What are the Functions of Blood in Human Body
Functions of Blood :
Blood perform the following functions :
- Transport of Oxygen and Carbondioxide :
Blood transports oxygen from the respiratory surface i.e. lungs, buccal cavity to body tissues and carbon dioxide from tissue to respiratory surface. - Transport of food :
Blood transports digested food to different cells of the body. - Transport of waste products :
Blood transports the waste products of cells and organs to the kidneys, lungs, skin and intestine, so that they may be eliminated. - Chemical coordination :
Hormones produced by endocrine glands are distributed to the vital tissues by the blood. - Defence against infection :
When bacteria or any other disease causing pathogen enters the body. It is distroyed by WBCs (one type of WBCs; called lymphocytes produce Antibodies against specific pathogen) and so immunity against the disease is created in the body. - Clotting of blood :
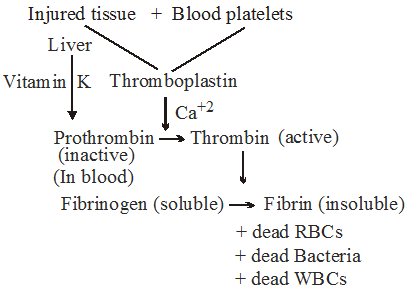
To prevent excess bleeding, blood-platelets and some protein form clot so as to prevent further bleeding. - Water balance :
Blood maintains body temperature constant and distributes and exchanges water between cytoplasm of cells. - Temperature regulation :
Heat produced by deeper tissues is taken to the body surface, so that it may be given out and thus body temperature is maintained. - Maintainance of body pH :
In RBC, some carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) that is disossociated into H+ and HCO3–. These ions combines with ions of plasma to maintain a constant pH. - Maintenance of pressure :
Arteries produce a proper pressure of blood that helps to balance the atmospheric pressure. - Blood Clotting :
Flow Chart Showing Clotting of Blood