Frank ICSE Class 10 Biology Solutions – Cell Division
PAGE NO-11:
Solution 1:
Cell division is important for a variety of reasons. One reason is that cell division is important for the growth of an organism. It is also important for cells to divide so that they can remain efficient. As all the cells are produced by the division of pre-existing cells, so each organism needs new cells for growth, replacement, repair and reproduction.
Solution 2:
The cell cycle is a series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication
Solution 3:
Interphase is a long resting phase in the cell cycle during which the cell grows, multiplication of DNA, synthesis of RNA and proteins takes place. Thus interphase is important in the cell cycle as it allows the cell to grow and develop into a mature cell before it is able to reproduce.
Solution 4:
Meiosis results in the formation of ova.
Solution 5:
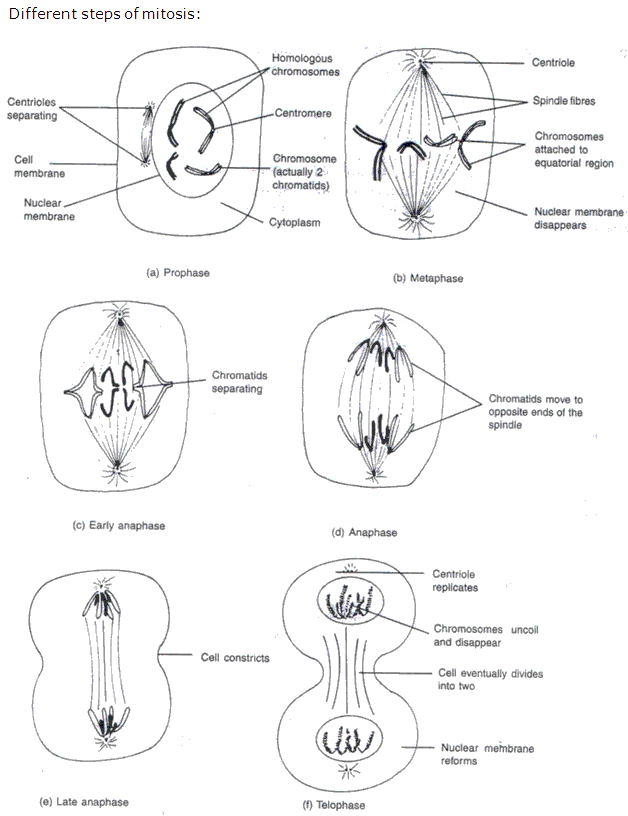
Solution 6:
In anaphase, the two chromatids separate at the centromere and begin to move in opposite direction towards either end of the spindle network called the poles. The chromosomes bend around the centromere showing a ‘V’ or ‘J’ or ‘L’ shaped structure based on the length of its arms.
Solution 7:
The different phases of mitosis are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
Solution 8:
Mitosis takes place in the body cells or somatic cells of the organisms.
Solution 9:
Mitosis is important because:
- It helps in the growth of tissues, organs and thus the entire organism.
- It helps in the repair of damaged tissues and organs.
- It is the method by which lower organisms reproduce.
- It helps in the maintenance of the hereditary characters by the replication of chromosomes
Solution 10:
Some characteristic features of mitosis are:
- It takes place in somatic cells.
- Chromosome number is preserved.
- Daughter cells produced are identical to the parent cell.
- It results in increase in the number of cells.
Solution 11:
Few important characteristics of Meiosis are:
- Meiosis occurs in germ cells only.
- It results in the formation of gametes.
- Chromosome number of the parent cell is halved.
- Daughter cells differ from the parent cell.
Solution 12:
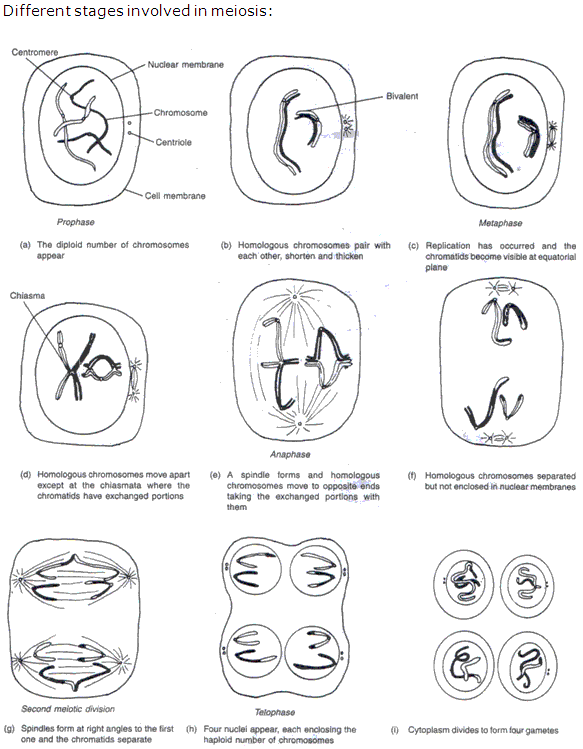
Solution 13:
In humans, meiosis occurs in testes producing sperms and in the ovaries resulting in ova.
Solution 14:
Significance of Meiosis:
- Due to meiosis, chromosome number is reduced to half in gametes and chromosome number of species is maintained.
- Genetic variations occur due to meiosis.
- The zygote on fertilization gets one maternal and one paternal chromosome in each homologous pair.
Solution 15:
Significance of Crossing over:
- As a result of crossing over, the paternal and maternal homologous chromosomes of an organism pair up and exchange certain portions of their chromatids which lead to genetic variations.
- It makes the genetic information in each haploid cell unique
Solution 16:

Solution 17:
No, cytokinesis is not necessary after karyokinesis in meiosis I. It generally takes place at the end of meiosis II when the four daughter cells are formed.
Solution 18:
- Karyokinesis – It is the nuclear division where nucleus divides into two.
- Cytokinesis – It is the division of cytoplasm in which the entire cell splits separating each nuclei.
- Chiasmata – is the point where two homologous non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material in chromosomal crossover during meiosis.
Solution 19:
In an animal cell, the cytoplasm between the two daughter nuclei constricts i.e. a furrow starts forming in the plasma membrane at the middle. This deepens towards the interior of the cell and the cytoplasm splits into two similar daughter cells.
In plant cells on the other hand, the constriction is not observed during cytokinesis. Instead a new cell wall is laid down along the equatorial region of the spindle network beginning at the centre. Thus, two distinct, daughter cells are cut off.
Solution 20:
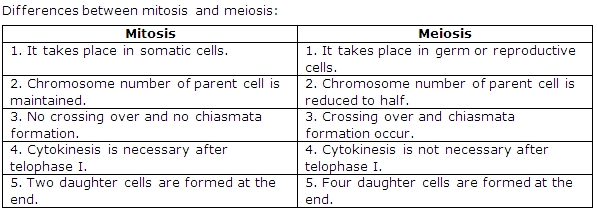
Solution 21:
Meiosis is a reductional division as in meiosis the number of chromosomes of parent cell is reduced to half in the daughter cells. Now, this reductional division is significant because it restores the number of chromosomes in a species.
PAGE NO-12:
Solution 22:
Yes, meiosis is responsible for maintaining the chromosome number of a species as meiosis being a reductional division involves formation of daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
Solution 23:
- If four cells undergo mitosis, eight daughter cells will be produced.
- Sixteen daughter cells will be produced.
- Eight daughter cells will be produced if four cells undergo amitosis.
Solution 24:
- Mitosis
- ATP
- Homotypic
- Reduction
- Mitosis
Solution 25:
- Anaphase in a plant cell
- A – Spindle fibre
B – Cell wall - The homologous daughter chromatids or chromosomes begin to move towards opposite poles.
- This type of cell division occurs usually in the somatic cells.
- Two daughter cells are formed from this type of cell division.
- The dividing cell shown is a plant cell because of the presence of cell wall and the absence of centriole.
Solution 26:
- A – Duplicated chromosomes
B – Centromere - The structure C is Spindle fibre. Its function is to help in the movement of chromosomes.
- The type of cell division is mitosis because all chromosomes appear to be same as there is no crossing over.
- Metaphase.
- Prophase occurs before metaphase and after metaphase anaphase takes place
Solution 27:
- (c) Meiosis
- (a) Mitosis
- (c) Both of these
- (a) 1/2
- (b) Growth and repair
- (a) Movement of chromosomes
- (a) Meiosis
- (d) Both (a) and (c)
- (b) Chromatin
- (c) Both (a) and (b)
- (b) Metaphase
- (a) Meiosis I
- (d) One cell, two nuclei
- (a) Meiosis
- (d) Telophase
- (d) Prophase
- (c) Telophase
