DAP Fertilizer Advantages And Disadvantages: Di-ammonium Phosphate prominently known as DAP is a favoured manure in India since it contains both Nitrogen and Phosphorus which are essentially large scale supplements and part of 18 fundamental plant supplements. Di-ammonium Phosphate prominently known as DAP is favoured manure in India since it contains both Nitrogen and Phosphorus which are essentially large scale supplements and part of 18 fundamental plant supplements.
Any nursery worker who has planned a treatment program for local plants is probable mindful of the wide scope of materials accessible to grounds-keepers for use as compost. Every compost enjoys explicit benefits and detriments, so it can now and then be restrictively confounding to pick manure that suits the necessities of your plants. Phosphate composts, for instance, convey with them explicit advantages and dangers. Understanding these dangers is critical to staying away from issues connected with ill-advised utilization of phosphate manures.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is DAP Fertilizer? Advantages and Disadvantages of DAP Fertilizer 2022
One of the foremost manners by which manures vary from each other are in the materials they use to convey supplements to establish soil. A phosphate or phosphorus manure is one that conveys higher convergences of phosphorus than of other plant supplements like nitrogen and potassium. A few normal natural wellsprings of phosphorus utilized in composts incorporate superphosphate, concentrated superphosphate, monoammonium phosphate, diammonium phosphate (DAP), ammonium polyphosphate (APP) and rock phosphate.
DAP (NH4)2HPO4: Fertilizer grade DAP Contains 18% Nitrogen and 46% Phosphorus (P2O5). DAP is fabricated by responding Ammonia with Phosphoric corrosive under controlled conditions in manure plants.
- Advantages of DAP Fertilizer
- Disadvantages of DAP Fertilizer
- Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of DAP
- FAQs on Pros and Cons of DAP Fertilizer
Advantages of DAP Fertilizer
- Soil Testing: For productive utilization of this compost, the soil should be tried for nitrogen and phosphorus content to decide the necessary measure of DAP.
- Basal Dose: DAP is the most appropriate compost for the basal portion as through this we can apply a full portion of phosphorus and 33% to half portion of nitrogen. The remaining dose of nitrogen can be applied through parts of urea at different phases of harvest. So DAP gives the best blend with urea manure. DAP is likewise the best manure for beats where less nitrogen and higher phosphorus is required as a starter portion.
- Position of DAP: Since phosphorus is stationary in soil, its source (DAP) ought to be put a ways off where plant roots can without much of a stretch reach. Inappropriate utilization of DAP might make seedling injury due to arrival of alkali. DAP ought to be put underneath seed, somewhat aside.
- Soil Amendments: Nitrogen as well as phosphorus, give the best outcomes in nonpartisan soils. However, if there should arise an occurrence of basic, volatilization misfortunes of smelling salts are higher. So nitrogen use effectiveness is diminished. Correspondingly unnecessary presence of calcium in basic soils makes buildings with phosphorus and eventually brings about unfortunate phosphorus recuperation. So carrying soil pH to nonpartisan by adding gypsum and draining can further develop N and P use effectiveness of DAP.
Disadvantages of DAP Fertilizer
- Overfertilization is a significant and normal issue for phosphate manures. Numerous grounds-keepers erroneously add phosphate manures to soils that they accept to be inadequate in phosphorus when nitrogen inadequacies are a substantially more typical reason for supplement lack side effects in plants. In these cases, an excess of phosphorus in the dirt not just neglects to determine the supplement lack issue yet can really exacerbate the situation by causing leaf chlorosis and hurting advantageous microorganisms living in the soil.
- One more significant disservice of phosphate manures is the high likelihood of water contamination. Phosphorus that advances into the soil through phosphate manures and ties firmly to soil particles is probably not going to move out of the dirt. However, on the off chance that a lot of phosphate manure is applied to soil, overabundance phosphorus can without much of a stretch find its direction into water frameworks by means of tempest depletes and plumbing. Grass clippings and leaves from plants that have been developed in soils with an excess of phosphorus will deliver their phosphorus into the water, promoting green growth and microorganisms flare-ups and water pollution issues.

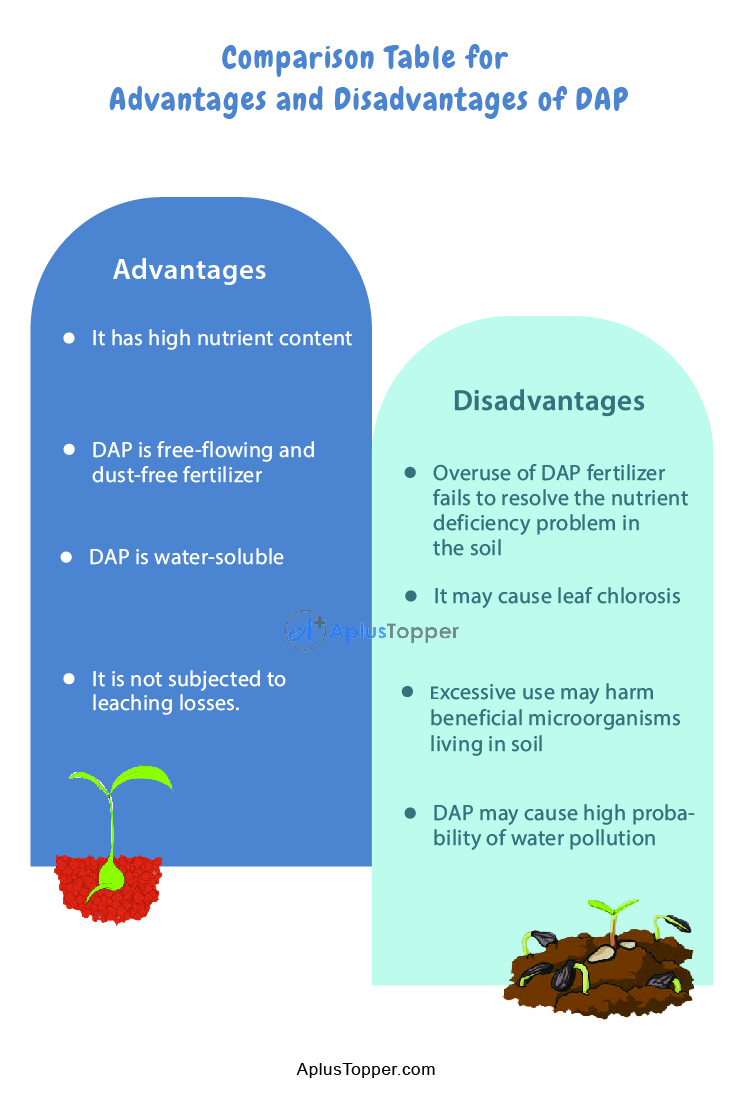
Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of DAP
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It has high nutrient content | Overuse of DAP fertilizer fails to resolve the nutrient deficiency problem in the soil |
| DAP is free-flowing and dust-free fertilizer | It may cause leaf chlorosis |
| DAP is water-soluble | Excessive use may harm beneficial microorganisms living in soil |
| It is not subjected to leaching losses. | DAP may cause high probability of water pollution |
FAQs on Pros and Cons of DAP Fertilizer
Question 1.
What is the full form of DAP?
Answer:
The full form of DAP is Diammonium fertilizer.
Question 2.
What is DAP fertilizer?
Answer:
Di-ammonium Phosphate prominently known as DAP is the favoured manure in India since it contains both Nitrogen and Phosphorus which are essentially large scale supplements and part of 18 fundamental plant supplements.
Question 3.
What is DAP fertilizer good for?
Answer:
It is ideal for any farming yield to give full phosphorus nourishment all through crop development and advancement, as well as a starter portion of nitrogen and low sulfur.
Question 4.
Is DAP fertilizer good for vegetables?
Answer:
DAP compost is an amazing wellspring of P and nitrogen (N) for plant sustenance. It’s exceptionally solvent and subsequently breaks up rapidly in soil to deliver plant-accessible phosphate and ammonium.
