How do you detect radioactivity?
Detection of Radioactive Emission:
- Radioactive emission is invisible to the naked eye. It cannot be detected by any of our senses because it has no smell, no taste and makes no sound.
- The detection of radioactive emissions is by the ionising effect of radiation on the atoms of matter.
- An energetic particle or photon that passes through a medium can knock an electron out of an atom in that medium. This process is known as ionisation and it produces charged particles called ions.
- Figure illustrates the ionising process when an energetic particle interacts with an atom of a medium.
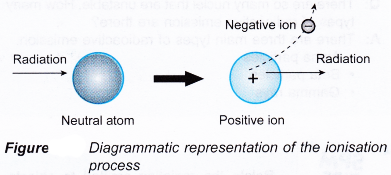
- The ionisation of an atom produces an ion pair which consists of an electron as the negative ion and a positively charged atom as the positive ion.
- Therefore radioactive emission is also known as ionising radiation.
- Detectors of radioactive emission detect the ion pairs produced by the radioactive emission.
- Table gives a list of detectors and the type of radioactive emission they can detect.
Name of detector Type of radiation that can be detected Observation when radiation is detected Photographic badge β-particles
γ-raysDarkening of the photographic plate in the badge Geiger- Muller tube with ratemeter α-particles
β-particles
γ-raysThe ratemeter shows a count rate higher than the background count. Cloud chamber α-particles
β-particles
γ-raysTracks with specific characteristics are formed in the cloud chamber. Spark counter α-particles Sparks are seen and heard between the wire gauze and the wire below it.
People also ask
- Radioactivity: Types of Radioactive Emissions
- What are the different types of radioactive decay?
- What are the Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones of an Element
- Importance of Proper Management of Radioactive Substances
- What is nucleus of an atom?
- What is Nuclear Energy?
- What is nuclear fission and how does it occur?
- How is energy released in a nuclear fusion reaction?
- What happens in a nuclear chain reaction?
- How does a nuclear power plant works?
Geiger-Muller Tube
- The Geiger-Muller tube (or the GM tube) is a very sensitive and useful detector of radiation. It can detect a-particles, /3-particles and y-rays.
- A radioactive emission enters the tube through the mica window and ionises the argon gas inside the GM tube.
- The ions produce a pulse of current that is counted by a scaler or ratemeter.
- The scaler gives the number of counts over a certain period of time
- The ratemeter gives the count rate in counts per second or counts per minute.
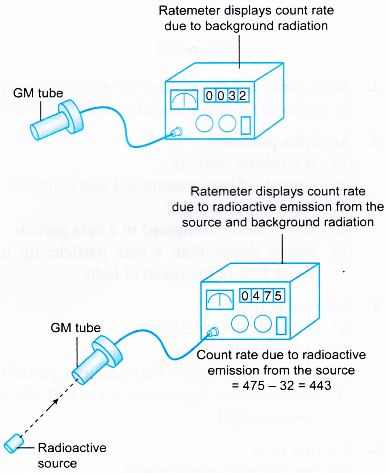
- Initially the GM tube is switched on without the presence of any radioactive substance. The reading displayed by the ratemeter is known as the background count rate.
- When the GM tube is used to detect radiation from a radioactive substance, the background count rate is subtracted from the count rate obtained.
Cloud Chamber
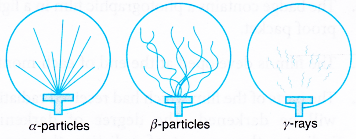
- A cloud chamber shows the path travelled by ionising radiation in air.
- In a cloud chamber, radiation produces ions in the air that is saturated with alcohol vapour.
- The alcohol vapour condenses on the ions to make the tracks of the radiation visible.
- Figure shows the tracks-of alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays.
Spark Counter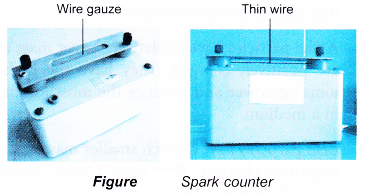
- A spark counter consists of a wire gauze and a thin wire below it.
- A high voltage is applied between the gauze and the wire. The voltage is adjusted until it is just below the value required to produce sparks.
- When a radioactive source is brought near the wire gauze, the radiation ionises the air between the wire gauze and the thin wire. The motion of the ions to the gauze and the wire causes sparks to be produced. The sparks can be seen and heard.
- Spark counters are suitable for detecting alpha particles. Beta-particles and gamma rays produce too few ions to produce sparks.
Photographic Badge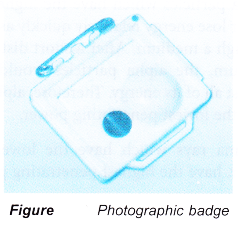
- The photographic badge is worn by workers in nuclear power stations and in radiation laboratories.
- The badge contains a photographic film in a light¬proof packet.
- The film is developed at the end of each month.
- The parts of the film which had received radiation will be darkened. The degree of darkening indicates the amount of radiation the person had been exposed to.
