Difference Between Orbit And Orbital: The universe is a vast and complex place, full of fascinating phenomena that scientists have been trying to understand for centuries. Two terms that often come up in scientific discussions are “orbit” and “orbital”. While they sound similar, they have different meanings and applications in different fields of science. In this article, we will explore the difference between orbit and orbital, and why it’s important to understand the distinction.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more. You can get more information through the aplustopper about the differences between orbit and orbital.
Definition And Explanation Of Orbit
An orbit is a path that a celestial object, such as a planet, satellite, or asteroid, follows as it revolves around another object, such as a star or a planet. The force of gravity between the two objects keeps the orbiting object in a stable path around the larger one. Orbits can be circular, elliptical, or even parabolic or hyperbolic, depending on the velocity and distance of the orbiting object. Examples of objects with orbits include the planets in our solar system, the Moon around the Earth, and artificial satellites in Earth’s orbit.
Understanding orbits is essential for space exploration and satellite communications. Scientists use mathematical models to predict the position and velocity of objects in orbit, which allows them to plan space missions and design satellites with precise trajectories. Knowing the characteristics of different orbits also helps scientists study the properties of planets, moons, and other celestial bodies, and develop theories about the formation and evolution of the solar system.
Definition And Explanation Of Orbital
An orbital, on the other hand, is a region of space around an atom’s nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found. Electrons, which have a negative charge, are attracted to the positively charged nucleus by electromagnetic forces. However, electrons cannot exist anywhere within the atom’s space but instead are confined to specific regions, known as orbitals. The shape and size of an orbital depend on the electron’s energy level and are described mathematically by quantum mechanics. Examples of atoms with orbitals include carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen, among others.
Understanding orbitals is crucial for chemistry and physics, as they help explain the behavior of atoms and molecules. The arrangement of electrons in orbitals determines the chemical properties of an element, such as its reactivity and bonding behavior. By studying the electron density and distribution within an orbital, scientists can predict the chemical reactions that will occur when two or more atoms come into contact. This knowledge is critical for fields such as materials science, drug discovery, and environmental chemistry.
Key Differences Between Orbit And Orbital
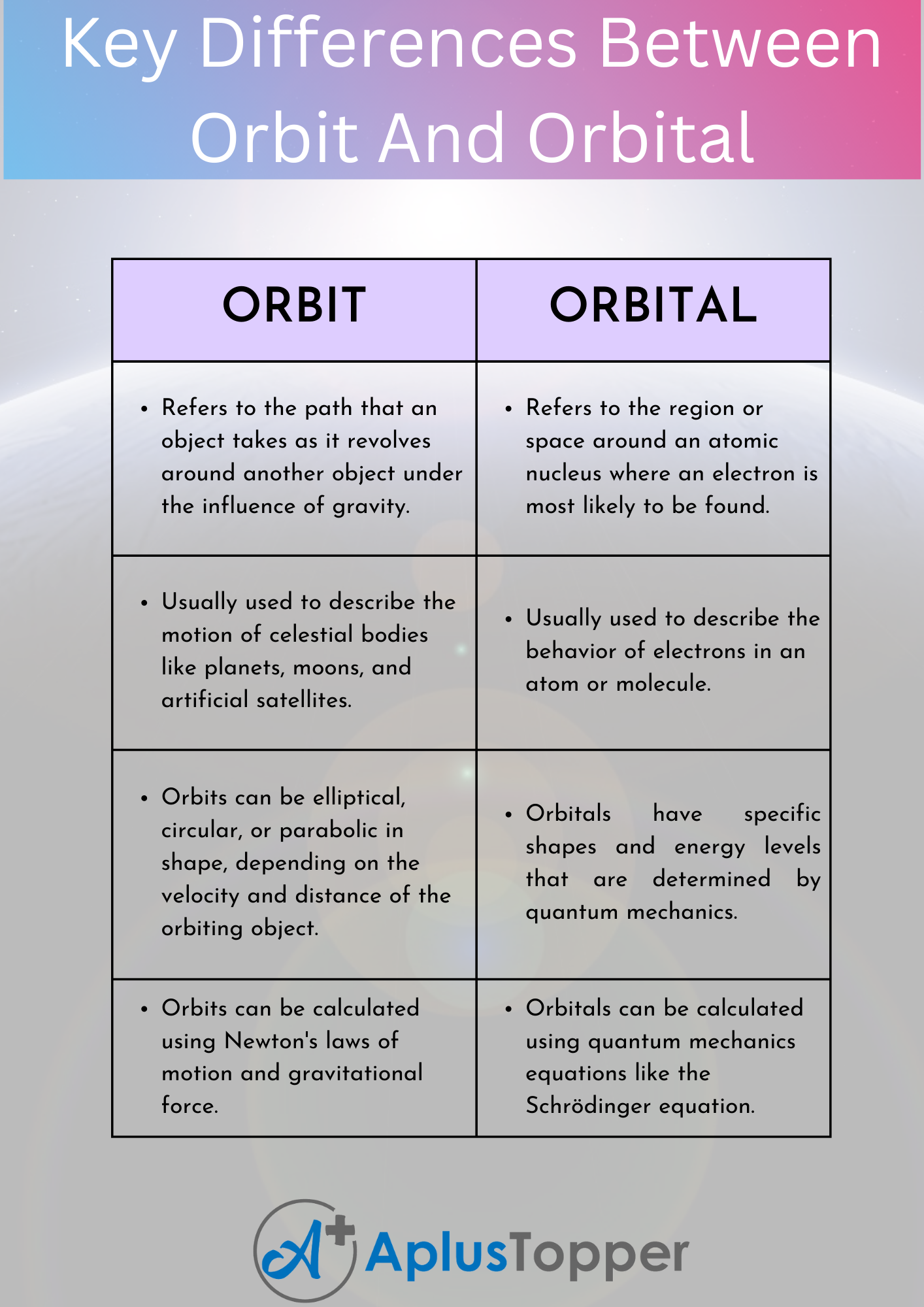
Sure, here’s a tabular form that summarizes the key differences between orbit and orbital:
| ORBIT | ORBITAL |
|---|---|
| Refers to the path that an object takes as it revolves around another object under the influence of gravity. | Refers to the region or space around an atomic nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found. |
| Usually used to describe the motion of celestial bodies like planets, moons, and artificial satellites. | Usually used to describe the behavior of electrons in an atom or molecule. |
| Orbits can be elliptical, circular, or parabolic in shape, depending on the velocity and distance of the orbiting object. | Orbitals have specific shapes and energy levels that are determined by quantum mechanics. |
| Orbits can be calculated using Newton’s laws of motion and gravitational force. | Orbitals can be calculated using quantum mechanics equations like the Schrödinger equation. |
| Orbits are macroscopic in scale and can be observed and measured using telescopes and other instruments. | Orbitals are microscopic in scale and cannot be directly observed or measured, but their properties can be inferred from experimental data and theoretical models. |
| Orbits do not change unless affected by external forces or interactions with other objects. | Orbitals can change in response to changes in the electronic configuration of the atom or molecule, or due to external factors like temperature and pressure. |
The main difference between orbit and orbital is that orbit refers to the path of an object in space, while orbital refers to the region of space around an atom’s nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. Orbit is a term used in astronomy, while orbital is used in chemistry and physics. Additionally, orbits are described using classical mechanics, while orbitals are described using quantum mechanics.
Another difference between orbit and orbital is the scale at which they operate. Orbits involve objects that are large and massive, such as planets, moons, and stars, while orbitals involve particles that are tiny and light, such as electrons. The forces that govern the motion of objects in orbit, such as gravity and inertia, are different from those that govern the behavior of electrons in orbitals, such as electrostatic and magnetic forces.
Importance Of Knowing The Difference Between Orbit And Orbital
Understanding the difference between orbit and orbital is essential for scientific communication and collaboration. Using the correct term in the appropriate context can avoid confusion and ensure that information is accurately conveyed. Confusing orbit and orbital could lead to misunderstandings or errors, particularly in interdisciplinary fields such as astrochemistry or astrobiology.
Moreover, precise language is critical in science and technology, where small details can have significant consequences. In space exploration, a slight miscalculation in an object’s orbit could result in a missed rendezvous or a failed mission. In chemistry, a misunderstanding of orbitals could lead to the wrong molecule being synthesized or a dangerous chemical reaction occurring.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between orbit and orbital is crucial for scientists and professionals in various fields. While the two terms may sound similar, they have distinct meanings and applications in different areas of science. Orbit refers to the path of an object in space, while orbital refers to the region of space around an atom’s nucleus where electrons are likely to be found.
The forces and scales that govern their behavior are also different. Knowing the difference between the two terms can enhance scientific communication, avoid misunderstandings, and promote accurate and effective research.
As we continue to explore the mysteries of the universe and advance our understanding of the building blocks of matter, the importance of precise and accurate language will only grow. By being mindful of the distinction between orbit and orbital, we can contribute to a more robust and collaborative scientific community, one that is capable of making groundbreaking discoveries and addressing some of the world’s most pressing challenges.
Read More: Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 4
FAQs On the Difference Between Orbit And Orbital
Question 1.
What are the two main differences between orbit and orbital?
Answer:
The two main differences between orbit and orbital are:
An orbit is a path traced by a celestial body around another celestial body under the influence of gravity, while an orbital is the probability distribution of an electron around the nucleus of an atom.
Orbits are generally circular or elliptical in shape, while orbitals have different shapes and orientations depending on the energy level and sublevel of the electron.
Question 2.
What is the difference between orbit and orbital brainly?
Answer:
The difference between orbit and orbital is that an orbit refers to the path of a celestial object, such as a planet or satellite, around another object due to the influence of gravity. On the other hand, an orbital refers to the probability distribution of an electron in an atom or molecule. In simpler terms, an orbit is a physical path, while an orbital is a mathematical description of the electron’s position in an atom or molecule.
Question 3.
What is the difference between orbit and orbital topper?
Answer:
The difference between orbit and orbital is that an orbit is the path traced by a celestial body around another celestial body under the influence of gravity, while an orbital is a mathematical function that describes the behavior of an electron in an atom. An orbit is a physical concept, while an orbital is a quantum mechanical concept used to describe the location and energy of an electron in an atom. Orbits are generally circular or elliptical in shape, while orbitals have different shapes and orientations depending on the energy level and sublevel of the electron.
Question 4.
How many orbitals are in an orbit?
Answer:
An orbit is a path traced by a celestial object, such as a planet or a moon, around another object due to the influence of gravity. On the other hand, an orbital is a mathematical function that describes the behavior of an electron in an atom. In an orbit, there are no orbitals. Orbits and orbitals are two distinct concepts that belong to different domains. Orbits are a part of classical mechanics, while orbitals are a part of quantum mechanics. Orbitals describe the probability distribution of an electron in an atom, while orbits describe the path of a celestial body around another celestial body.
Question 5.
What is orbital class 11?
Answer:
In Class 11, students learn about orbitals in the context of atomic structure and chemical bonding. The concept of orbitals is a fundamental part of quantum mechanics and is essential for understanding the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules. In Class 11, students learn about the different types of orbitals, such as s, p, d, and f orbitals, and their properties, including their energy levels, shapes, and orientations. They also learn how to use quantum numbers to describe the electronic configuration of atoms and predict the reactivity and bonding behavior of molecules. Overall, the study of orbitals in Class 11 is a crucial foundation for further studies in chemistry and other related fields.
