Food From Plants
Green plants are known as producers because they prepare their own food. They use light, air (carbon dioxide), water, and chlorophyll (present in their leaves) to prepare their food by the process of photosynthesis.
Different plant parts serve as sources of food for us. Fruits, vegetables, cereals, and pulses that we eat are obtained from different parts of a plant.
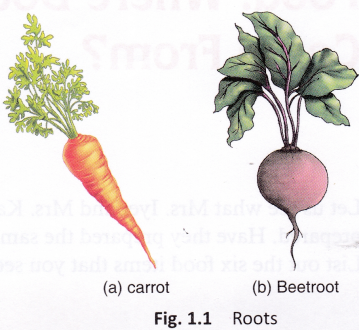
Roots: Roots of plants like carrot, radish, turnip, sweet potato, and beetroot are eaten.
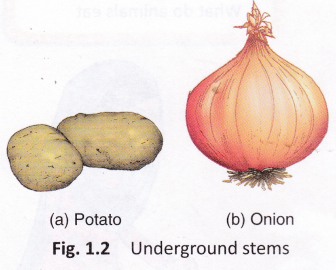
 Stems: Stems of certain plants are eaten. For example, the stem of sugarcane plant is eaten and is also used to make sugar. The stem and flower of banana plant is cooked and eaten in different parts of India. Certain plants have underground stems that we eat. Examples are potato, onion, garlic, and ginger.
Stems: Stems of certain plants are eaten. For example, the stem of sugarcane plant is eaten and is also used to make sugar. The stem and flower of banana plant is cooked and eaten in different parts of India. Certain plants have underground stems that we eat. Examples are potato, onion, garlic, and ginger.
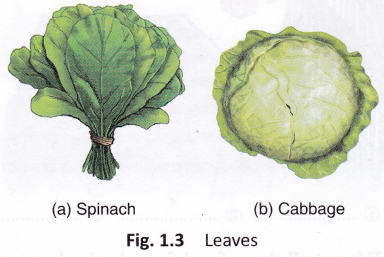
 Leaves: Leaves of plants like lettuce, spinach, cabbage, coriander, mint, and basil are eaten.
Leaves: Leaves of plants like lettuce, spinach, cabbage, coriander, mint, and basil are eaten.
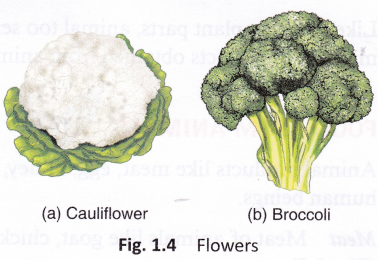
 Flowers: Flowers of certain plants like cauliflower, broccoli, and banana are also eaten.
Flowers: Flowers of certain plants like cauliflower, broccoli, and banana are also eaten.
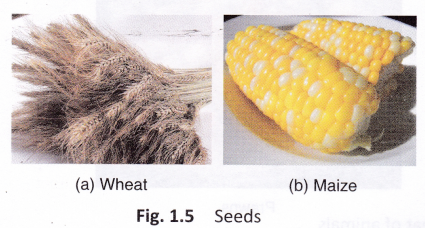
 Seeds: Pulses like mung bean, kidney bean, chickpea, and cereals (wheat, maize, and rice) that we eat are seeds of plants. Wheat grains are ground to make flour (atta) which is used to make chapattis. Cumin seeds, pepper, and cardamom that we eat as spices are also seeds of different plants.
Seeds: Pulses like mung bean, kidney bean, chickpea, and cereals (wheat, maize, and rice) that we eat are seeds of plants. Wheat grains are ground to make flour (atta) which is used to make chapattis. Cumin seeds, pepper, and cardamom that we eat as spices are also seeds of different plants.
Sprouted seeds (or sprouts) of mung bean and chickpea (Bengal gram) are very nutritious. Sprouting involves soaking seeds and draining the water and then leaving them till they germinate. Sprouts can be eaten raw as salads or cooked.
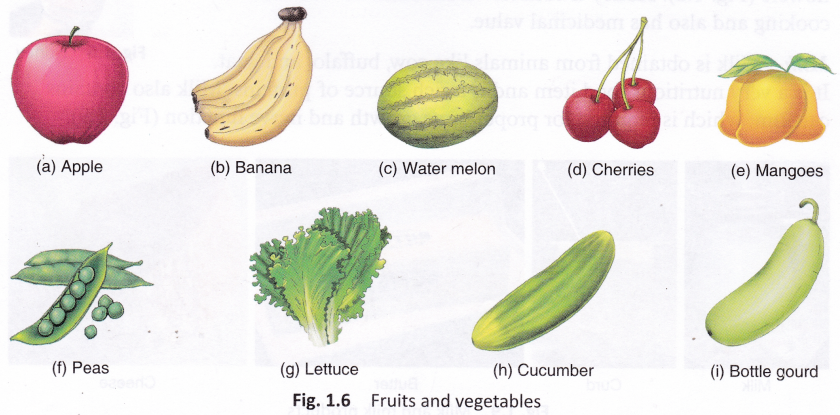
 Fruits and vegetables: Plants also provide us fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables: Plants also provide us fruits and vegetables