Difference Between Shares And Debentures: In the world of finance, two commonly used terms are shares and debentures. Both are important tools used by companies to raise capital, but they are fundamentally different from each other. In this article, we will explore the definitions, characteristics, differences, uses, and applications of shares and debentures.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more. You can get more information through the aplustopper about the differences between shares and debentures.
I. Introduction
Shares and debentures are two types of financial instruments that are used by companies to raise capital. Shares represent ownership in a company, while debentures represent a loan to a company. Understanding the differences between shares and debentures is important for investors, company executives, and anyone interested in finance.
II. Definition And Characteristics Of Shares
Shares represent ownership in a company. When a person buys a share, they become a shareholder of that company. There are two types of shares: common shares and preferred shares.
- Common shares give shareholders the right to vote at shareholder meetings and receive dividends, but they have a lower priority in case of liquidation. Preferred shares give shareholders a higher priority in case of liquidation and usually pay a fixed dividend, but they do not have voting rights.
- Shares have several characteristics. They represent a portion of ownership in a company and give shareholders the right to vote at shareholder meetings. They also give shareholders the right to receive dividends, which are a portion of the company’s profits paid out to shareholders.
III. Definition And Characteristics Of Debentures
Debentures represent a loan to a company. When a person buys a debenture, they are lending money to the company for a fixed period of time at a fixed interest rate.
- Debentures are usually secured against the assets of the company, which means that the assets can be sold to repay the debt if the company cannot repay the loan.
- There are two types of debentures: convertible debentures and non-convertible debentures. Convertible debentures can be converted into shares of the company at a fixed price, while non-convertible debentures cannot.
- Debentures have several characteristics. They represent a loan to a company and pay a fixed interest rate. They are usually secured against the assets of the company and have a higher priority in case of liquidation.
IV. Differences Between Shares And Debentures
Shares and debentures are fundamentally different from each other. The main differences between shares and debentures are in a tabular form:
| SHARES | DEBENTURES |
|---|---|
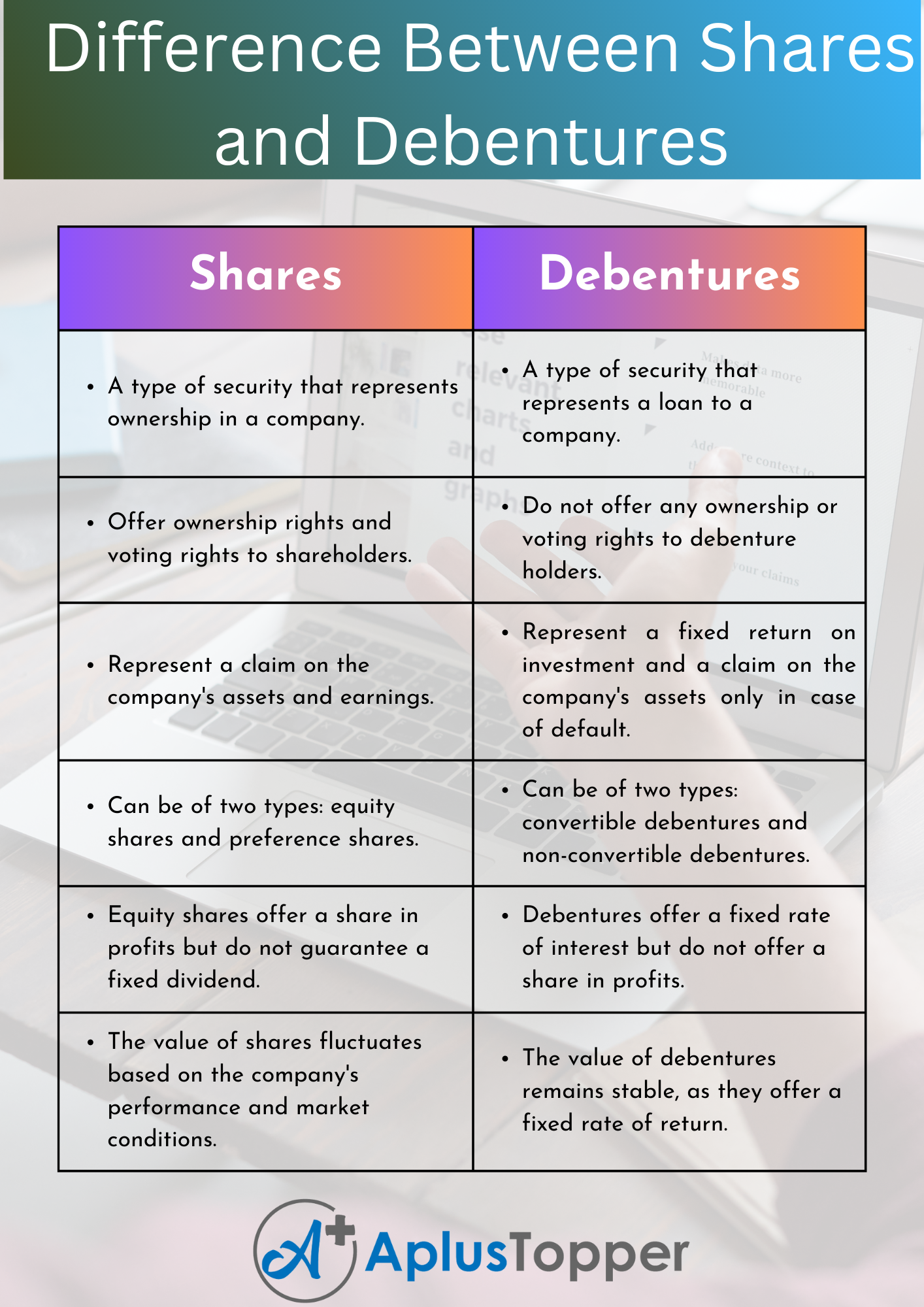
| A type of security that represents ownership in a company. | A type of security that represents a loan to a company. |
| Offer ownership rights and voting rights to shareholders. | Do not offer any ownership or voting rights to debenture holders. |
| Represent a claim on the company’s assets and earnings. | Represent a fixed return on investment and a claim on the company’s assets only in case of default. |
| Can be of two types: equity shares and preference shares. | Can be of two types: convertible debentures and non-convertible debentures. |
| Equity shares offer a share in profits but do not guarantee a fixed dividend. | Debentures offer a fixed rate of interest but do not offer a share in profits. |
| The value of shares fluctuates based on the company’s performance and market conditions. | The value of debentures remains stable, as they offer a fixed rate of return. |
| Shares have a higher potential for capital appreciation, but also higher risk. | Debentures offer lower risk, but a lower potential for capital appreciation. |
| The company can issue new shares through a rights issue or bonus issue. | The company can issue new debentures through a public issue or private placement. |
| Shareholders have the right to attend and vote in shareholder meetings. | Debenture holders do not have the right to attend or vote in shareholder meetings. |
- Ownership vs. loan: Shares represent ownership in a company, while debentures represent a loan to a company.
- Voting rights vs. no voting rights: Shareholders have the right to vote at shareholder meetings, while debenture holders do not.
- Dividends vs. interest: Shareholders receive dividends, which are a portion of the company’s profits, while debenture holders receive interest, which is a fixed payment.
- Risks and returns: Shares are riskier than debentures, but they also offer a higher potential return.
- Priority in case of liquidation: Debenture holders have a higher priority in case of liquidation than shareholders.
V. Uses And Applications
Shares and debentures are used by companies to raise capital. Companies can issue shares to raise money from investors, and they can issue debentures to borrow money from investors. The choice between shares and debentures depends on the company’s needs and goals.
- Shares are used by companies that want to raise equity capital. By issuing shares, companies can raise money without taking on debt. This can be beneficial for companies that want to expand or invest in new projects. Shares also give companies access to a large pool of investors, which can be beneficial for raising large amounts of capital.
- Debentures are used by companies that want to raise debt capital. By issuing debentures, companies can borrow money from investors without giving up ownership or control of the company. This can be beneficial for companies that want to raise capital without diluting their ownership. Debentures also offer a fixed interest rate, which can be attractive to investors who are looking for a steady income stream.
VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, shares and debentures are two important financial instruments that are used by companies to raise capital. Shares represent ownership in a company and give shareholders the right to vote at shareholder meetings and receive dividends. Debentures represent a loan to a company and pay a fixed interest rate. They are usually secured against the assets of the company and have a higher priority in case of liquidation.
- Understanding the differences between shares and debentures is important for investors, company executives, and anyone interested in finance. The choice between shares and debentures depends on the company’s needs and goals. Companies that want to raise equity capital can issue shares, while those that want to raise debt capital can issue debentures.
- Investors should carefully consider the risks and potential returns of both shares and debentures before making an investment decision. Shares offer a higher potential return, but they are also riskier than debentures. Debentures offer a fixed income stream, but they are also subject to the credit risk of the issuing company.
- Overall, shares and debentures are important tools that enable companies to raise capital and investors to earn a return on their investment. By understanding the differences between these financial instruments, investors can make informed investment decisions and companies can make strategic financing decisions.
Read More: Plus Two Business Studies Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10
FAQs On the Difference Between Shares And Debentures
Question 1.
What is the difference between shareholders and debenture holders?
Answer:
Shareholders and debenture holders are two distinct types of investors in a company. The main differences between shareholders and debenture holders are:
- Ownership: Shareholders are the owners of the company, while debenture holders are creditors who have lent money to the company.
- Returns: Shareholders earn returns in the form of dividends and capital appreciation, while debenture holders receive fixed interest payments on their investments.
- Risk: Shareholders bear the risk of the company’s performance and are exposed to fluctuations in the stock market, while debenture holders have a lower risk as their investments are secured by the assets of the company.
- Voting rights: Shareholders have the right to vote on important company decisions, while debenture holders do not have voting rights.
- Priority in liquidation: In case of liquidation or bankruptcy, debenture holders have priority over shareholders in getting their money back.
Question 2.
What is the difference between shares debentures and equity?
Answer:
Shares and debentures are financial instruments used to raise funds by a company. Shares represent ownership in the company and offer voting rights to shareholders. Debentures, on the other hand, are a type of debt instrument that provide a fixed rate of return to the debenture holders. Equity refers to the value of the assets after all debts and liabilities are paid off. It represents the residual interest in the company that belongs to shareholders.
Question 3.
Are debentures better than shares?
Answer:
There is no straightforward answer to this question as it depends on various factors such as the investor’s preference, financial goals, and market conditions. Debentures are generally considered less risky than shares, but they also offer lower returns. On the other hand, shares have a higher risk but the potential for higher returns. Ultimately, it’s up to the individual investor to weigh the pros and cons and make an informed decision based on their financial situation and goals.
Question 4.
What is the difference between shares and debentures investopedia?
Answer:
Shares represent ownership in a company, while debentures are a form of debt that a company issues to raise funds. Shareholders are entitled to vote on company matters and receive dividends, while debenture holders receive fixed interest payments and have no voting rights. Additionally, shares represent a variable return on investment based on the company’s performance, while debentures have a fixed rate of return.
Question 5.
What is debenture for example?
Answer:
A debenture is a type of long-term debt security that is not secured by physical assets or collateral. Instead, it is backed only by the issuer’s creditworthiness. For example, a company may issue debentures to raise funds for a new project or to refinance existing debt. The debentures typically have a fixed interest rate and a maturity date when the principal must be repaid.
