Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Physics – Light: Spherical Mirrors
PAGE NO: 258
Solution 1:
A spherical mirror is a part of a hollow glass sphere silvered on one side.
Solution 2:
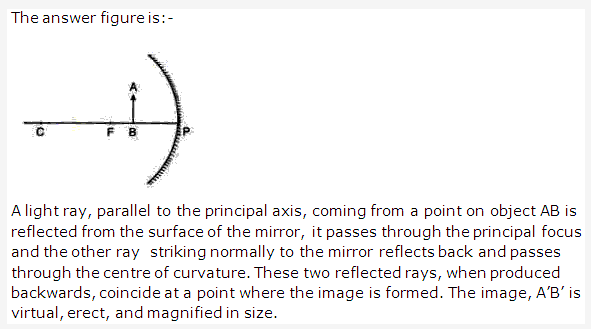
Solution 3:
Focal length = 1/2 of radius of curvature
= 1/2 x 30 = 15cm.
Solution 4:
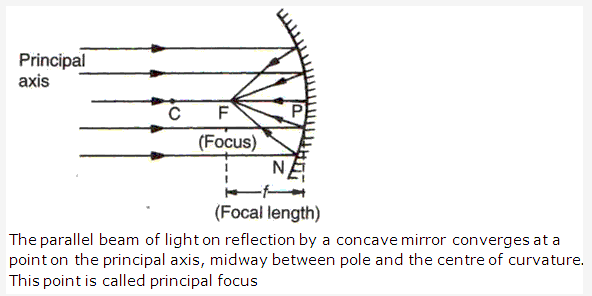
Focal point is the principal focus of the mirror where a parallel beam of light meets(or appear to meet) after reflection from the mirror.
Solution 5:
Solution 6:
- Pole is the centre of the reflecting surface, in this case spherical mirror.
- Centre of curvature is the centre of the imaginary sphere to which the mirror belongs
- Aperture is the distance between the extreme points on the periphery of the mirror.
- Principal axis is the straight line passing through the pole and the centre of curvature.
- The principle focus of a spherical mirror may be defined as a point on its principle axis where a beam of light parallel to the principle axis converges to or appears to diverge from after reflection from the spherical mirror.
Solution 7:
Convex mirror has a wider field of view.
Solution 8:
Concave mirrors are used in reflecting microscope, in shaving and make up glasses and in ophthalmoscope.
Solution 9:
Convex mirrors are used as a rear view mirror in automobiles as it provides a wider view of following traffic.
Solution 10:
Convex mirror is used in vehicles to see the traffic following it.
Solution 11:
The relationship between the focal length, f and radius of curvature, r is
f = 1/2 x r.
Solution 12:
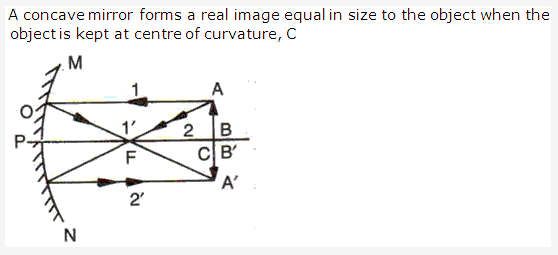
Solution 13:
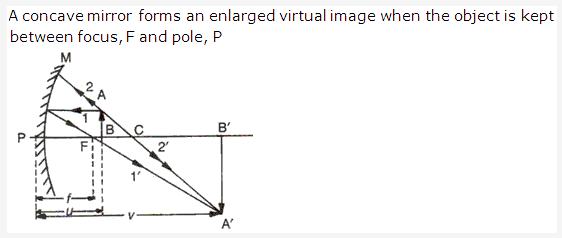
Solution 14:
Concave mirror can produce real and diminished image of the object.
Solution 15:
The focal length of plane mirror is infinity.
Solution 16:
The object should be placed between F and P to obtain its magnified and erect image.
Solution 17:
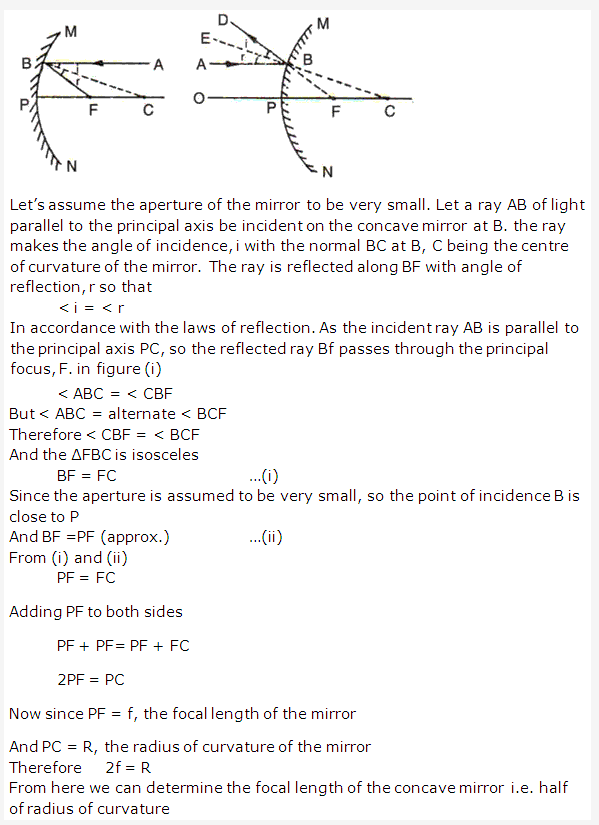
Solution 18:
Linear magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. It is taken to be positive for an image to be virtual and erect and negative when image is real and inverted.
Magnification = height of image / height of object.
Solution 19:
SI unit of focal length is meter.
Solution 20:
The top mirror is convex mirror, the middle mirror is concave mirror and bottom mirror is a plane mirror.
Solution 21:
The mirror having +15 cm as its focal length is a convex mirror because focal length is taken positive only in case of convex mirror.
Solution 22:
The mirror having -20 cm as its focal length is a concave mirror because focal length is taken negative only in case of concave mirror.
Solution 23:
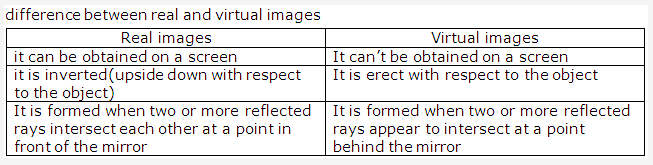
When we look into a plane mirror, the image of our face is virtual because the image cannot be obtained on a screen.
Solution 24:
When an object is brought towards the concave mirror, the position of the image moves away from the mirror and the size increases and it remains inverted but at object position between F and P, the image is virtual, magnified and erect.
Solution 25:
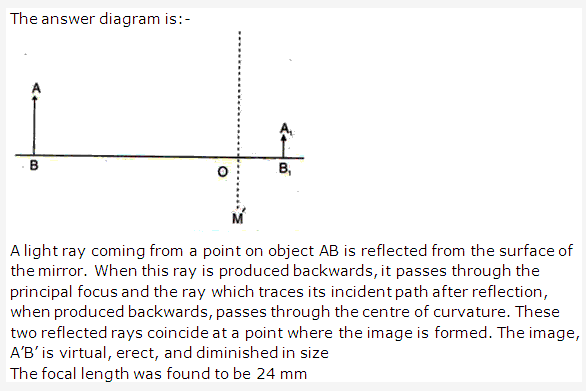
PAGE NO : 259
Solution 26:
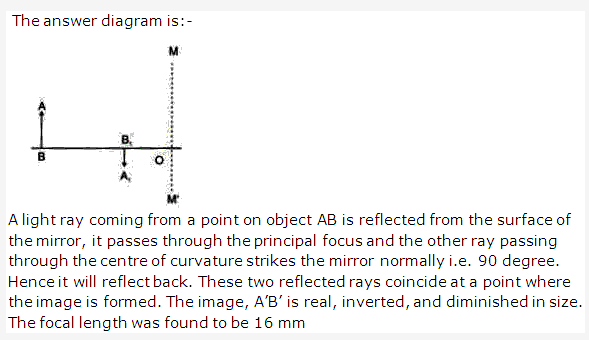
Solution 27:

Solution 28:

Solution 29:

Solution 30: