Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology – Respiratory System
PAGE NO:176
Solution 1:
Respiration: It is a process of release of energy from food substances such as glucose and fats under the control of enzymes, to carry out life processes, by the living organisms.
Respiration is essential for life as energy produced during this process is utilized by the organisms to carry out various biological activities.
Solution 2:
Structure of nasal chamber:
The nasal chamber is divided into left and right chambers by nasal septum. Each chamber is divided into three regions –
- Vestibule: It is the anterior most part of nasal chambers bearing hairs which filters the dust particles.
- Respiratory region: It is rich in mucous glands and marked by nasal turbinates which traps the dust and humidify the air.
- Olfactory chamber: It is lined by olfactory epithelium which sense the smell.
Solution 3:
Turbinates: The respiratory region of nasal chamber is marked by three nasal turbinates.These are Ethmoturbinate, nasoturbinate and maxilloturbinates.
Function of turbinates: It increases the surface area, so that dust particles can be removed and air become humidified.
Solution 4:
Adam’s apple : It is a prominent elevation formed by the laminae of thyroid cartilage. It is more pronounced in male than female.
Solution 5:
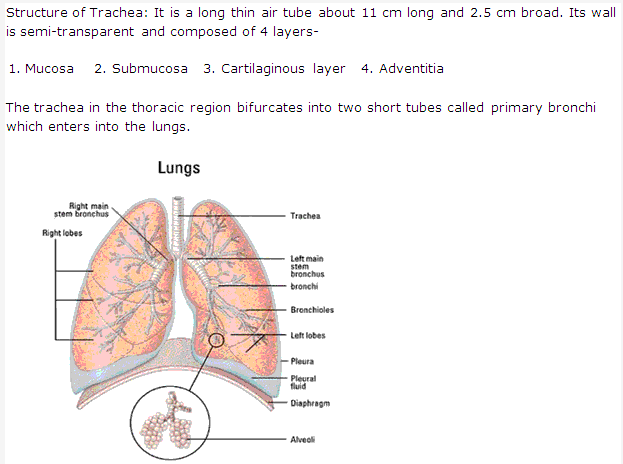
Solution 6:
The function of lecithin film in the lungs is to decrease the surface tension and keeps the alveoli open.
Solution 7:
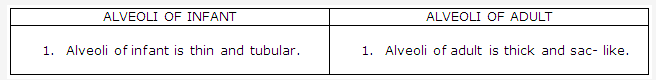
Solution 8:
Breathing: It is the physical process of taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide.
The function of diaphragm: It helps in breathing by contracting and relaxing thereby increase and decrease the volume of thoracic cavity. During inspiration diaphragm flattens while during expiration it becomes dome – shaped
Solution 9:
- Cough Reflex: It is a type of reflex whose stimulus is any foreign particle which results from deep inspiration followed by strong expiration that forcefully expel the air through the mouth.
- Sneeze Reflex: It is a type of reflex whose stimulus is in the nasal passage which causes spasmodic contraction of expiratory muscles that forecefully expel the air through the nasal passage.
- Eupnea: Eupnea is a normal breathing.
- Dyspnea: A condition in which breathing is painful.
- Apnea: A condition in which no breathing takes place.
Solution 10:
Internal respiration: It is the transport of oxygen in the blood from the lungs to the cells and the transport of carbon dioxide from the tissue cells into the blood and to the lungs.
Solution 11:
Respiratory quotient (RQ): It is the ratio of CO2 output to O2 uptake. It is denoted by R.
R = Rate of CO2 output / Rate of O2 uptake
RQ for carbohydrate = 1.00
RQ for fat = 0.70
RQ for protein = 0.85
Solution 12:
(i) Vestibule
(ii) Larynx
(iii) Alveoli
(iv) Lecithin
(v) Hyperpnea
(vi) Dyspnea
(vii) Apnea
(viii) Hypopnea
(ix) Thoracic cavity
Solution 13:
(i) Pleura
(ii) Eupnea
(iii) 500 cc
(iv) 0.70
(v) 38 ATP
Solution 14:
- Larynx = To produce voice
- Alveoli = To increase the surface area for exchange of gases.
- Conchae = It is also called turbinate and its function is to increase the surface area so that the dust particles can be removed and air become humidified.
- Epiglottis = It closes the glottis during swallowing of food.
- Lecithin covering = It lowers the surface tension and keeps the alveoli open.
- Cartilaginous rings = It prevents the collapsing of trachea.
Solution 15:
- Alveoli – Gaseous exchange
- Larynx – Sound production
- Thoracic cage – Breathing
PAGE NO:177
Solution 16:
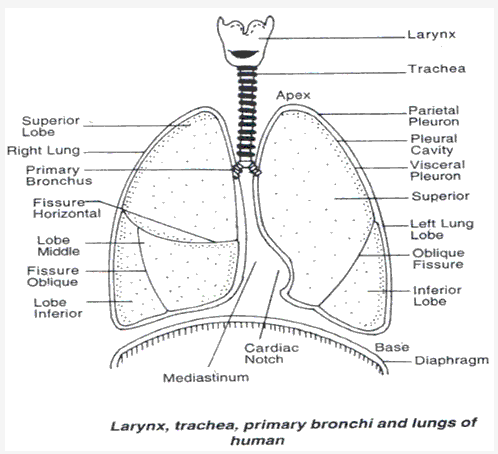
Solution 17:
(i)(b) Pleural membrane
(ii)(b) Alveoli
(iii)(d) All the above
(iv)(d) shows no change
(v)(d) 3000 – 4500 ml
(vi)(d) 158 and 116 mm Hg
