Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry – Analytical Chemistry
PAGE NO : 75
Solution 1:
- Cuprous salts = Colourless
- Cupric salts = Blue
- Aluminium salts = Colourless
- Ferrous salts= Light green
- Ferric salts = Yellow
- Calcium salts = Colourless
Solution 2:

Solution 3:

Solution 4:
K2SO4.
Solution 5:

Solution 6:

Solution 7:

Solution 8:

Solution 9:
Examples of amphoteric hydroxides are: Zn(OH)2, Al(OH)3.
Solution 10:

Solution 11:
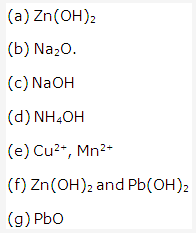
PAGE NO : 76
Solution 12:

Solution 13:
The chloride of a metal which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide is zinc chloride i.e. ZnCl2.
Solution 14:

Solution 15:
- PbO
- Al2O3
- Na2ZnO2
Solution 16:
- transition, Cr3+, Fe2+, MnO44-.
- Zn(OH)2
- NH4Cl
- Al2O3, Al
- NH4OH
Solution 1992-1:
- Addition of KCN
- Addition of excess of NaOH.
- Addition of excess ofNH4OH
Solution 1993-1:

PAGE NO : 77
Solution 1995-1:
- The metal ion present in solution A is Pb2+
. - The cation present in solution B is Cu2+. The probable colour of solution B is blue.
Solution 1996-1:

Solution 1996-2:
The solutions for the tests will be prepared by dissolving the given powders separately in water.
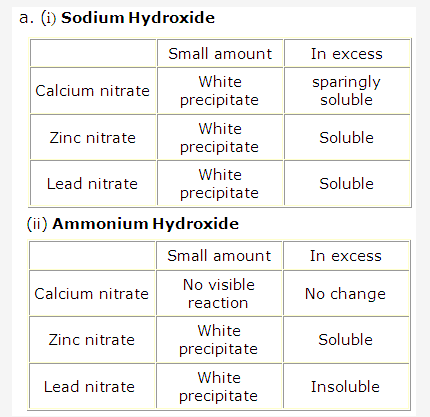
- Solution of Calcium carbonate:
Calcium carbonate is CaCO3 and contains Ca2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Ca2+ since its addition to calcium carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Ca(OH)2 which are sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
- Solution of Lead carbonate:
Lead carbonate is PbCO3and contains Pb2+ ions. Ammonium hydroxide solution NH4OH can be used to identify Pb2+ since its addition to lead carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Pb(OH)2 which are insoluble in excess of NH4OH. - Solution of Zinc carbonate:
Zinc carbonate is ZnCO3 and contains Zn2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Zn2+ since its addition to zinc carbonate solution will give white gelatinous precipitates of Zn(OH)3 which are soluble in excess of NaOH.
Solution 1996-3:

Solution 1997-1:
Solution 1998-1:

Solution 1999-1:

Solution 2000-1:
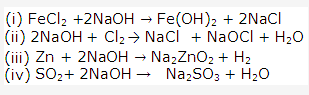
PAGE NO : 78
Solution 2001-1:

Solution 2003-1:
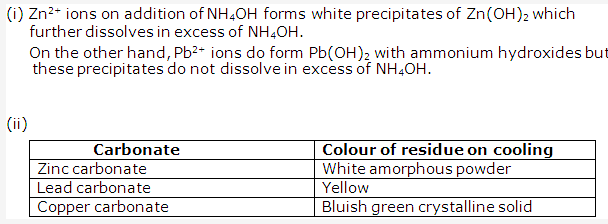
Solution 2003-2:

Solution 2004-1:

PAGE NO : 79
Solution 2005-1:
- B and E (Iron (II) sulphate and Magnesium sulphate)
- C and F (Iron (III) chloride and Zinc chloride)
- D (Lead nitrate)
- A (Copper nitrate)
- F (Zinc chloride)
Solution 2006-1:
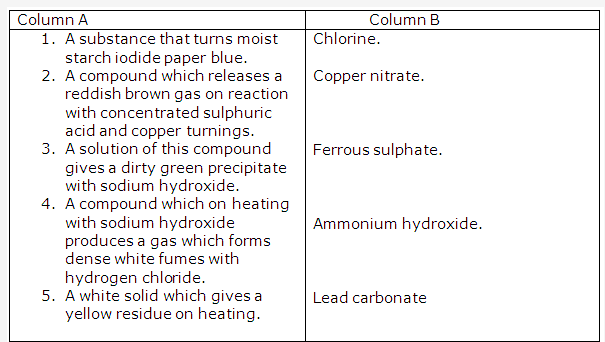
Solution 2009-1:
C ( Aluminium oxide)
Solution 2009-2:
- P is Ferric chloride
- Q is an ammonium salt
- R is ferrous sulphate
Solution 2009-3:
- When BaCl2
- solution is added to the given solution ZnSO4
- gives a white precipitate while no precipitate is obtained with ZnCl2 solution.
- When NaOH solution is added to the given solution, iron (II) chloride gives dirty green precipitate while reddish brown precipitate is obtained with iron(III) chloride.
