What are the Different Types of Asexual Reproduction
The ability of the living organisms to produce new living beings similar to themselevs is called reproduction.
Single organism commonly multiply through asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction is the process of formation of new individuals from specialised or unspecialised parts of a single parent without the formation and fusion of gametes. Because of the formation of new individuals from a parent, asexual reproduction is called uniparental.
Fission
It is a mode of asexual of asexual reproduction in which a parent undergoes division to form two or more individuals. Fission is of two types, binary fission and multiple fission.
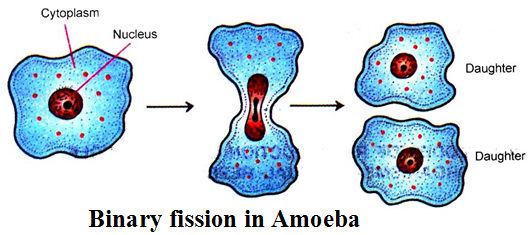
Binary Fission :
It means ‘splitting into two’. In binary fission, the nucleus or nuclear matter elongates and then divides into two. It is followed by cleavage of cytoplasm in between the two daughter nuclei to form two daughter individuals.
Read More:
Methods of Asexual Reproduction :
Multiple Fission :
- In multiple fission, many individuals are formed from a single individual.
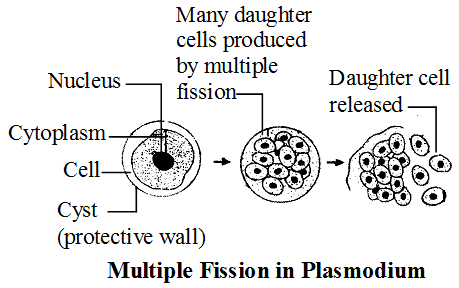
- The nucleus of cell divides repeatedly, producing many nuclei.
- Each nucleus is surrounded by a small amount of cytoplasm & many daughter cells are produced within the cyst.
- The cyst breaks up under favourable conditions & small off springs are liberated.
- In plant, multiple fission is seen in many algae & in animals, a common example of multiple fission is that of the malarial parasite (Plasmodium).
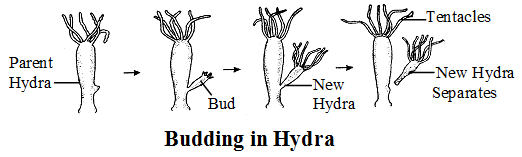
Budding :
- In budding a small part of the body of the parent organism grows out as a ”bud” which then detaches and become new organism.
- The nucleus of the parent divides and one of the daughter nuclei passes into the bud.
- The bud detaches itself from the parent body & becomes a new individual after growing to full size.
- In plants, budding takes place in yeast and in animals budding is seen in hydra & sponges.
Spore Formation :
- In spore formation, the parent plant produces hundreds of tiny spores which can then produce new plants. During the growth of a fungus plants like. Rhizopus, tiny round bulb like structure called sporangium develops at the top of the hyphae.
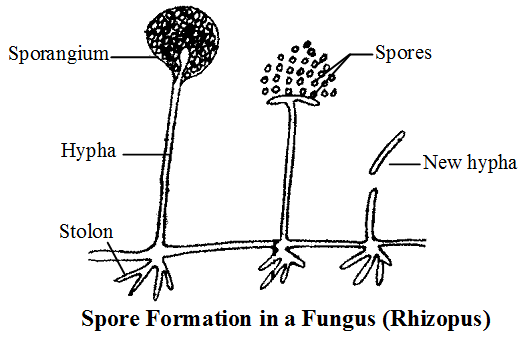
- Non-flowering plants like fungi (mucor, Rhzopus, penicillium) bacteria, ferns or mosses, formation of spores is method of reproduction.
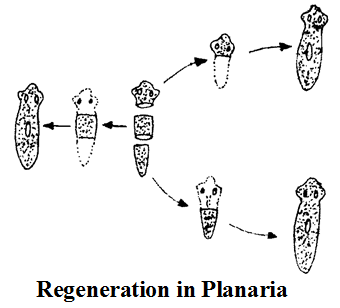
Regeneration :
- It is the ability of an organism to replace its lost body parts.
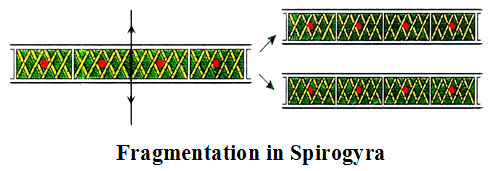
- A special case of regeneration is fragmentation, in which a parent multicelluar organism on maturing breaks up naturally to produce two or more daughter organisms.
- Among plants, filamentous algae like spirogyra reproduce by this method.
- Hydra, Planaria & Sponges exhibit regeneration.
Fragmentation :
It is the process of bracking up of the body of an organism into two or more parts called fragments, each of which grows into a new individual. Fragmentation is quite common in algae, fungi, bryophytes and some marine ribbon worms. It is caused by mechanical disturbance, chemicals, death and decay of older parts, emptying of intervening cells, etc. Fragmentation is common method of multiplication in green filamentous alga, Spirogyra (figure). Here all the cells are capable of photosynthesis, growth and division. Therefore, each fragment grows into a new filament.
Vegetative Propagation :
In vegetative propagation, new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants like stems, roots & leaves, without the help of any reproduction. It can be achieved naturally or artificially.
There are two ways of vegetative propagation.
(a) Natural Vegetative Propagation :
Various sturcture that take part in this type of reproduction are roots, stem, leaves.
Natural Vegetative Propagation by Roots :
In some plants like Dahlia, sweet potato, etc., the adventitious roots become thick, swollen and tuberous due to storage of food.
Natural Vegetative Propagation by Stems :
Some plants reproduce by means of stems. They may be aerial like runners, suckers or underground like ginger (rhizome), potato (tuber), and sugarcane.
Natural Vegetative Propagation by Leaves :
The fleshy leaves of Bryophyllum bear adventitious buds in the notches along the leaf margin.
(b) Artificial Vegetative Propagation :
Some plant growers have developed artificial methods of vegetative propagation like cutting, layering and grafting which are used in agriculture and horticulture.
