Difference Between Blood And Lymph: Blood and lymph are two essential fluids in the human body that perform distinct functions. While both are vital for our health and survival, they have different compositions, circulatory systems, and functions. Understanding the differences between blood and lymph is crucial for medical professionals, researchers, and anyone who wants to learn more about the human body.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more. You can get more information through the aplustopper about the differences between blood and lymph.
Definition And Functions Of Blood
Blood is a fluid that circulates throughout the body and is responsible for transporting nutrients and oxygen to tissues and organs, removing waste products, and protecting against infections. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is a yellowish liquid that makes up about 55% of the blood and contains water, proteins, hormones, and other substances.
- Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and removing carbon dioxide from the body. White blood cells, or leukocytes, are responsible for fighting infections and diseases. Platelets are tiny blood cells that help the blood to clot, which is crucial for stopping bleeding after an injury.
- The functions of blood are diverse and crucial for our health. One of the primary functions of blood is to transport nutrients and oxygen to tissues and organs. Blood carries glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and other nutrients to the cells, which use them to produce energy. Blood also carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells, where it is used to produce energy through a process called cellular respiration.
- Another function of blood is to remove waste products from the body. Blood carries carbon dioxide, urea, and other waste products to the lungs, kidneys, and liver, where they are eliminated from the body. Blood also plays a vital role in the immune system, as white blood cells are responsible for identifying and attacking foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells.
- Blood also plays a critical role in blood clotting. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets adhere to the site of injury, forming a plug that stops the bleeding. The clotting process involves a complex series of chemical reactions, which are essential for stopping bleeding and preventing blood loss.
Definition And Functions Of Lymph
Lymph is a fluid that circulates in the lymphatic system and is responsible for transporting lymphocytes, draining interstitial fluid, absorbing fats and fat-soluble vitamins, and immune response. Lymph is composed of lymphatic fluid, lymphocytes, and other immune cells.
- Lymphatic fluid is a clear, colorless liquid that is similar in composition to plasma. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. Lymphocytes are responsible for identifying and attacking foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells. Other immune cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, are also present in lymph.
- One of the primary functions of lymph is to transport lymphocytes from one part of the body to another. Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow and travel to the lymphatic system, where they mature and are activated. Once activated, lymphocytes travel throughout the body, identifying and attacking foreign substances.
- Another function of lymph is to drain interstitial fluid from the tissues. Interstitial fluid is a clear, colorless liquid that surrounds the cells and provides them with nutrients and oxygen. Lymphatic vessels collect excess interstitial fluid and return it to the bloodstream.
- Lymph also plays a vital role in absorbing fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system. The lymphatic system absorbs fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the small intestine and transports them to the bloodstream.
Key Differences Between Blood And Lymph
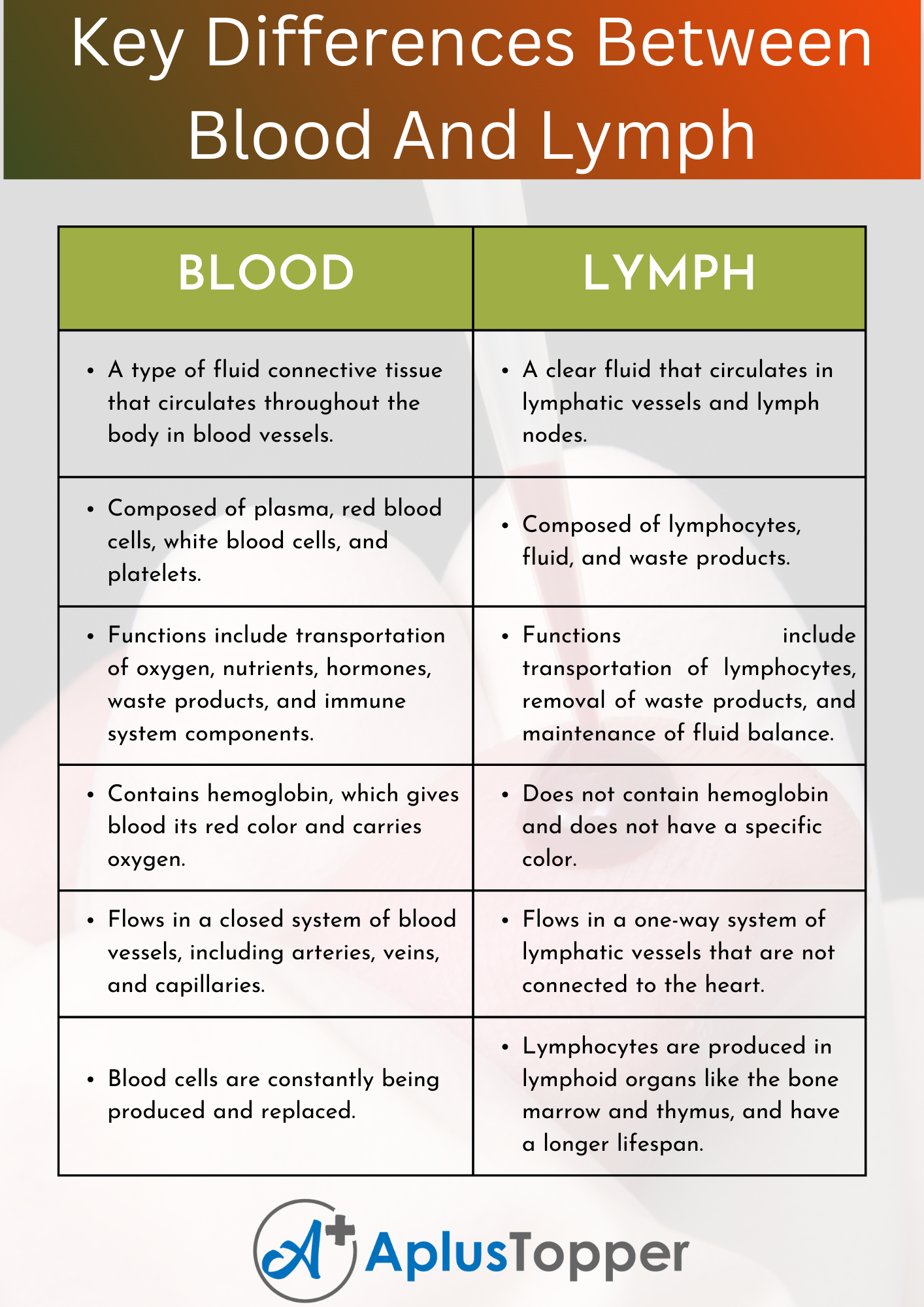
Blood and lymph have several key differences, including composition, color, presence of cells, circulatory system, and functions. The
composition of blood is different from that of lymph. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, while lymph is composed of lymphatic fluid, lymphocytes, and other immune cells.
Another key difference between blood and lymph is their color. Blood is bright red when oxygenated and dark red when deoxygenated due to the presence of hemoglobin in red blood cells. In contrast, lymph is clear or slightly yellowish in color.
Certainly, here are the key differences between blood and lymph in a tabular form:
| BLOOD | LYMPH |
|---|---|
| A type of fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body in blood vessels. | A clear fluid that circulates in lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes. |
| Composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. | Composed of lymphocytes, fluid, and waste products. |
| Functions include the transportation of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, waste products, and immune system components. | Functions include the transportation of lymphocytes, removal of waste products, and maintenance of fluid balance. |
| Contains hemoglobin, which gives blood its red color and carries oxygen. | Does not contain hemoglobin and does not have a specific color. |
| Flows in a closed system of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries. | Flows in a one-way system of lymphatic vessels that are not connected to the heart. |
| Has a higher viscosity and density than lymph. | Has a lower viscosity and density than blood. |
| Is pumped by the heart and has a continuous flow. | Is propelled by contractions of lymphatic vessels and has a slower flow rate. |
| Blood cells are constantly being produced and replaced. | Lymphocytes are produced in lymphoid organs like the bone marrow and thymus and have a longer lifespan. |
The presence of cells is also a key difference between blood and lymph. Blood contains all types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In contrast, lymph contains mainly lymphocytes and other immune cells.
The circulatory systems of blood and lymph are also different. Blood circulates through the body in a closed system of blood vessels, while lymph circulates in the lymphatic system, which is a network of vessels and organs that work together to remove excess interstitial fluid, transport lymphocytes, and fight infections.
Finally, the functions of blood and lymph are different. Blood is primarily responsible for transporting nutrients and oxygen to tissues and organs, removing waste products, and protecting against infections. Lymph is primarily responsible for transporting lymphocytes, draining interstitial fluid, absorbing fats and fat-soluble vitamins, and immune response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood and lymph are two essential fluids in the human body that perform distinct functions. While both are vital for our health and survival, they have different compositions, circulatory systems, and functions. Understanding the differences between blood and lymph is crucial for medical professionals, researchers, and anyone who wants to learn more about the human body. By understanding the functions and characteristics of these two vital fluids, we can better appreciate the complexity and wonder of the human body.
Read More: Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7
FAQs On the Difference Between Blood And Lymph
Question 1.
What is the difference between blood and lymph brainly?
Answer:
Blood and lymph are two types of fluids found in the body that serve different functions. The main differences between blood and lymph are:
- Composition: Blood is composed of plasma, red and white blood cells, and platelets, while lymph is composed of a clear fluid called lymphatic fluid, lymphocytes, and other white blood cells.
- Functions: Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the body’s tissues and removes waste products, while lymph helps to remove excess fluid, waste products, and foreign substances from the body’s tissues.
- Overall, blood and lymph are both essential for maintaining the body’s internal environment, but they have distinct roles and compositions.
Question 2.
What is the function of blood and lymph?
Answer:
The function of blood and lymph is different and essential for the proper functioning of the body.
Blood has several functions, including:
- Transportation: Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the body’s tissues and removes waste products such as carbon dioxide and urea.
- Regulation: Blood helps regulate body temperature, pH levels, and electrolyte balance.
- Protection: Blood contains white blood cells and antibodies that help fight infections and diseases. It also forms blood clots to prevent excessive bleeding after an injury.
Lymph, on the other hand, has the following functions:
- Drainage: Lymph helps drain excess fluid, waste products, and foreign substances from the body’s tissues.
Immune response: Lymph contains lymphocytes and other white blood cells that help fight infections and diseases by identifying and destroying harmful microorganisms and foreign substances. - Absorption: Lymphatic vessels in the small intestine absorb fats and fat-soluble vitamins and transport them to the bloodstream.
In summary, blood and lymph play vital roles in the body’s internal environment and are essential for maintaining good health.
Question 3.
What are 5 differences between blood and lymph?
Answer:
Here are five differences between blood and lymph:
- Composition: Blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma, while lymph is composed of lymphocytes, lymph fluid, and waste products.
- Circulatory system: Blood circulates through the body in a closed system of blood vessels, while lymph circulates through the body in lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes.
- Color and texture: Blood is thicker and darker in color, while lymph is thin and transparent.
- Function: Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the body’s tissues, and removes waste products, while lymph helps to maintain fluid balance and immune function.
- Formation: Blood is formed in the bone marrow, while lymph is formed in the lymphatic tissues such as the spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes.
Question 4.
Is blood also called lymph?
Answer:
No, blood and lymph are two different bodily fluids and should not be confused with each other. Blood is a fluid that circulates through the arteries, veins, and capillaries, carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body’s cells and removing waste products. Lymph, on the other hand, is a colorless fluid that is derived from the blood plasma and helps in the transportation of white blood cells, oxygen, and nutrients to the body tissues.
Question 5.
What is the difference between lymphocytes and blood cells?
Answer:
Lymphocytes and blood cells are both types of cells found in the body, but they differ in their functions and locations.
Here are some differences between lymphocytes and blood cells:
- Location: Blood cells are primarily found in the blood, while lymphocytes are found in the lymphatic system, which includes lymph nodes, spleen, and other lymphatic tissues.
- Function: Blood cells have various functions, such as carrying oxygen, fighting infections, and clotting blood. On the other hand, lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. They recognize and fight against foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses.
- Types: Blood cells include erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), and platelets. Lymphocytes are a type of leukocyte and include three main types: T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
- Formation: Blood cells are formed in the bone marrow, while lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus gland.
- Lifespan: Blood cells have a relatively short lifespan, ranging from a few days to a few months. Lymphocytes, on the other hand, can live for several years.
