Decimal Representation Of Rational Numbers
Example 1: Express in the decimal form by long division method.
Solution: We have,
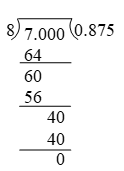
∴ = 0.875
Example 2: Convert into decimal form by long division method.
Solution: We have,
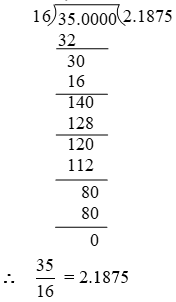
Example 3: Express in the decimal form.
Solution: We have,
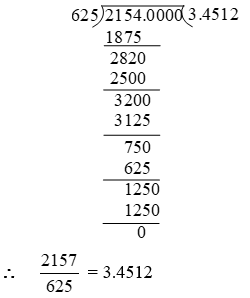
Example 4: Express in decimal form by long division method.
Solution: In order to convert in the decimal form, we first express in the decimal form and the decimal form of will be negative of the decimal form of
we have,
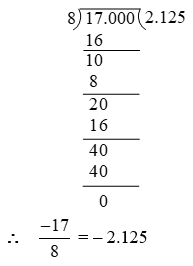
Example 5: Find the decimal representation of .
Solution: By long division, we have
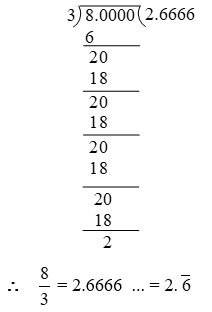
Example 6: Express as a decimal fraction.
Solution: By long division, we have
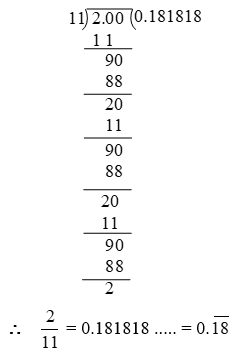
Example 7: Find the decimal representation of
Solution: By long division, we have
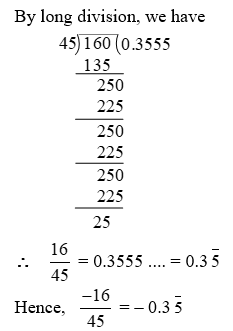
Example 8: Find the decimal representation of
Solution: By long division, we have
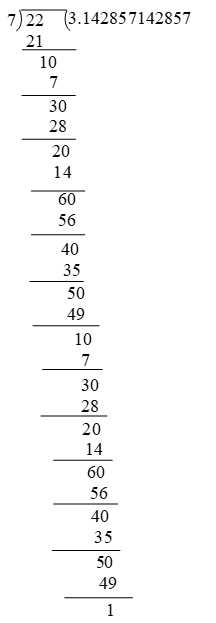
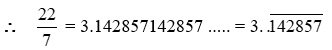
So division of rational number gives decimal expansion. This expansion represents two types
(A) Terminating (remainder = 0)
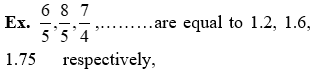
So these are terminating and non repeating (recurring)
(B) Non terminating recurring (repeating)
(remainder ≠ 0, but equal to devidend)

These expansion are not finished but digits are continusely repeated so we use a line on those digits, called bar .
So we can say that rational numbers are of the form either terminating, non repeating or non terminating repeating (recurring).
