Expansion and Contraction in Solids, Liquids and Gases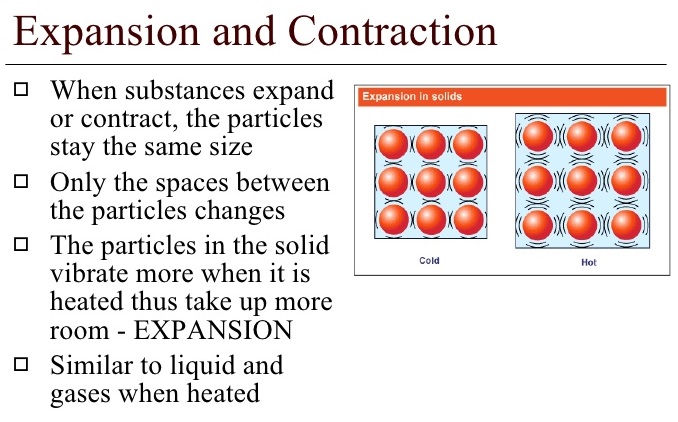
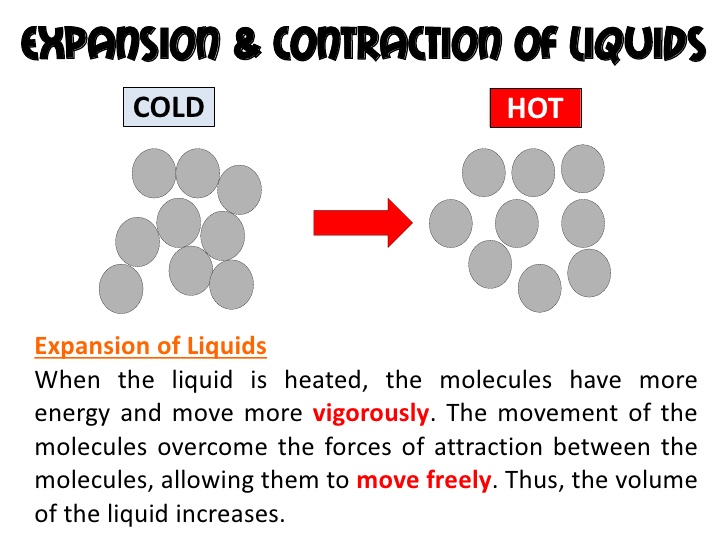
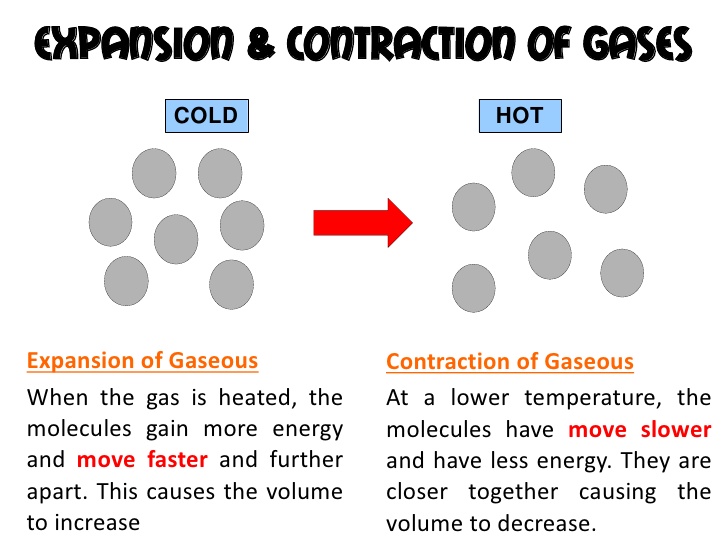
Some materials expand on heating and some contract on cooling. Heating makes the particles (that form the material) expand or become loose. Cooling makes the particles (that form the material) contract or become tight.
The amount of expansion differs in solids, liquids, and gases. Gases expand the most while solids expand the least. Table shows some examples of expansion.
Expansion in solids | Expansion in liquids | Expansion in gases |
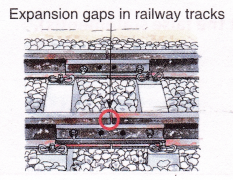
Railway tracks consist of two parallel metal rails joined together. Small gaps, called expansion gaps, are deliberately left between the rails as there is an expansion of the rails in hot weather.
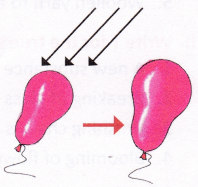
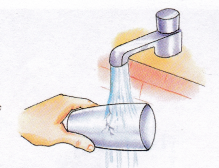
| Water expands on heating. Try this with the help of an adult. Take a glass filled with water to its brim. Pour the water into a container and heat It (do not boil). Now try to pour the water back into the same glass. The water overflows. | If you keep an inflated balloon in the sun for some time, what will happen? It will grow in size as the air inside it expands on taking heat from the surroundings.
|
Cooling does the opposite of heating. Cooling causes a material to contract. Solids contract the least while gases contract the most. Table lists some examples of contraction.
Contraction in solids | Contraction in liquids | Contraction in gases |
If we hold a very hot glass tumbler under cold water, it cracks. This is because the outer surface of the glass comes in direct contact with cold water and contracts more as compared to the inner surface.
| We observed that water expanded on heating. Can you say what will happen if the water is allowed to cool down and then poured back into the glass? Would it still overflow? No. This is because of contraction.
| If an inflated balloon is tied at the mouth of a bottle and the bottle is placed in ice-cold water, what will happen? The balloon will shrink in size, as the air inside the balloon contracts on cooling.
|
Applications of Expansion and Contraction
Expansion by heating can be used in several everyday activities.
- The jammed metal lid of a jam jar can be opened by heating. The jar is inverted and just the lid is dipped in hot water. After some time, the lid can be opened easily as the lid gets slightly expanded.
- The fact that materials expand on heating is used in thermometers. In many thermometers, mercury is used. When the bulb of the thermometer comes in contact with a hot object, the mercury expands and its level rises in the glass tube, indicating the temperature.
- Why the electric lines are never hung tautly between the poles? Wires in the outside
environment are subjected to extreme weather conditions ranging from acute hot to cold temperatures. A taut wire on contraction in winters can snap.