Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Physics – Light: Reflection of Light
PAGE NO: 245
Solution 1:
Light may be defined as the radiant energy which produces in us the sensation of sight. Light itself is invisible but makes other objects visible.
Solution 2:
Yes, light is a form of energy that produces the sensation of vision in our eyes.
Solution 3:
The velocity of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 m/s.
Solution 4:
Two sources of light are
- Natural, for e.g. Sun
- Artificial, for e.g. Light bulb.
Solution 5:
Four characteristics of light are :-
- Light waves can travel through vacuum
- Light waves are transverse waves
- Wavelength of light waves is short so that their length is measured in centi-microns.
- The velocity of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 m/s.
Solution 6:
The Sun and the stars are the two luminous bodies.
Solution 7:
Two non -luminous bodies are moon, chair.
Solution 8:
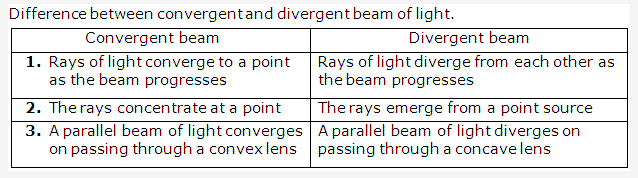
Solution 9:
A ray of light is the path along which light travels.
Solution 10:
Three distinctions between light and sound waves are
- Light waves can travel through vacuum while sound waves cannot.
- Light waves are transverse waves while sound waves are longitudinal waves.
- The velocity of light in air is 3 x 108 m/s while the speed of light in air is just about 330 m/s.
PAGE NO : 246
Solution 11:
- A ray of light
- Divergent beam of light
- Divergent beam of light
- Parallel beam of light
Solution 12:
The substance through which light is made to pass is called medium.
Solution 13:
Rectilinear propagation of light is that the light travels along a straight line.
Solution 14:
No, glass is a transparent medium.
Solution 15:
No, no metal is transparent by nature.
Solution 16:

Solution 17:
Waxed paper is the translucent medium among the given substances.
Solution 18:
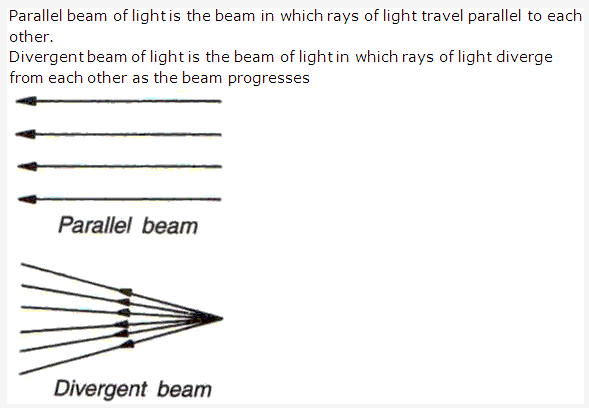
Solution 19:
Two observations that proves that light travels in a straight line are :-
- Sunlight coming through a hole in a dark room, we can easily see that light travels in a straight line
- Light coming from a laser light, used for presentation, can also be seen to travel in straight line.
Solution 20:
When rays of light fall on a surface, they are turned back into the same medium in accordance with some definite laws. This process is known as reflection.
Solution 21:
A smooth and polished flat surface is the cause of regular surface.
Solution 22:
Reflection obeys following two laws
- The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always equal.
Solution 23:
The height of plane mirror should be half of the size of the object to get a full image of the object. So for a man of height 1.6 m tall should use a 0.8m tall plane mirror.
Solution 24:
Rectilinear propagation of light is that the light travels along a straight line.
Solution 25:
Lateral inversion is the reversal of image experienced in a plane mirror. The image is of the same size and equidistant from the object but the left and right sides are transposed.
Solution 26:
Formation of image is the phenomenon based on laws of reflection.
Solution 27:
The principle employed in a periscope is successive reflections from two plane mirrors.
Solution 28:
The point at which the light is incident on the reflecting surface is called the point of incidence.
Solution 29:
Any smooth, highly polished reflecting surface is called mirror.
Solution 30:
A smooth, highly polished plane surface is called plane mirror.
Solution 31:
The angle between the incident ray and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence is called the angle of incidence.
Solution 32:
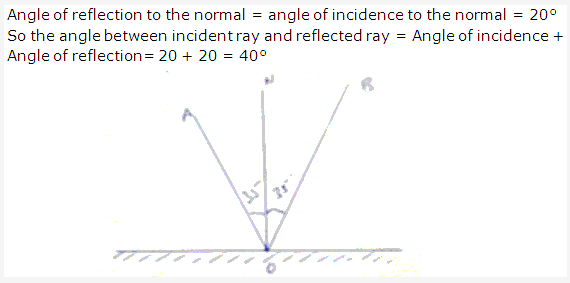
Solution 33:
Given, angle between incident ray and mirror = 35°
- Angle of incidence = angle of mirror to the normal – angle between incident ray and mirror
= 90 – 35 = 55° - Angle of reflection = angle of incidence = 55°
- Total angle turned = angle of incidence + angle of reflection
= 55 + 55 = 110° - The angle between incident ray and reflected ray = Angle of incidence + Angle of reflection
= 55 + 55 = 110°
Solution 34:
Given, distance of boy from the mirror = 3 m
- Distance of image from mirror = distance of boy from the mirror = 3 m
Distance between boy and his image = distance of boy from the mirror + distance of image from mirror = 3+3 = 6 m - Now, distance of boy from the mirror = 4 m
Distance of image from mirror = 4 m
Distance between boy and his image = distance of boy from the mirror + distance of image from mirror = 4+4 = 8 m.
Solution 35:

PAGE NO : 247
Solution 36:
Two characteristics of image formed by plane mirror are
- Image is erect and virtual
- Image and object are of same size.
Solution 37:

Solution 38:
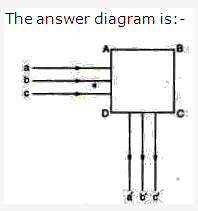
Solution 39:

