Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry – Mole Concept And Stoichiometry
PAGE NO : 103
Solution 1:
- Gay-Lussac’s law: It states that ‘when gases react, they do so in volumes which bear a simple ratio to one another, and also to the volume of the gaseous product, provided all the volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure’.
- Avogadro’s law : It states that ‘Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of molecules’.
Solution 2:
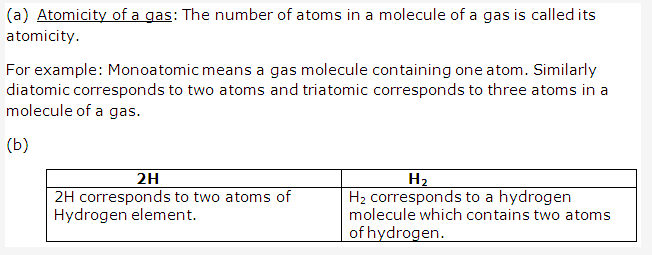
Solution 3:
When stating the volume of a gas, the pressure and temperature should also be given because the volume of a gas is highly susceptible to slight change in pressure and temperature of the gas.
Solution 4:

Solution 5:

Solution 6:

Solution 7:
- Gram atom: “The quantity of the element which weighs equal to its gram atomic mass is called one gram atom of that element”.
For example: The gram atomic mass of hydrogen is 1g. So, 1g of hydrogen is 1 gram atom of hydrogen. - Gram mole: “A sample of substance with its mass equal to its gram molecular mass is called one gram molecule of this substance or one gram mole”.
For example: Gram molecular mass of oxygen is 32 g. So One gram mole of oxygen is 32g.
Solution 8:

Solution 9:
Empirical formula:“Empirical formula of a compound is the formula which gives the number of atoms of different elements present in one molecule of the compound, in the simplest numerical ratio”.
Molecular formula: “Molecular formula of a compound denotes the actual number of atoms of different elements present in one molecule of the compound”.
Solution 10:
- The empirical formula of C6H6 is: CH
- The empirical formula of C6H12O6 is: CH2O.
- The empirical formula of C2H2 is: CH
- The empirical formula of CH3COOH is: CH2O.
Solution 11:
Three pieces of information conveyed by the formula H2O is that:
- It shows that there are 2 hydrogen atoms and 1oxygen atoms present in H2O.
- The hydrogen and oxygen atoms are present in simplest whole number ratio of 2:1.
- It represents one molecule of compound water.
Solution 12:
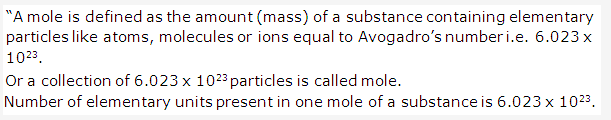
Solution 13:
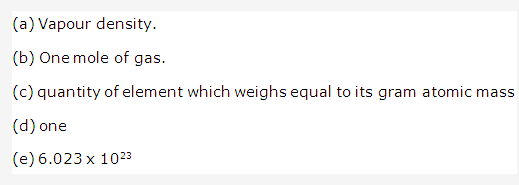
PAGE NO : 104
Solution 14:
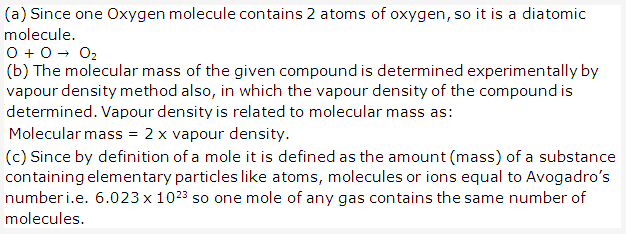
Solution 15:
- Na2SO4.10H2O.
- C6H12O6.
Solution 16:

Solution 17:
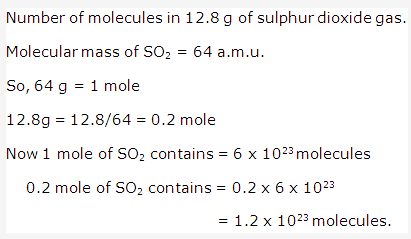
Solution 18:
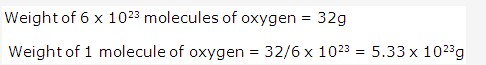
Solution 19:

Solution 20:

Solution 21:
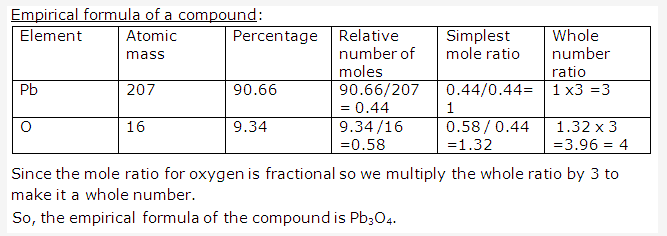
Solution 22:

Solution 23:
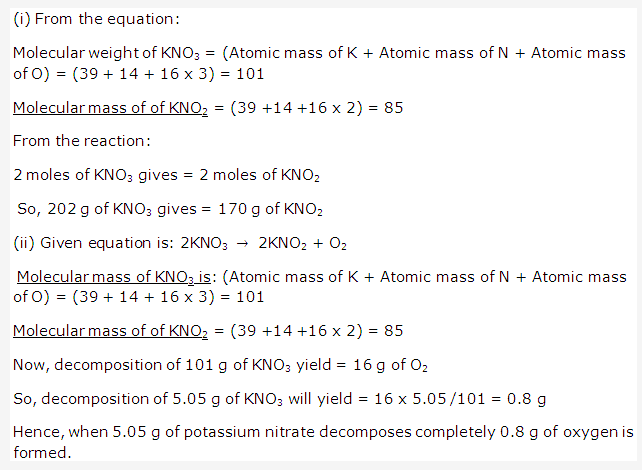
Solution 24:

PAGE NO : 105
Solution 25:

Solution 26:

Solution 27:
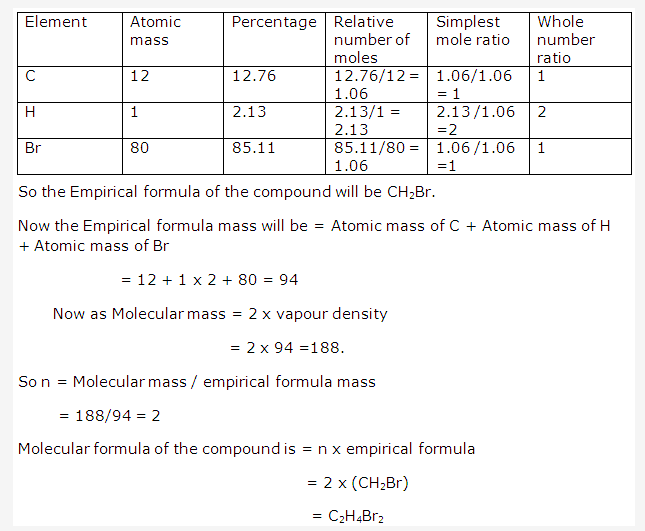
Solution 28:
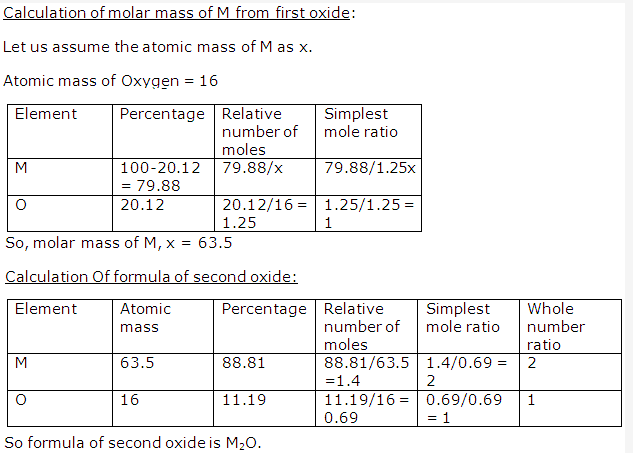
Solution 29:

Solution 30:

Solution 31:
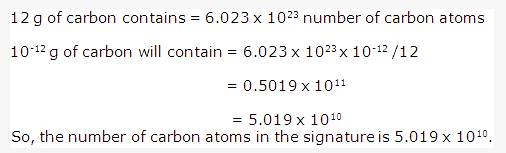
Solution 1996-1:

Solution 1996-2:

Solution 1996-3:

Solution 1996-4:
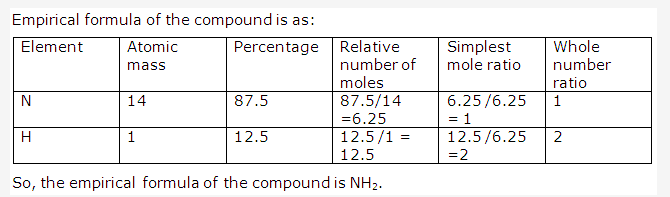
PAGE NO : 106
Solution 1997-1:

Solution 1997-2:
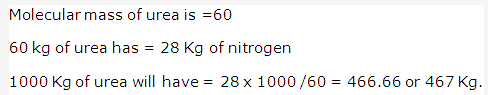
Solution 1997-3:

Solution 1997-4:

Solution 1998-1:
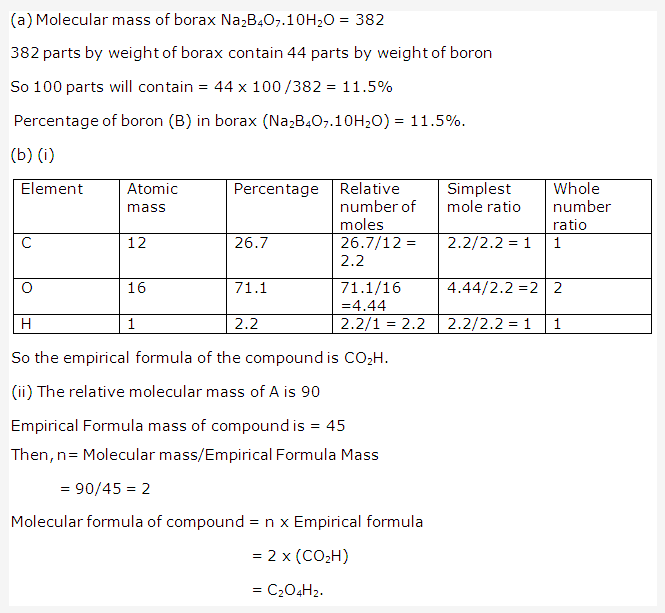
Solution 1998-2:

Solution 1999-1:

PAGE NO : 107
Solution 1999-2:

Solution 1999-3:

Solution 2000-2:
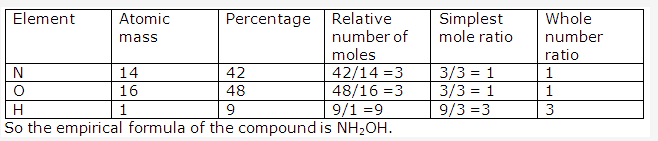
Solution 2000-1:

Solution 2000-1:
Gay – Lussac proposed this law.
Solution 2001-2:
Molecular mass of ethane = 30
According to Gay-Lussac’s law:
2 vol. of C2H6 requires= 7 vol. of oxygen
Vol. of C2H6 = 2 vol. = 100 L
Vol. of oxygen required = 7 vol. =350 L
Solution 2001-3:
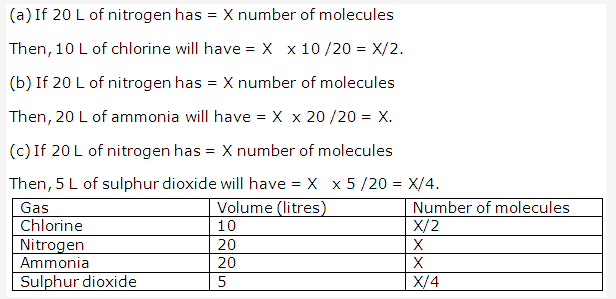
PAGE NO : 108
Solution 2001-4:
The term is vapour density.
Solution 2001-5:
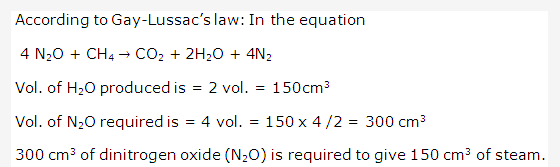
Solution 2001-6:

Solution 2001-7:
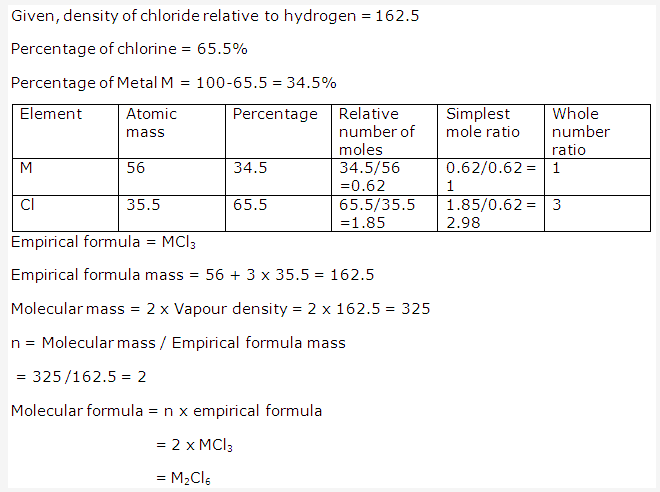
Solution 2002-1:
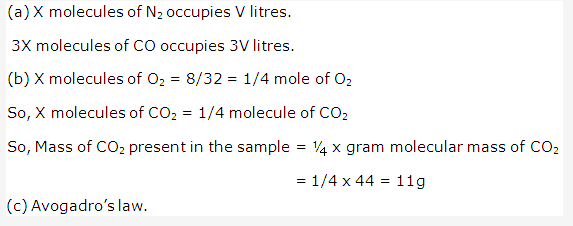
Solution 2002-2:

Solution 2002-3:
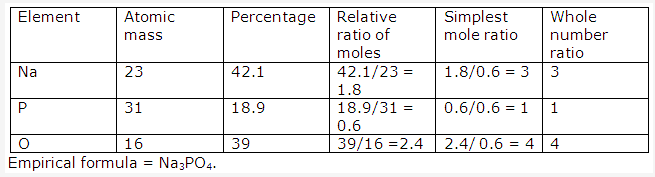
Solution 2003-1:

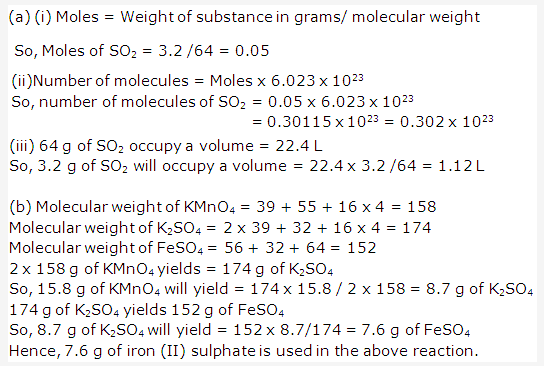
Solution 2004-1:
PAGE NO : 109
Solution 2004-2:

Solution 2005-1:

Solution 2006-1:

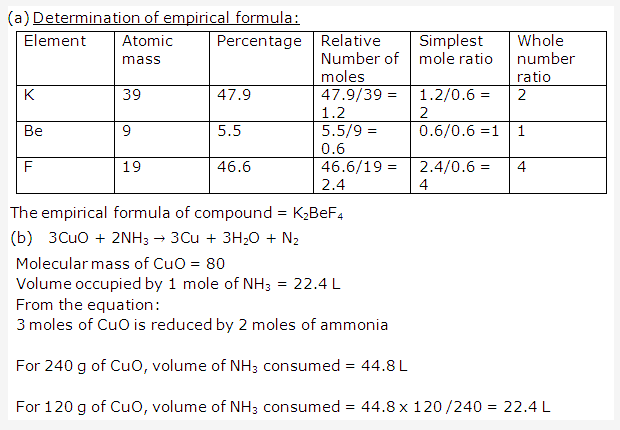
Solution 2006-2:
PAGE NO : 110
Solution 2006-3:

Solution 2006-4:

Solution 2007-1:

Solution 2007-2:
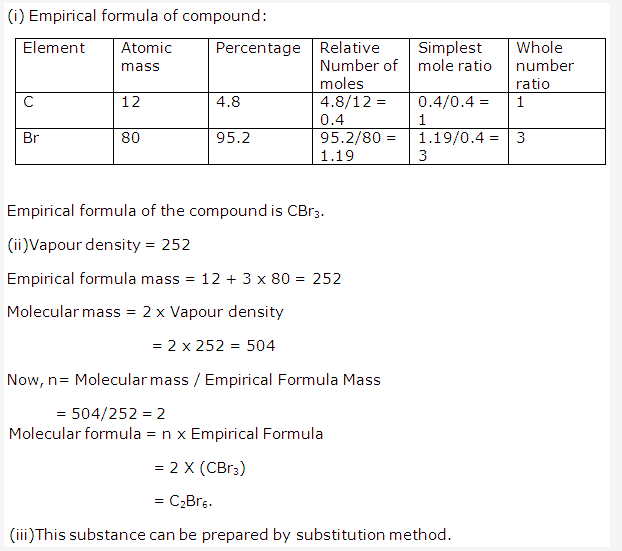
Solution 2008-1:
The gas laws which relates the volume of a gas to the number of molecules of the gas is avogadro’s law
PAGE NO : 111
Solution 2008-2:

Solution 2008-3:


Solution 2009-2:

Solution 2009-3:
The correct statement is that equal volumes of all gases under identical conditions contain the same number of molecules.
Solution 2009-4:

Solution 2009-1:
The relative molecular mass of the gas is 10.
