Difference Between Isotopes And Isobars: Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter, and they are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. However, not all atoms are the same. Some have different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses. This is where isotopes and isobars come in. In this article, we will explore the key differences between isotopes and isobars.
You can read more Essay Writing about sports, events, festivals, personalities, and other differences between any of the two.
What Are Isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. This means that isotopes have the same atomic number, but different atomic masses. Isotopes are formed when the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom changes. For example, the element carbon has three naturally occurring isotopes: carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14.
Isotopes can have different properties, such as radioactivity. Radioactive isotopes emit radiation as they decay, which can be used in a variety of applications such as medical imaging, cancer treatment, and carbon dating.
What Are Isobars?
Isobars are atoms of different elements that have the same atomic mass. This means that isobars have different atomic numbers, but the same total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isobars are formed when different elements have the same total number of nucleons (protons and neutrons).
For example, chlorine-37 and potassium-37 are isobars. Chlorine-37 has 17 protons and 20 neutrons, while potassium-37 has 19 protons and 18 neutrons. Even though they have different atomic numbers and chemical properties, they have the same atomic mass.
Differences Between Isotopes And Isobars
The main difference between isotopes and isobars is their atomic structure. Isotopes have the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons, while isobars have different numbers of protons and the same number of neutrons. This leads to differences in their mass numbers and nuclide notation.
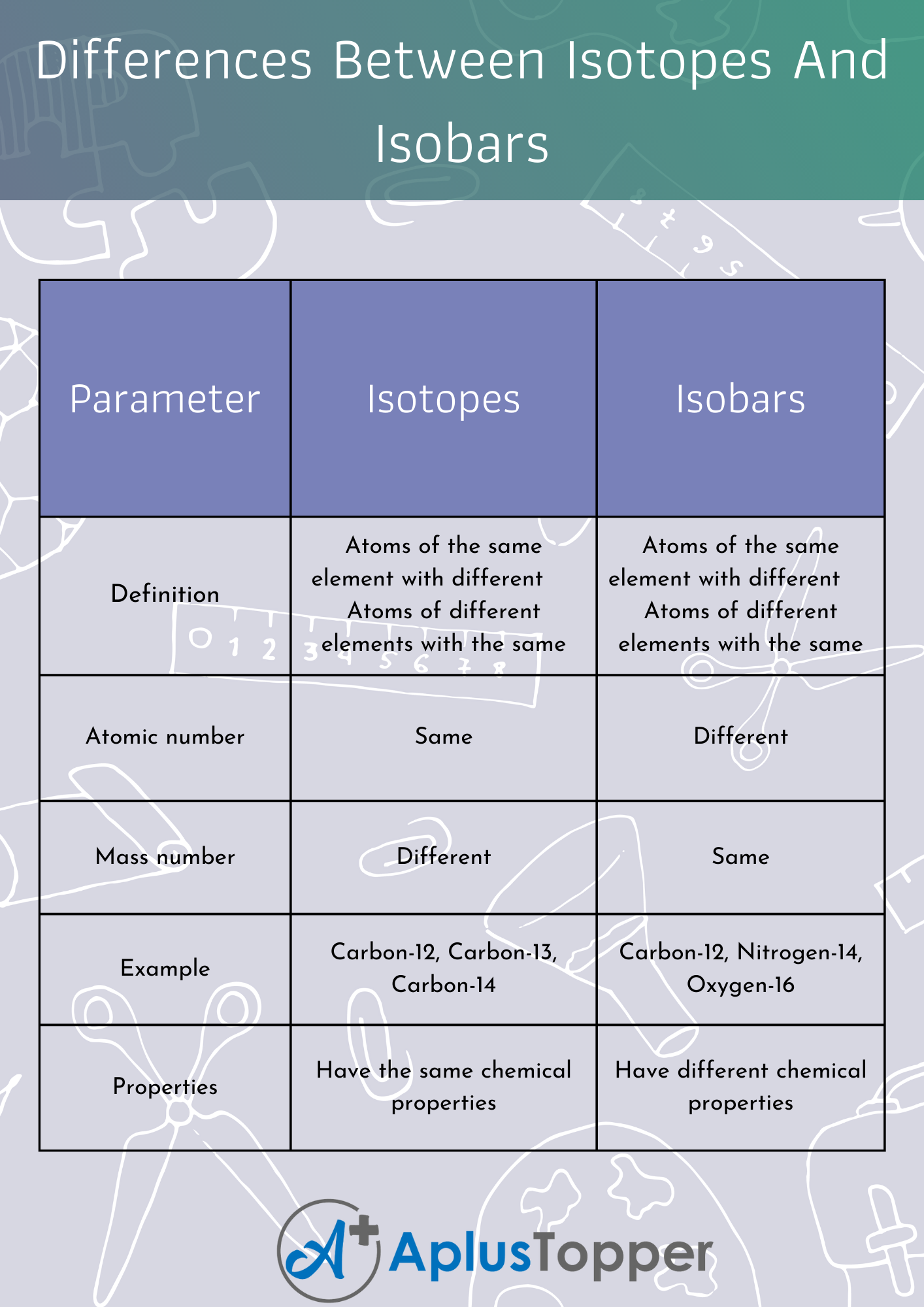
| Parameter | Isotopes | Isobars |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Atoms of the same element with different | Atoms of different elements with the same |
| numbers of neutrons | number of nucleons (i.e., the sum of protons and | |
| neutrons) | ||
| Atomic number | Same | Different |
| Mass number | Different | Same |
| Example | Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14 | Carbon-12, Nitrogen-14, Oxygen-16 |
| Properties | Have the same chemical properties | Have different chemical properties |
| Have different physical properties (such as | Have different physical properties (such as | |
| atomic mass, density, melting, and boiling | atomic mass, density, melting, and boiling | |
| points, etc.) | points, etc.) |
Conclusion
Isotopes and isobars are two terms used in nuclear chemistry to describe different types of atoms. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons, while isobars are atoms of different elements that have the same number of nucleons. The main difference between isotopes and isobars is that isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers, while isobars have different atomic numbers but the same mass numbers. Isotopes and isobars have different properties and behaviors due to their differing atomic structures.
Isotopes, being atoms of the same element, have the same chemical properties, but their physical properties can be different due to the different masses of their nuclei. Isobars, on the other hand, have different chemical properties due to the differences in the number of protons in their nuclei, but they can have similar physical properties due to their similar mass numbers.
Also Read: Isotopes, Isobars, Isotones Element
