Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology – Bacteria and Fungi Their Importance
PAGE NO:127
Solution 1:
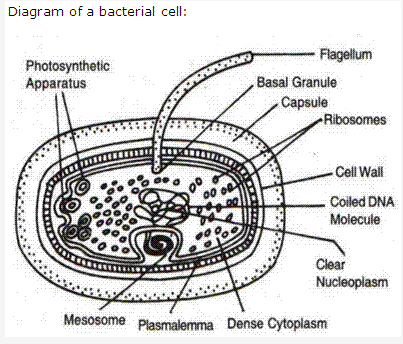
- Bacteria are a large group of unicellular, prokaryotic microorganisms.
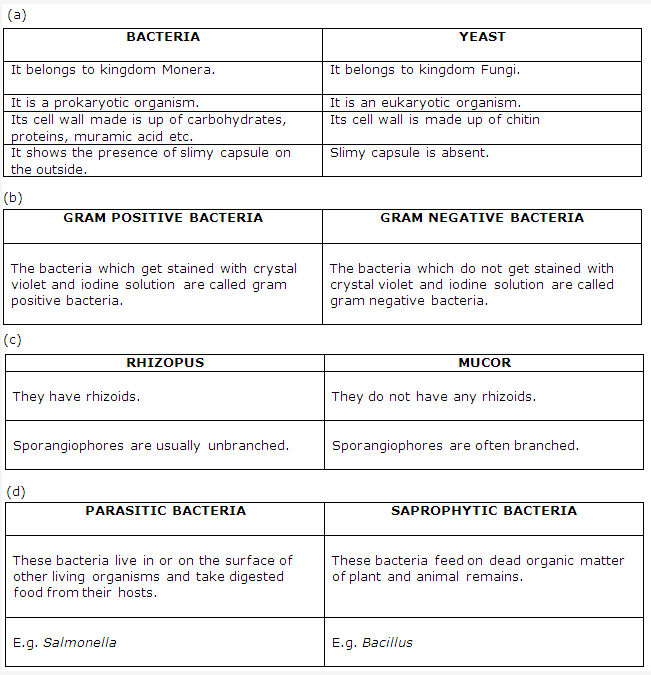
- The bacteria which do not get stained with crystal violet and iodine solution are called gram negative bacteria while those bacteria which get stained with crystal violet and iodine solution are called gram positive bacteria.
Solution 2:
- Bacteria shows the presence of cell wall, hence they are included under plants.
- Spore formation helps bacteria to survive during adverse environmental conditions. Hence it is a survival technique.
- Bacteria as friends :
Bacteria are useful to us in many ways like producing antibiotics, forming curd and cheese, tanning leather, producing various industrial products, nitrogen fixation, digesting cellulose etc.
Bacteria as foes:
They are harmful in many ways like causing diseases, bio-weapons , food spoilage etc. - Yeast is used in breweries since the fermentation activity of yeast produces different types of beverages like wine, beer, alcohol toddy etc. In bakeries, when yeast is added to the flour its fermentation results in the production of carbon dioxide which produces soft bread and other bakery products.
Solution 3:
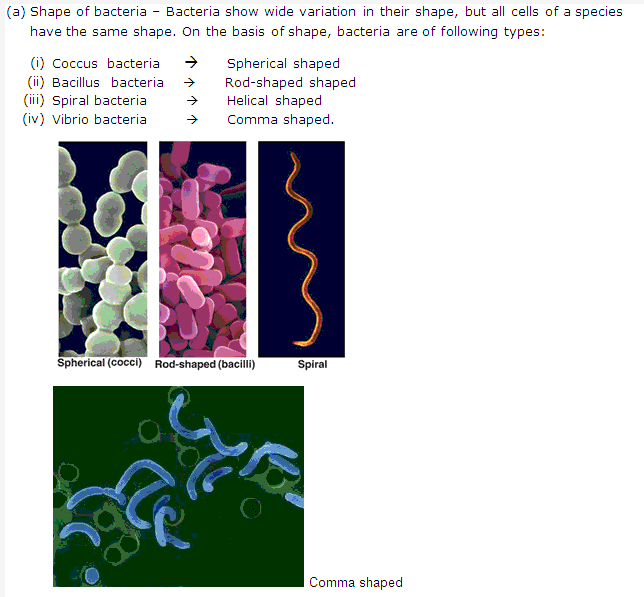
Solution 4:
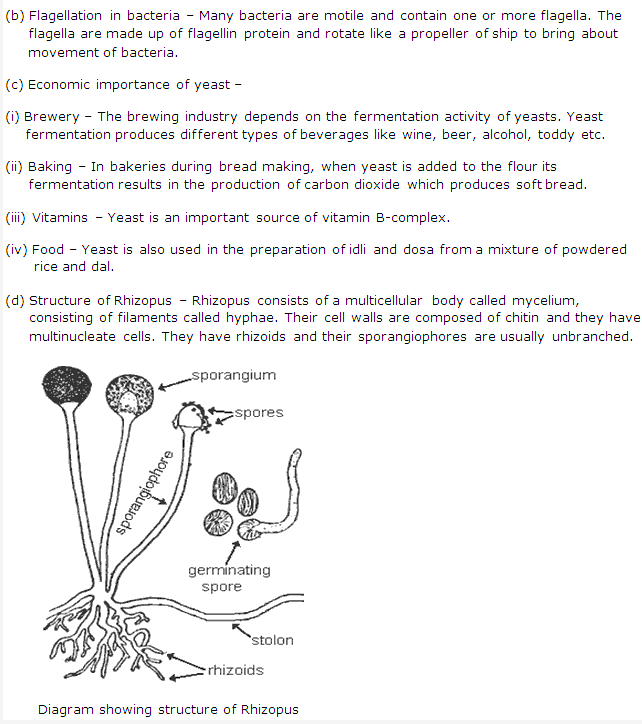
Solution 5:
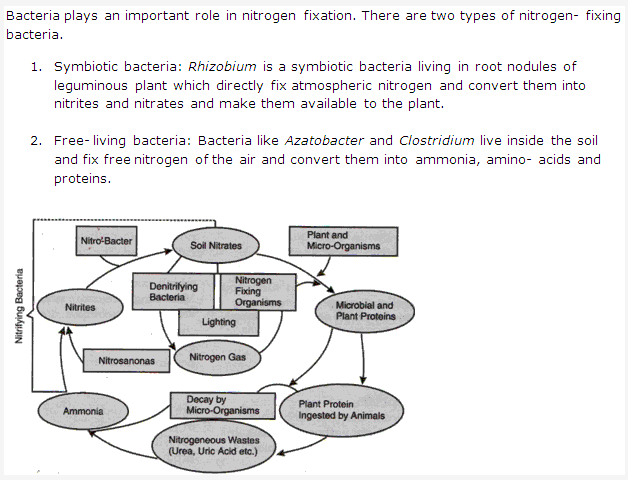
PAGE NO:128
Solution 6:
Solution 7:
(a) Penicillium notatum
(b) Aspergillus fumigatus
(c) Candida albicans
(d) Aspergillus
Solution 8:
(a) chitin
(b) saprophytic
(c) obligate aerobes
(d) Agaricus campestris
Solution 9:

Solution 10:
Fungi are cooked like vegetables or used in pulao or prepared as soups. Some common edible fungi are Agaricus, Ramaria, Clavaria, Morchella.
Also yeast is used in preparing idli and dosa from a mixture of powdered rice and dal.
Solution 11:
Yes. Many types of antibiotics are obtained from fungi which are used in medical sciences. Today about 25 types of antibiotics are commercially produced from moulds.
For example: Penicillin is obtained from the fungus Penicillium notatum.
Griseofulvin is extracted from the fungus Penicillium griseofulvum.
Solution 12:

Solution 13:
- (b) Leeuwenhoek
- (a) bacteria
- (b) Bacillus
- (a) Tuberculosis
- (d) Rhizobium
- (b) Lactobacillus
- (d) Agaricus
- (a) ethyl alcohol