Frank ICSE Class 10 Biology Solutions – Nervous System
PAGE NO 115
Solution 1:
- Central Nervous System
- Autonomic Nervous System
- Conus medullaris / Medullary cone
- Mixed neurons
- Neuroscience
- Sensory neurons
- Motor neurons
- White matter
- White matter
- Dura mater
- Neuron
- Meninges
- Cranium
- Neocortex / Neopallium
- Limbic system
- Corpora quadrigemina
- Olfactory Lobes
- Median fissure
- Agraphia
- Brain
- Aphasia
- Trigeminal nerve
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Dendrites
- Bipolar neuron
- Sclera
- Myopia
- Semicircular canal
- Rhodopsin
PAGE NO : 116
Solution 2:
- Ear pinna – The pinna or the external ear collects the sound waves from different directions and send them to the middle ear.
- External auditory meatus It forms a passage from the pinna to the eardrum.
- Cochlea – It converts vibrations into nerve impulses and thus helps in hearing.
- Semicircular canals – It responds to change in position and maintains balance.
- Lachrymal gland – It secretes a watery fluid which washes the surface of eyes.
- Eyelids – It blinks to clean the dust and grit from the cornea.
- Retina – It is a photosensitive layer to receive the image.
- Eye lens – It focuses the image on the retina.
- Pupil – It regulates the amount of light that enters the eye.
- Olfactory lobe – These are concerned with the sense of smell.
- Optic lobe – These are concerned with vision.
- Medulla oblongata – It controls involuntary functions of the body like – coughing, swallowing, breathing, heartbeat, etc.
Solution 3:
- Nephron
- Blind spot
- Myelin
- Olfactory lobe
- Cranial nerve
Solution 4:

Solution 5:
- Nerve impulse – It is an electrochemical change occurring in the membrane of a nerve fibre produced by a stimulus.
- Axon – It is a fibre like process of the neuron which carries impulses away from the cell body.
- Cyton – It is an oval, angular, polygonal or stellate body which contains a large central nucleus.
- Action potential – A momentary change in electrical potential on the surface of a cell, or a nerve or muscle cell, that occurs when it is stimulated, resulting in the transmission of an electrical impulse.
- Reflex action – It is an immediate and involuntary response to a stimulus.
- Yellow spot – It is the region of best vision where more cone cells are present.
- Blind spot – It is the region of no image formation because of lack of cone cells.
- Power of accommodation – It is the ability of the lens to focus on far and distant objects.
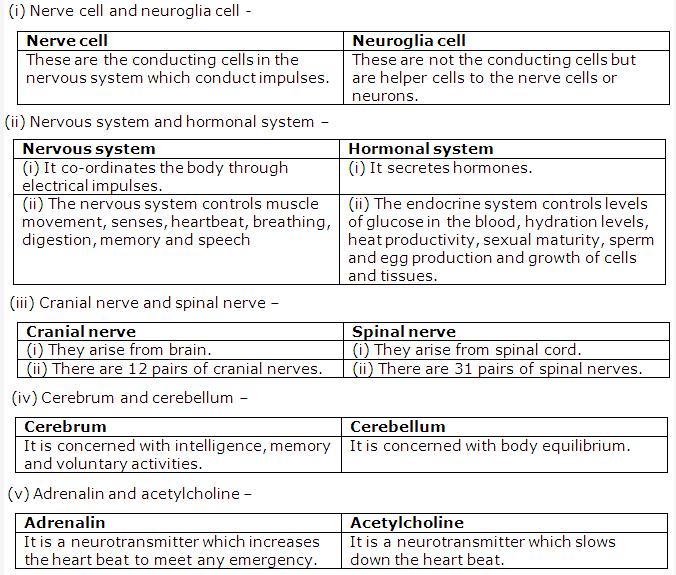
Solution 6:
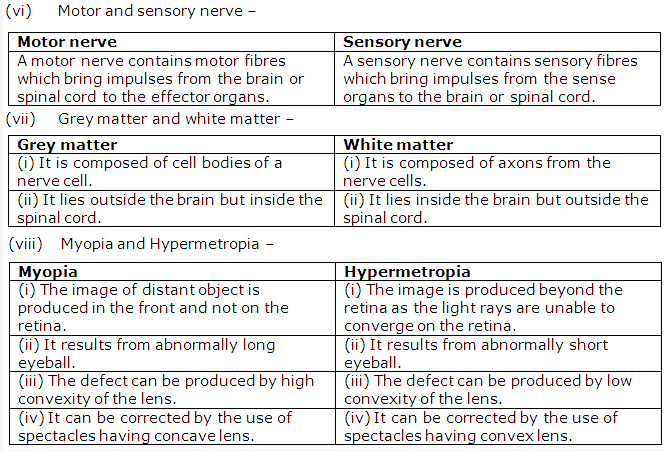
Solution 7:
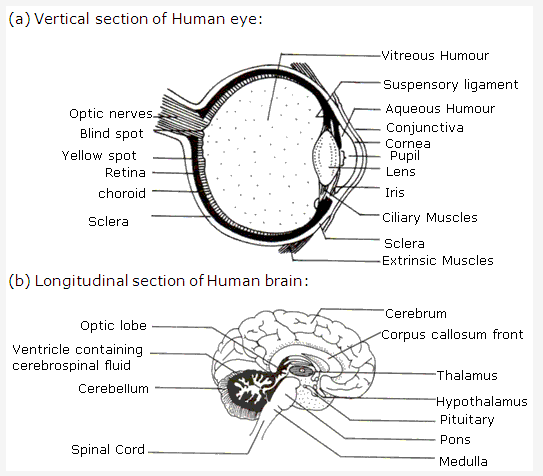
PAGE NO : 117
Solution 8:
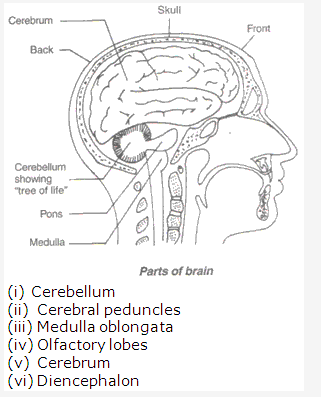
Solution 9:
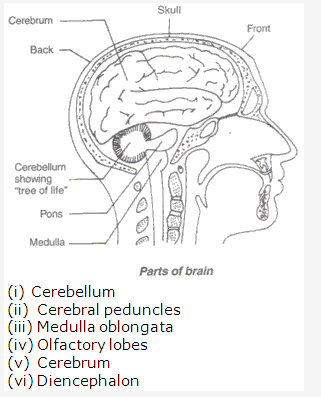
Solution 10:
- A – Cerebrum; B – Cerebellum; C – Medulla oblongata
- (A) Cerebrum – It is concerned with intelligence, memory and voluntary activities.
- Cerebellum – It is concerned with body equilibrium.
- Medulla oblongata It controls all involuntary activities like heart beat, respiration, etc.
The three protective membranes covering the brain are :- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Pia mater.
- Neuron is the basic unit of the brain.
PAGE NO : 118
Solution 11:
- Meninges – It is located around the brain and spinal cord.
- Ganglia – It is located outside the brain and spinal cord.
- Cerebellum – It is located behind cerebrum and above medulla oblongata in the brain.
- Nodes of Ranvier – It is located on the unmyelinated areas on the axon.
- Effector organs – It is located in muscle , gland or any organ of the body.
Solution 12:
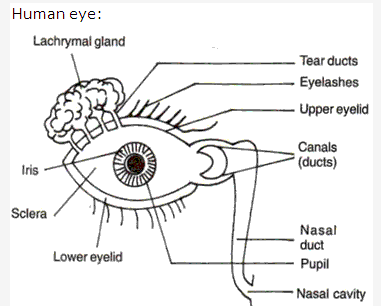
Solution 13:
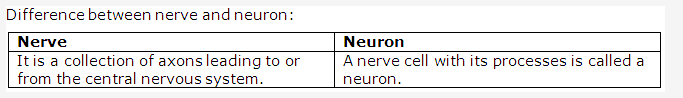
Solution 14:
- Iris: It is located in the eye. Its function is to protect the eyeball and controls the size of the pupil.
- Semicircular canals: It is located in the inner ear. These are concerned with the body equilibrium.
Solution 15:
Following are the two examples of reflex actions in our daily life :
- Removing hand suddenly when pricked by a thorn.
- Blinking of eyelids on exposure to light.
Solution 16:
- Reflex action – It is an immediate and involuntary response to a stimulus.
- Example of a conditioned reflex: Tying one’s shoe lace.
Solution 17:
- (a) Bone of skull
- (b) Inner ear
- (c) Eardrum
- (d) Bone of skull
- (e) Bone of middle ear
- (f) Middle ear
- (g) Air filled
- (ii) (b) Inner ear – It transmits the impulse to brain.
- (d) Bone of skull – It helps in fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds.
- (g) Air filled – It keeps the pressure in the middle ear equalized with pressure in the outside.
- (iii) The main division of the ear are: outer ear, middle ear and inner ear.
- (iv) Stirrup
- (v) The labyrinth is the inner ear which consists of utriculus, sacculus, cochlea and three semicircular canals.
Solution 18:
- A – Semi-circular canal
B – Utriculus
C – Sacculus
D – Cochlea
(ii) Auditory nerve.
(iii) 1. Utriculus and sacculus - Semi-circular canal
- Cochlea
- Sensory cells of organ of Corti
- Perilymph
Solution 19:
- Cochlea – It helps in hearing by transmitting impulses to the brain through auditory nerves.
- Fovea centralis – It is a point at retina where more cone cells are concentrated and thus produces sharpest vision.
- Three semicircular canals – It maintains the dynamic equilibrium.
- Retina – It prevents the reflection of light.
- Lachrymal glands – It produces tear to lubricate the eyeball.
Solution 20:
The arrangement of neurons in
Cerebrum: cytons are present outside and axons are inside
Spinal cord: cytons are present inside and axons are outside.
Solution 211:
Functions of medulla oblongata –
- It controls the involuntary activities like – respiration, circulation, digestion, etc.
- It controls the dilation and constriction of blood vessels.
Solution 22:
Reflex action – It is an immediate and involuntary response to a stimulus.
Example – 1. Blinking of eyelids on exposure to light .
2. Knee jerk.
PAGE NO : 119
Solution 23:
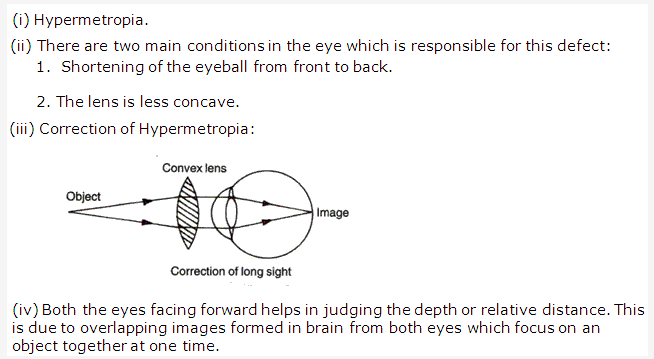
Solution 24:
Cone cells.
Solution 25:
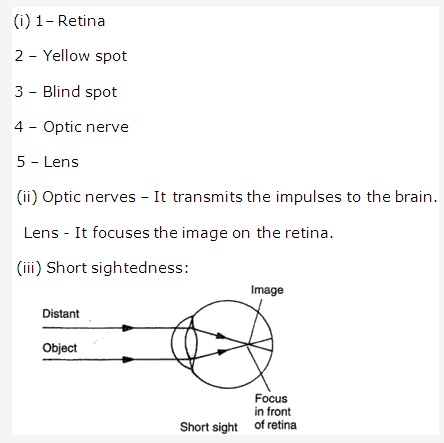
Solution 26:
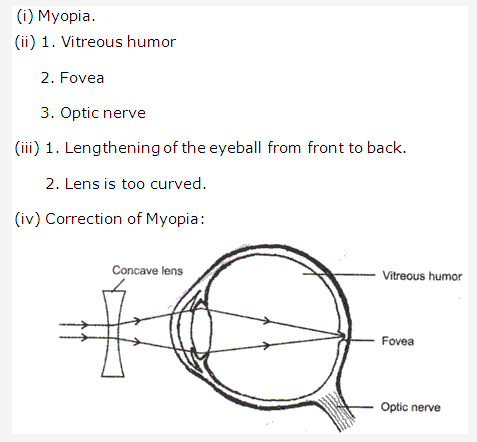
Solution 27:
- Cochlea: It helps in hearing by transmitting impulses to the brain through auditory nerves.
- Meninges: It provides protection to brain and spinal cord.
Solution 28:
One feels blinded for a short while on coming out of a dark room.This is called light adaptation of the eye.It is due to the constriction of the pupil to prevent the entry of light into the eye and pigment rhodopsin is bleached to reduce the sensitivity of the rods.
Solution 29:
- Iris
- Cerebrospinal fluid
Solution 30:
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
PAGE NO : 120
Solution 31:
- (d) nerve cell
- (b) cerebrum
- (a) 31
- (b) 12
- (a) dura mater
- (a) ear
- (c) rhodopsin
- (a) twilight vision
- (d) macula
- (d) two nerves
- (c) hearing
- (b) 31
- (a) eustachian
- (c) iris
- (b) cones
- (b) Ear
- (d) corpus callosum
- (d) eye
- (d) filter light
- (b) the two cerebral hemispheres
