What are the different types of medicine?
Medicine:
- A medicine is used to prevent or cure a disease or to relieve pain.
- Medicines can be classified into traditional medicines and modern medicines.
What is a traditional medicine?
Traditional medicine
- Traditional medicines are derived from plants or animals.
- Traditional medicines are usually not processed.
- Any medicinal plant containing alkaloid is potentially toxic to the liver. Alkaloid is a nitrogen-containing alkaline compound found in plants.
- Traditional medicines can cause serious side effects.
- More research on the toxic and adverse effects of traditional medicines should be carried out in order to ensure the safety of these medicines to the public.
- Tables show the functions of some common medicinal plants and animals.
Table: Some common medicinal plants and their functions
| Medicinal plant | Function |
| Aloe vera (lidah buaya) | To treat skin wounds. |
| Centella asiatica (pegaga) | To treat depression and for longevity. |
| Eurycoma longifolia (tongkat ali) | To increase the male libido. |
| Orthosiphon aristatus (misai kucing) | To treat gout, diabetes and rheumatism. |
| Andrographis paniculata (hempedu bumi) | To treat diarrhoea, fever and diabetes. |
| Ocimum basilicum (selasih) | To treat coughs, colds and bronchitis. |
Table: Animals that are claimed to have medicinal properties
| Medicinal animal | Function |
| Sea cucumber | To treat Japanese encephalitis and |
| (gamat) | hole in the heart. |
| Centipede | To treat lockjaw and convulsions. |
| Ant | To treat hepatitis B. |
People also ask
- What is saponification in soap making?
- How do you make detergent?
- Explain the cleansing action of soap and detergent
- How are soaps and detergents different?
- What are the Advantages of Synthetic Detergents over Soap?
- Types of food additives and their functions
- The Existence of Chemicals
What is the definition of modern medicine?
Modern medicine:
- Modern medicines are made by scientists in laboratories and are based on substances found in nature.
- The active ingredients in the substances are identified, extracted and purified.
- The medicine is then tested repeatedly in many different ways before it is marketed. This allows scientists to make sure that the medicine is safe and to identify its side effects.
- Modern medicines may come in many forms such as liquids, powders, capsules and tablets.
- There are many types of modern medicines. These include analgesics, antibiotics and psychotherapeutic medicines.
Analgesics:
- Analgesics are medicines used to relieve pain without causing numbness or affecting consciousness.
- These medicines do not treat the cause of the pain but merely provide enough relief to the patients to allow them to carry out their daily routines.
- Examples of common analgesics are aspirin, paracetamol and codeine.
Aspirin is used for pain relief, particularly where there is inflammation involved, such as arthritic pain and dental pain.
- The active ingredient in aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid.
- Aspirin has the following structural formula.
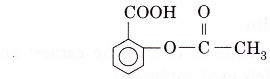
- Aspirin is acidic in nature.
The side effects of aspirin are as follows.
- It causes internal bleeding and ulceration. To reduce irritation of the stomach wall, aspirin is swallowed with plenty of water and is taken after food.
- It is believed to cause brain and liver damage if given to children with flu or chicken pox. Therefore, aspirin should never be given to children.
Paracetamol can be taken to relieve mild to moderate pain such as headaches, muscle and joint pains, backaches and period pains.
- Unlike aspirin, paracetamol can be given to children as it does not irritate the stomach or cause it to bleed.
- The side effects of paracetamol are rare when it is taken at the recommended dose.
- However, it causes skin rashes, blood disorders and acute inflammation of the pancreas when it is taken on a regular basis for a long time.
- An overdose of paracetamol can cause liver damage.
Codeine is an analgesic used in headache tablets and in cough medicines.
- Most codeine is synthesised from morphine.
- Codeine may cause drowsiness when it is taken.
- Abuse of this medicine may lead to addiction, depression and nausea.
Antibiotics:
- Antibiotics are used to kill or to slow down the growth of bacteria.
- They are used to treat infections caused by bacteria. They will not cure infections caused by viruses, such as colds and flu.
- Antibiotics are obtained from microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. Different antibiotics can fight different kinds of bacteria.
- Examples of antibiotics are penicillin and streptomycin.
Penicillin
- Penicillin is one of the earliest and most widely used antibiotics.
- Penicillin is extracted from the fungus, Penicillium notatum.
- This antibiotic is used to cure bacterial diseases such as tuberculosis (TB) and pneumonia.
Streptomycin
- Streptomycin is an antibiotic produced by soil bacteria of the genus Streptomyces.
- It is used to treat tuberculosis, whooping cough and some forms of pneumonia. Pneumonia is a serious illness affecting the lungs that makes breathing difficult.
Both penicillin and streptomycin can be broken down by the acid in the stomach. Therefore, these antibiotics are usually given by injection and are not taken orally.
The patient should take the full course of the antibiotics that the doctor prescribes to him even if he feels better.
This is to make sure that all the bacteria are killed. Otherwise, he may become ill again and the bacteria may become more resistant to the antibiotic. When this happens, the antibiotic is no longer effective. The doctor will then have to prescribe a different and stronger antibiotic to fight the same infection.
Side effects of antibiotics are:
(a) headache
(b) allergic reaction
(c) diarrhoea
Psychotherapeutic medicine:
- People with mental illnesses are not in control of their thoughts, feelings and behaviours.
- Psychotherapeutic medicines are used to alter abnormal thinking, feelings or behaviours.
- These medicines do not cure mental illness. However, they can reduce many of the symptoms of mental illnesses and help a person to get on with life.
- Psychotherapeutic medicines are divided into stimulant, antidepressant and antipsychotic.
Table: The functions and side effects of some psychotherapeutic medicines
| Psychotherapeutic medicine | Function | Example | Side effects |
| Stimulant | To reduce fatigue and elevate mood. | Methylphenidate, dextroamphetamine, amphetamine | A high dose or an excessive use of stimulants over long periods of time can lead to anxiety, hallucinations, severe depression, or physical and psychological dependence. |
| Antidepressant | To reduce tension and anxiety. | Tranquillisers | Tranquillisers cause drowsiness, poor coordination or light-headedness. An overdose of these drugs can lead to respiratory difficulties, sleeplessness, coma and even death. |
| Barbiturates | Barbiturates cause addiction. People who rely on barbiturates to fight insomnia sometimes kill themselves accidentally by taking an overdose. | ||
| Antipsychotic | To treat psychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia. | Chlorpromazine, haloperidol and clozapine | Antipsychotic medicines cause drowsiness, rapid heartbeats and dizziness. |
Drug abuse
- Taking drugs excessively and without a doctors prescription is called drug abuse.
- The use of certain drugs like ecstasy and ice produces harmful side effects.
(a) Ecstasy causes depression which can last for weeks after it is consumed.
(b) Ice causes stroke and injuries to the liver and kidneys.
