Insurable interest implies monitary interest, without which no insurance contract is valid in the eye of law. Insurable interest is said to exist when the insured party is benefited by safety of the property and is prejudiced by its loss. If a person goes in for insurance without insurable interest in the insured commodity, the contract will be null and void.
3. Contract of Indemnity : The word ‘indemnity’ means security against loss. In other words, indemnity implies a promise to compensate in case of a loss. The principle of indemnity is applicable to all types of insurance policies, except life insurance. The insured will be compensated only up to the amount of loss suffered by him. The insured party cannot make a profit out of this insurance contract.
An insured can get nothing more than the actual amount of the loss suffered. Here, the insurer undertakes to compensate the insured for the loss caused to him by the damage or destruction of the property insured. The principle of indemnity is applicable in case of fire insurance and marine insurance.
4. Doctrine of Subrogation : According to the doctrine of subrogation, after the insured is compensated for the loss caused by the damage to die property insured by him, the right of ownership of such property passes on to the insurer. It signifies that, if the insurer indemnifies the insured the loss in full, the insurer is entided to recover any benefit due to the insured from a third party.
If the insured party gets compensation for the loss suffered by him, he cannot claim the same amount of loss from any other party. If the insured claims compensation from both the sides, he will be in a better position than earlier. The principle of subrogation is applicable to fire insurance and marine insurance.
5. Causa Proxima (or proximate cause) : Causa proxima means the nearest cause and not the remote cause to be looked into. Causes of loss may be of two kinds : (a) insured perils ; and (b) uninsured perils. The insurer is liable for a loss when such loss must have been proximately caused by the insured perils. The insurer is, in no case, liable to compensate for the damages arising directly or indirectly on uninsured perils.
Suppose, a property is insured against fire, but it is damaged due to a road accident; in this case the insurance company is not responsible. Therefore, an insured can recover damages, if the cause is immediate or proximate to the loss.
(b) Importance of Warehousing are as follows :
1. Seasonal Production : Several commodities such as rice, wheat, sugar, etc., are produced during a particular season but they are consumed throughout the year. For example, potato is produced mostly in winter season but is demanded throughout the year. Perishable products like vegetables, fruits, eggs, butter etc. are stored in cold storage to make them available to consumers throughout the year.
2. Production in Anticipation of Demand : Factory goods are generally produced in anticipation of future demand. All the goods are not sold off as and when they are produced. They have to be kept in warehouses until the demand is created. Manufacturers store goods for wholesalers, wholesalers store goods for retailers and retailers store goods for consumers. Thus, need for warehousing arises at every stage in the process of marketing.
3. Storage of Raw Materials : Manufacturers have to store raw materials in order to ensure uninterrupted or regular production. Raw material prices are low dining certain seasons. Manufacturers buy them in bulk and store them for use throughout the year.
4. Seasonal Demand : Some products such as electric fans, coolers, umbrellas, rain coats, woollen cloth, etc., are demanded in a particular season. But they are produced throughout the year. Such products have to be stored in warehouses so that the demand during the particular season can be met.
5. Stability in Prices : It is necessary to store goods to avoid violent fluctuations in prices. Producers and merchants can secure better prices by storing goods in warehouses.
Question 9.
(a) Discuss the role and concepts of Eco efficiency and Eco friendly technology. [5]
(b) “Budgets are useful for management”. Justify. [5]
Answer:
(a) Eco Efficiency : These are those technologies which help us to increase the productivity in less time. These also lower the cost that is involved in the production of the goods, products and services. In this, high efficiency production methods and technologies are used. Eco efficient technologies preserve natural resources, it also improve the industrial efficiency and the economic development. Conceptually, Eco efficient technology is a “cleaner approach”. Eco efficiency provides both environmental and economic benefits through production efficiency.
- It increase the resource productivity
- Reduce the material and energy usage
- Reduce pollution
- Increase service intensity of goods and services
- Improve recyclability of materials
Eco-Friendly Technology : This technology can help to preserve the environment through energy efficiency and reducing the harmful waste. It does not have any negative effect on ecology or on the natural environment. This technology mainly involves reduction in the usage amount of raw material and energy. It also reduce pollution, recycle material. By using renewable material it ensure that goods are durable and judicious and we should use these resources by keeping in mind their effects on the future.
Role of Eco-efficiency and Eco-friendly technology :
- Adoption of efficient and eco-friendly technologies helps in achieving sustainable development.
- Use of solar cooker, solar heaters, solar cells and bio-gas plants leads to saving of energy.
- Greater use of fuel cells and alternative fuels like hydrogen, ethanol etc. can save natural resources.
- We should tap solar energy and hydel energy, nuclear energy etc. for development in sustained manner.
- They improved recyclability of materials.
(b) Budgets are very useful in management. They offer the following advantages.
1. Sound Hanning : Budgets make planning purposeful and precise. Objectives and programmes are expressed in physical or monetary units in budgets. Budgets are prepared on the basis of forecasts. Therefore, budgets force managers to think about the future. Budgets help to minimise snap judgments and unplanned actions. Budgets guard against undue optimism, because budgetary targets are fixed after careful thought. Budgets also act as a safeguard by providing an automatic check on the judgement of executives.
2. Higher Efficiency : Budgets bring efficiency and economy to the working of a business firm. They help management in obtaining the most profitable combination of different factors of production.
3. Sense of Responsibility : Budgets helps to establish divisional and departmental responsibility. They prevent “buckpassing” and create a sense of responsibility among managers.
4. Source of Motivation : Budgets represent the ‘milestones’ to be reached. They tell people what is expected. Budgets become the goals or targets to be attained. The budget is an impersonal policeman that maintains ordered effort in the organisation.
5. Coordination : Budgets force executives to think as a group. Budgets are prepared in consultation with one another. Therefore, they help in achieving co-ordination between different departments of the enterprise. The interaction between persons working in different departments that takes place during the process of budgeting facilitates uniformity of policies and united action.
6. Effective Control : Budgets are an important tool of managerial control. Use of budgets for evaluation and control of performance is known as ‘budgetary control’. Budgetary control facilitates ‘control by exception’ by focusing attention on deviations from budgeted targets. Budgets provide exact standards with which actual results can be evaluated and variations between actual performance and budgetary targets can be analysed.
Question 10.
The value of stock on 31st December 2014 was ₹ 14,920 .
Prepare a Trading Account and a Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st December 2014 and a Balance Sheet as at that date in the books of ABC enterprises. [10]
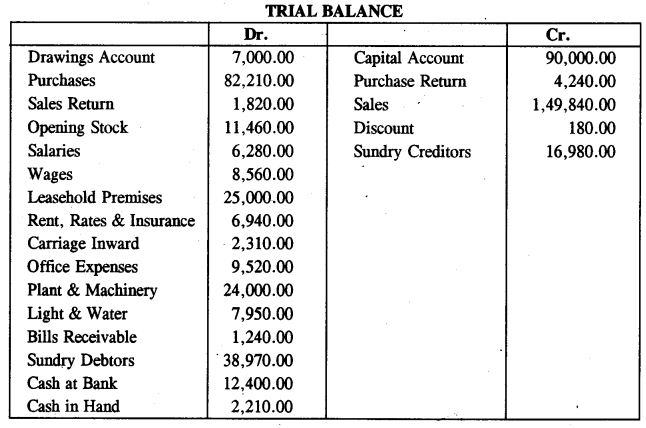
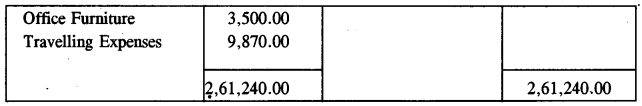
Answer :
ABC Enterprises Trading & Profit And Loss Account for the year ended 31st December, 2014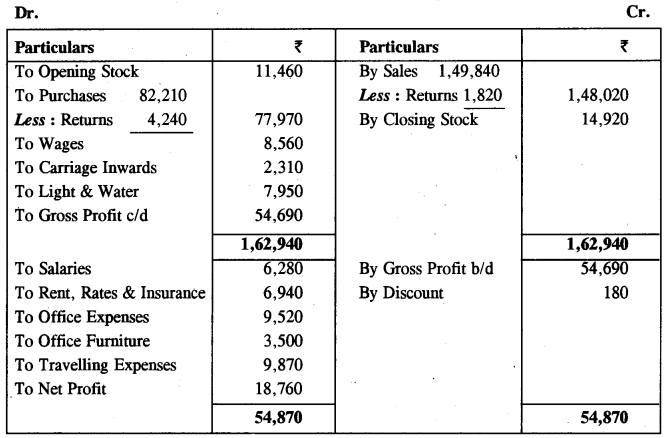
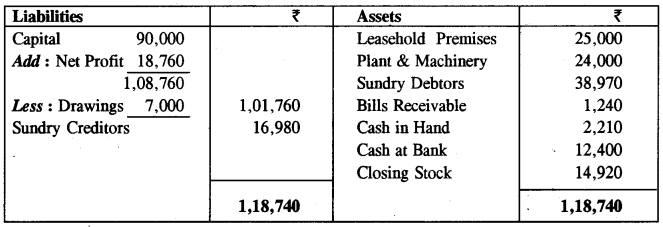
Balance Sheet as at 31st December, 2014
ICSE Class 10 Commercial Studies Previous Years Question Papers
