Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry – Ammonia
PAGE NO : 204
Solution 1:
Ammonia is found both in free state and in combined state. In free state, it is formed in traces amount by decaying urine and other organic matter.
In combined state, ammonia is found as ammonium salts mainly as ammonium chloride and ammonium sulphate.
Solution 2:
- (i) Liquid ammonia – Compressed ammonia gas at 6 atmospheric pressure. Chemical formula -NH3
- (ii) Liquor ammonia – It is saturated solution of ammonia in water. It is very dilute solution of ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
- A saturated solution of ammonia in water is called liquor ammonia Fortis.
Solution 3:

Solution 4:

Solution 5:

Solution 6:

Solution 7:

PAGE NO : 205
Solution 8:
- Liquid ammonia is used as refrigerant as:
- It is highly volatile
- It has high specific latent heat of vaporization. 1 mole (17g) of liquid ammonia vaporises by absorbing 5.7 kcals of heat from the surroundings, which is there by cooled.
- It easily liquefies under pressure at room temperature.
- Ammonia emulsifies fats and grease. Thus it is used to clean oils, fats and body grease etc. from clothes.
- Liquid hydrogen is dangerous to transport as it is highly combustible. Thus, hydrogen is converted to liquid ammonia and transported in cylinders. Later it is catalytically converted to hydrogen.
Key: Uses of ammonia
Solution 9:

Solution 10:

Solution 11:

Solution 12:
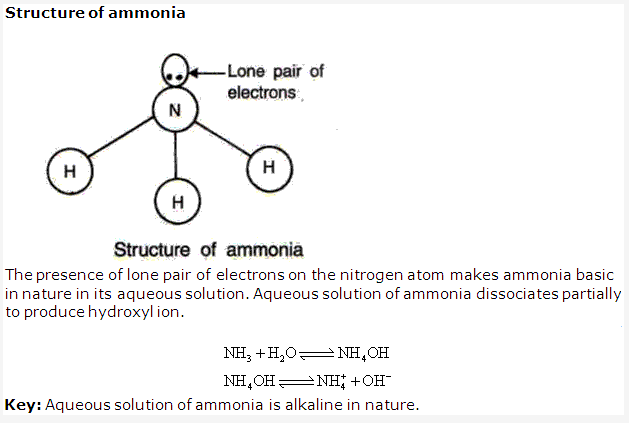
Solution 13:
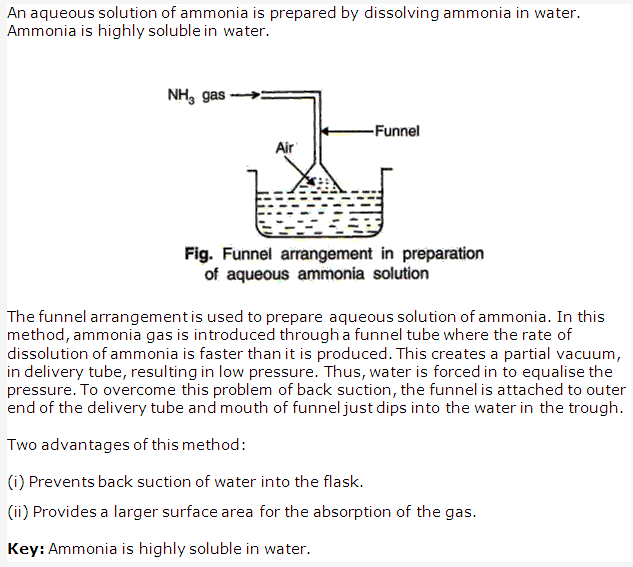
Solution 14:

Solution 15:

Solution 16:
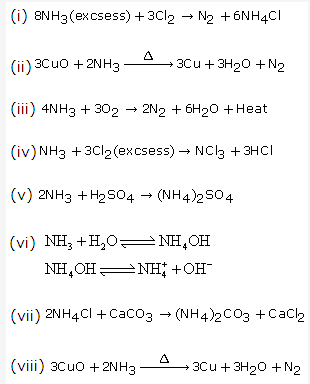
Solution 17:

PAGE NO : 206
Solution 18:
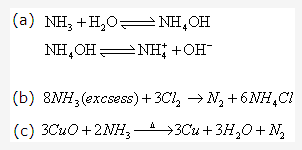
Solution 19:
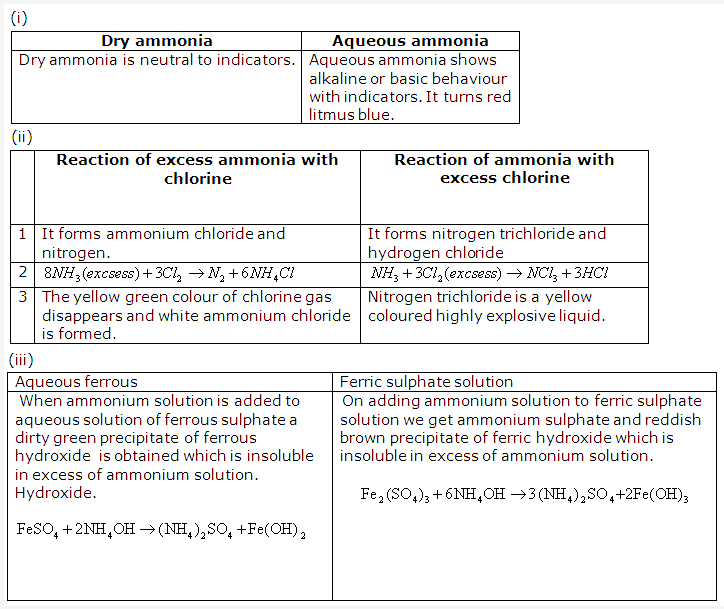
Solution 20:
- (i) Use of Ammonium Chloride
-Used in Leclanche cell and dry cell
(ii) Use of Ammonium Sulphate
-Used as a fertilizer
(iii)use of Ammonium nitrate
-Used in fireworks
(iv) Use of Ammonium Carbonate
-Used in baking powder - Test of ammonia and ammonium ions:
- Ammonia gas has a characteristic pungent smell
- A glass rod dipped in concentrated hydrochloric acid and is introduced into the gas produces thick white fumes of ammonium chloride.
Solution 21:
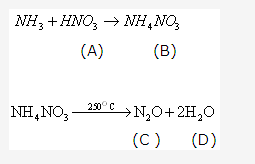
Solution 22:

Solution 1992-1:
Silver chloride
Solution 1992-2:
Ammonia is highly soluble gas in water and so cannot be collected over water.
Solution 1992-3:
Ammonia is the odd one out.
Ammonia forms weakly basic solution when dissolved in water.
The others give acidic solution when dissolved in water.
Solution 1992-4:
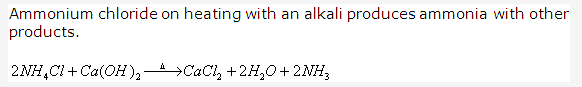
Solution 1992-5:
- Ammonia is used in the manufacture of fertilisers such as ammonium sulphate, ammonium nitrate, etc.
- It is used in the industrial preparation of nitric acid by Ostwald’s process.
Solution 1993-1:
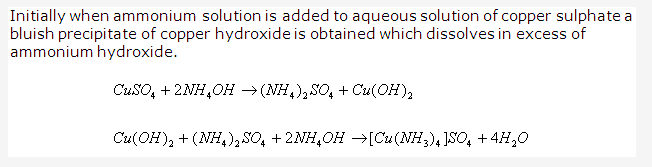
Solution 1993-2:
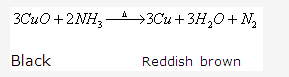
Solution 1994-1:

Solution 1994-2:

Solution 1994-3:
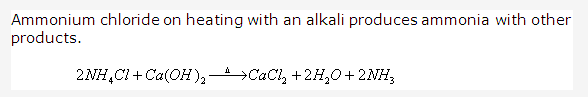
PAGE NO : 207
Solution 1995-1:
The cation is Cu2+ ion. Solution B is copper sulphate. It is bright blue in colour.
Solution 1995-2:
Three ways to identify ammonia gas:
- It is a pungent smell gas.
- It gives white precipitate when bubbles through a solution of lead nitrate.
- It gives a brown colour or precipitate when treated with Nessler’s reagent.
Solution1995-3:
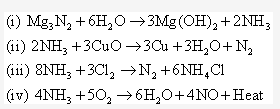
Solution 1995-4:
This reaction shows that ammonia is a reducing agent.
Solution 1995-5:
This process is called as Ostwald’s Process .The catalyst used is platinum.
Solution 1995-6:
During laboratory preparation of ammonia, it is passed through a drying tower containing quicklime (calcium oxide).
Ammonia is collected in an inverted dry gas jar by the downward displacement of air.
Solution 1995-7:
Ammonia gas
Solution 1996-1:
Ammonia forms ammonium hydroxide and turns red litmus blue as it is alkaline in nature.
Solution 1996-2:
![]()
Solution 1996-3:
Haber’s process is used in industrial preparation of ammonia.
Gaseous inputs in Haber’s process are dry nitrogen and dry hydrogen gas. They are mixed in the ratio of 1:3 by volume.
The following conditions favour maximum yield of ammonia:
- Low temperature
- High pressure
- Use of catalyst
The gases after reaction pass through condensing pipes of cooling chamber where ammonia gets liquefied and is collected in receiver.
Ammonia can also be collected by downward displacement of air.
Solution 1997-1:

Solution 1997-2:

Solution 1998-2:
Ammonium salts are used as fertilizers in fields.
Solution 1998-3:
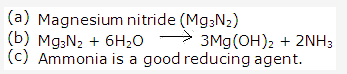
Solution 1998-1:
Dry ammonia are neutral to litmus. An aqueous solution of ammonia turns red litmus blue stating that it is basic in nature.
PAGE NO : 208
Solution 1998-4:

Solution 1998-5:

Solution 1991-1:
- Ammonia
- Nitrogen
Solution 2001-1:
Ammonia
Solution 2001-2:
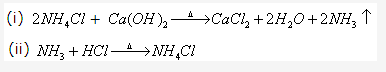
Solution2001-3:
![]()
Solution 2001-4:
Aqueous solution is acidic in nature due to presence of hydrogen ion.
Aqueous solution of ammonia is weakly basic in nature due to presence of hydroxyl ion.
Solution 2002-2:
Thermal dissociation.
Solution 2002-1:

Solution 2003-1:
![]()
Solution 2003-2:
Ammonia is collected by downward displacement of air.
Solution 2003-3:
Ammonia is highly soluble in water and so it is not collected over water.
Solution 2003-4:
Quick lime (calcium oxide) is used as a drying agent for ammonia.
Solution 2004-1:
![]()
Solution 2004-4:

Solution 2005-1:

PAGE NO : 209
Solution 2005-2:
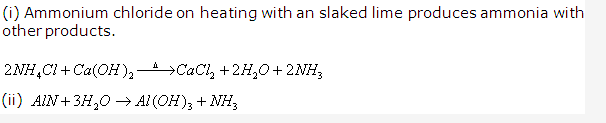
Solution 2006-1:

Solution 2006-2:

Solution 2007-1:
By the pungent smell of ammonia gas.
Solution 2007-2:
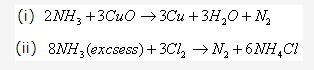
Solution 2008-1:
(c) Magnesium nitride
