Frank ICSE Class 10 Biology Solutions – Reproductive System
Solution 1:
- Testes
- Ovary
- Uterus
- Oviduct
- Fertilization
- Parthenogenesis
- Testes and ovaries
Solution 2:
- penis
- vagina
- oviduct
- female
- oviduct
Solution 3:
- Ovary: To produce ova and three female sex hormones i.e oestrogen, progesterone and relaxin.
- Fallopian tube: To transport eggs from ovary to uterus and it a site of fertilization.
- Uterus: To protect and provide nutrients for the developing embryo.
- Vagina: To receive the seminal fluid.
- Testes: To produce sperms and male sex hormone i.e. testosterone.
- Penis: deposition of semen into the female’s vagina.
Solution 4:
- Parthenogenesis: It is a type of asexual reproduction in which a female gamete or egg cell develops into an individual without fertilization.
- Asexual reproduction: It is the type of reproduction in which the offspring are formed without the production of gametes.
- Sexual reproduction: It is the type of reproduction in which the offspring are formed after the fusion of gametes.
- Dioceious: It is the individual / organism having male and female reproductive organs in separate individuals.
- Monoecious: It is the individual / organism having male and female reproductive organs in the same individual.
- Clone: It is a group of genetically identical cells or organisms asexually descended from a common ancestor.
Solution 5:
- Parturition: The expulsion of the foetus from the mother’s body is called parturition.
- Ovulation: The process of release of an egg from the ovary is called ovulation.
- Spermatogenesis: The production and development of sperms is called spermatogenesis.
- Gestation: The period in which an embryo develops in the uterus is called gestation.
- Implantation: The attachment of developing zygote to the uterine wall is called implantation.
Solution 6:
PAGE NO : 142
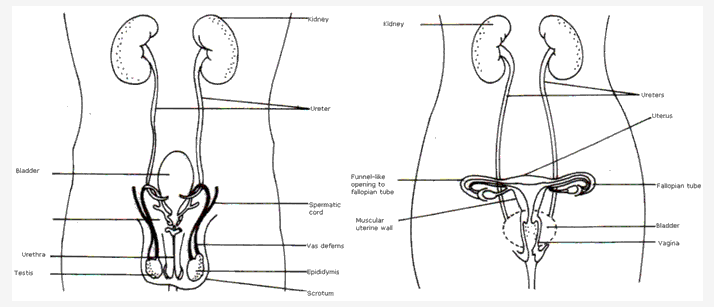
Solution 7:
- Graafian follicle
- Uterus
- Ovulation is the process of releasing of egg from the ovary.
- The hormones secreted by the ovary are: oestrogen and progesterone.
Solution 8:
- Peritoneum
- Ureter
- Backbone
- Rectum
- Seminal vesicle
- Glands
- Anus
- Vas deferens
- Epididymis
- Left testis
- Scrotum
- Penis
- Urethra
- Vascular erectile tissue
- Bladder
- Muscular wall of abdomen
The two functions of part 6 are :- Prostate gland secretes an alkaline milky secretion into semen that aids in sperm motility.
- Cowper’s gland also secretes a lubricant.
- The three components of urine are urea, uric acid, amino acids, glucose, sodium, potassium, vitamins etc.
- he main function of the part labelled 3 is backbone. Its function is to give support, movement and protection to the spinal cord.
Solution 9:
Solution 10:
- Graafian follicle
- Seminal vesicles and prostate gland
- Uterus
- Parturition
- Oviduct
PAGE NO : 143
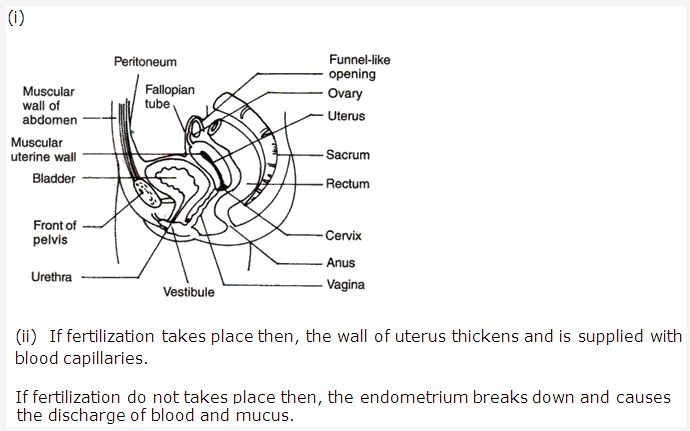
Solution 11:
- Fallopian tube
- Funnel like opening
- Uterus
- Sacrum
- Rectum
- Cervix
- Anus
- Vagina
- Front of pelvis
- Bladder
- Muscular uterine wall
- Muscular wall of abdomen
- Peritoneum
- Normally, after 28 days an ovary releases an egg.
- During coitus, sperm are released in the vagina.
- After ejaculation in vagina, sperms undergo fertilization where it fuses with an ovum of female to form zygote.
- The function of sacrum is to protect the pelvic organs or reproductive organs of female.
- The gestation period in human is 280 days.
Solution 12:
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
Solution 13:
False.
Pregnancy in women can be prevented by the method of tubectomy.
Solution 14:
Amnion.
Solution 15:
- Menarche
- Ovulation
- Menstruation
- Fertilization
- Implantation
Solution 16:
- (b) continuity of race
- (b) asexual reproduction
- (b) female gamete
- (c) Parthenogenesis
- (b) vagina
- (c ) castration
- (b) oviduct
- (c ) puberty
- (b) menarche
- (c ) 20-30C below the body temperature
- (d) menarche
- (b) 10 days
